Is Silicon Tetrafluoride Polar Or Nonpolar
Kalali
Mar 22, 2025 · 5 min read
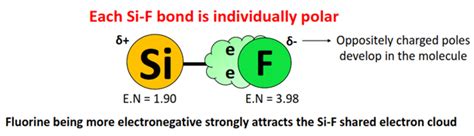
Table of Contents
Is Silicon Tetrafluoride (SiF₄) Polar or Nonpolar? A Comprehensive Analysis
Determining the polarity of a molecule like silicon tetrafluoride (SiF₄) is crucial for understanding its properties and behavior. This comprehensive analysis will delve into the intricacies of molecular polarity, focusing specifically on SiF₄. We'll explore the concepts of electronegativity, bond polarity, molecular geometry, and the overall dipole moment to definitively answer the question: Is SiF₄ polar or nonpolar?
Understanding Molecular Polarity
Before diving into the specifics of SiF₄, let's establish a foundational understanding of molecular polarity. A molecule's polarity is determined by the distribution of electron density within its structure. This distribution is influenced by two primary factors:
1. Electronegativity Differences
Electronegativity refers to an atom's ability to attract electrons within a chemical bond. When atoms with significantly different electronegativities bond, the electrons are pulled more strongly towards the more electronegative atom, creating a polar bond. This unequal sharing of electrons results in a partial positive charge (δ+) on the less electronegative atom and a partial negative charge (δ-) on the more electronegative atom.
2. Molecular Geometry
Even if a molecule contains polar bonds, the overall molecule may be nonpolar if the geometry cancels out the individual bond dipoles. Molecular geometry refers to the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms in a molecule. If the polar bonds are symmetrically arranged around the central atom, their individual dipole moments can cancel each other out, resulting in a nonpolar molecule. Conversely, an asymmetrical arrangement of polar bonds leads to a net dipole moment, resulting in a polar molecule.
Analyzing Silicon Tetrafluoride (SiF₄)
Now, let's apply these principles to silicon tetrafluoride (SiF₄).
1. Electronegativity of Silicon and Fluorine
Silicon (Si) and fluorine (F) have significantly different electronegativities. Fluorine is the most electronegative element, while silicon has a considerably lower electronegativity. This substantial difference in electronegativity leads to polar Si-F bonds. The electrons in each Si-F bond are pulled more strongly towards the fluorine atom, creating partial positive charges (δ+) on the silicon atom and partial negative charges (δ-) on the fluorine atoms.
2. Molecular Geometry of SiF₄: Tetrahedral Structure
Silicon tetrafluoride adopts a tetrahedral geometry. The silicon atom is located at the center of the tetrahedron, with four fluorine atoms positioned at the corners. This symmetrical arrangement is crucial in determining the overall polarity of the molecule.
3. Vector Sum of Bond Dipoles
Each Si-F bond possesses a dipole moment, represented as a vector pointing from the less electronegative atom (Si) to the more electronegative atom (F). Due to the tetrahedral symmetry, these individual bond dipoles cancel each other out. The vectors are equal in magnitude and point in opposite directions, resulting in a net dipole moment of zero.
Conclusion: SiF₄ is Nonpolar
Based on the analysis of electronegativity differences, molecular geometry, and the vector sum of bond dipoles, we can definitively conclude that silicon tetrafluoride (SiF₄) is a nonpolar molecule. Despite the presence of polar Si-F bonds, the symmetrical tetrahedral geometry ensures that the individual bond dipoles cancel each other out, resulting in no net dipole moment.
Further Implications of SiF₄'s Nonpolar Nature
The nonpolar nature of SiF₄ significantly influences its physical and chemical properties. For example:
-
Solubility: Nonpolar molecules tend to be insoluble in polar solvents like water but soluble in nonpolar solvents. SiF₄ exhibits this behavior.
-
Boiling Point: SiF₄ has a relatively low boiling point compared to other compounds with similar molecular weight, reflecting its weak intermolecular forces. Nonpolar molecules experience only weak London Dispersion Forces (LDFs), whereas polar molecules exhibit stronger dipole-dipole interactions and hydrogen bonding (if applicable).
-
Reactivity: The nonpolar nature influences SiF₄'s reactivity. It may participate in reactions that favor nonpolar environments or involve nonpolar reactants.
-
Applications: Understanding its nonpolar characteristics is important for its applications in various fields, including chemical synthesis and material science. SiF₄ has industrial applications, for instance in the production of semiconductors and other materials.
Comparing SiF₄ to other Tetrahedral Molecules
It's helpful to compare SiF₄ to other tetrahedral molecules to solidify the understanding of polarity. Consider carbon tetrachloride (CCl₄), another tetrahedral molecule. Similar to SiF₄, CCl₄ is also nonpolar due to the symmetrical arrangement of its polar C-Cl bonds. The dipole moments of the individual bonds cancel each other out, resulting in a zero net dipole moment.
However, if we consider a molecule like chloroform (CHCl₃), the replacement of one chlorine atom with a hydrogen atom breaks the symmetry. This asymmetry leads to a net dipole moment, making chloroform a polar molecule. This highlights the importance of molecular geometry in determining overall polarity.
Advanced Concepts and Considerations
While the explanation above provides a thorough understanding for most purposes, more advanced concepts can further refine the analysis:
-
Hybridization: The silicon atom in SiF₄ undergoes sp³ hybridization, leading to the tetrahedral arrangement. This hybridization affects the orbital overlap and electron distribution, further contributing to the molecule's nonpolar nature.
-
Quantum Mechanical Calculations: More precise calculations using quantum mechanics can provide a more accurate determination of the dipole moment, confirming the near-zero value predicted by the simpler vector analysis.
Conclusion Re-iterated: The Definitive Answer
To reiterate, silicon tetrafluoride (SiF₄) is nonpolar. This conclusion is firmly supported by its symmetrical tetrahedral geometry, which results in the cancellation of individual bond dipoles, leading to a net dipole moment of zero. This nonpolarity is crucial in understanding its various physical and chemical properties and its applications in diverse fields. The principles discussed here—electronegativity, molecular geometry, and vector summation of bond dipoles—are fundamental concepts in chemistry and essential for determining the polarity of any molecule.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 49 Inches In Feet
Mar 22, 2025
-
Cuanto Son 8 Onzas En Litros
Mar 22, 2025
-
How Many Milliliters Are In 10 Oz
Mar 22, 2025
-
Natural Numbers Their Opposites And Zero
Mar 22, 2025
-
How Many Cups Is 10 5 Oz
Mar 22, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is Silicon Tetrafluoride Polar Or Nonpolar . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
