Is Cn- An Acid Or Base
Kalali
Mar 21, 2025 · 5 min read
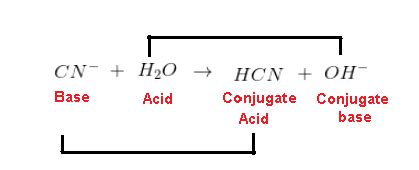
Table of Contents
Is CN⁻ an Acid or a Base? Understanding Cyanide's Behavior in Aqueous Solutions
The question of whether cyanide (CN⁻) is an acid or a base is not a simple yes or no answer. Its behavior depends heavily on the context, specifically the solution it's in and the other chemical species present. While it's often categorized as a base, understanding its amphoteric nature and its potential to act as a weak acid under certain conditions is crucial. This article delves deep into the chemical properties of cyanide, explaining its behavior in various scenarios and clarifying common misconceptions.
Understanding Acidity and Basicity: The Brønsted-Lowry Definition
To accurately classify CN⁻, we need to employ the Brønsted-Lowry definition of acids and bases. This definition states that an acid is a proton (H⁺) donor, while a base is a proton acceptor. In aqueous solutions (solutions containing water), the interaction with water plays a crucial role in determining acidity and basicity.
Cyanide's Behavior as a Base: Hydrolysis and Equilibrium
In most aqueous solutions, cyanide ion (CN⁻) acts as a weak base. This is because it can accept a proton from water molecules. The reaction is as follows:
CN⁻(aq) + H₂O(l) ⇌ HCN(aq) + OH⁻(aq)
This reaction establishes an equilibrium. The equilibrium constant for this reaction, denoted as Kb (base dissociation constant), indicates the strength of cyanide as a base. A higher Kb value represents a stronger base. The presence of hydroxide ions (OH⁻) indicates that the solution becomes slightly alkaline (basic).
Understanding Kb and pKb: The Kb value helps quantify the base strength. A smaller Kb value indicates a weaker base. The pKb value, calculated as -log₁₀(Kb), is often used for easier comparison; a lower pKb indicates a stronger base.
Factors Affecting Cyanide's Basicity
Several factors influence the extent to which CN⁻ acts as a base:
- Concentration: Higher concentrations of CN⁻ lead to a higher concentration of OH⁻ ions, making the solution more basic.
- Temperature: Temperature changes affect the equilibrium constant (Kb).
- Presence of other ions: The presence of other ions in the solution can impact the equilibrium, influencing the overall basicity. Common-ion effect, for example, can suppress the basicity of CN⁻.
The Amphoteric Nature of Cyanide: Acting as a Weak Acid
While predominantly acting as a base, cyanide also exhibits amphoteric behavior under specific conditions. Amphoteric substances can act as both acids and bases. In the presence of a very strong base, cyanide can donate a proton, behaving as a weak acid.
This acidic behavior is less common than its basic behavior, and the equilibrium constant for this reaction (Ka, acid dissociation constant) is much smaller than its Kb value.
HCN(aq) + OH⁻(aq) ⇌ CN⁻(aq) + H₂O(l)
Comparing Ka and Kb: Quantifying Cyanide's Acid-Base Properties
Comparing the Ka and Kb values provides a comprehensive understanding of cyanide's behavior. The relative magnitudes of Ka and Kb will determine whether the cyanide ion predominantly acts as an acid or a base in a given solution. In most cases, Kb >> Ka, confirming its primary role as a weak base.
The Role of Hydrogen Cyanide (HCN)
Hydrogen cyanide (HCN), the conjugate acid of CN⁻, is a weak acid. It's important to understand the relationship between HCN and CN⁻: they are a conjugate acid-base pair. The strength of HCN as an acid is directly related to the strength of CN⁻ as a base.
The dissociation of HCN in water is represented as:
HCN(aq) + H₂O(l) ⇌ H₃O⁺(aq) + CN⁻(aq)
This equilibrium is characterized by its Ka value.
Toxicity and Safety Considerations
It's crucial to acknowledge the extreme toxicity of both HCN and CN⁻. Even small amounts can be lethal. Always handle these compounds with extreme caution in a well-ventilated area, using appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE). Proper disposal of cyanide waste is also essential.
Applications of Cyanide: Understanding its Diverse Roles
Despite its toxicity, cyanide finds applications in various industries:
- Mining: Cyanide is used in gold extraction.
- Chemical Synthesis: It's a precursor in the synthesis of various organic compounds.
- Pesticide Production: Some pesticides utilize cyanide derivatives.
These applications highlight the dual nature of cyanide: while toxic, it also possesses useful chemical properties exploited in several industrial processes. However, the stringent safety regulations surrounding its handling and disposal remain critical.
Misconceptions about Cyanide's Acidity/Basicity
Several misconceptions often surround cyanide's acid-base behavior:
- Cyanide is always a strong base: This is incorrect. It's a weak base.
- Cyanide cannot act as an acid: This is also incorrect. It shows amphoteric behavior.
- The toxicity of cyanide is irrelevant to its acid-base properties: While separate concepts, understanding the chemical behavior of cyanide (including its acid-base properties) is crucial for comprehending its toxicity and handling it safely.
Conclusion: A nuanced understanding of CN⁻'s behavior
The classification of CN⁻ as an acid or base depends on the context. While predominantly a weak base in most aqueous solutions, it displays amphoteric properties, exhibiting weak acidic behavior under specific conditions. Understanding its equilibrium reactions, the relevant constants (Kb and Ka), and the relationship between CN⁻ and HCN are essential for a comprehensive grasp of cyanide's chemical behavior. Remember to always prioritize safety when handling cyanide due to its extreme toxicity. The information presented here is for educational purposes and should not be considered a substitute for proper training and guidance from qualified professionals in handling hazardous materials.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
45 8 As A Mixed Number
Mar 22, 2025
-
How Much Is 10 Of 10000
Mar 22, 2025
-
How Many Feet Is 103 Inches
Mar 22, 2025
-
What Are 4 Agents Of Erosion
Mar 22, 2025
-
How Many Inches Is 152 Cm
Mar 22, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is Cn- An Acid Or Base . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
