Is Sugar A Mixture Or Pure Substance
Kalali
Mar 10, 2025 · 5 min read
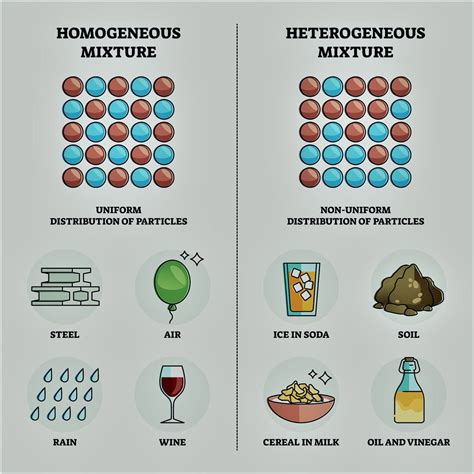
Table of Contents
Is Sugar a Mixture or a Pure Substance? Delving into the Chemistry of Sucrose
The seemingly simple question, "Is sugar a mixture or a pure substance?" opens a fascinating exploration into the world of chemistry and the properties of matter. While the answer might seem straightforward at first glance, a deeper dive reveals the nuances of chemical composition and the definitions that govern our understanding of substances. This article will dissect the nature of sugar, specifically sucrose (table sugar), examining its chemical makeup and exploring why it's categorized as a pure substance, despite its potential for impurities.
Understanding the Definitions: Mixture vs. Pure Substance
Before we delve into the specifics of sugar, let's establish a clear understanding of the key terms:
Pure Substance:
A pure substance has a fixed chemical composition and consistent properties throughout. This means it's made up of only one type of atom (like elemental gold, Au) or one type of molecule (like water, H₂O). Pure substances have a distinct melting and boiling point. They cannot be separated into simpler components by physical means like filtration or distillation. Examples: Water (H₂O), oxygen (O₂), sodium chloride (NaCl).
Mixture:
A mixture is a combination of two or more substances that are physically combined but not chemically bonded. The components retain their individual properties, and the composition can vary. Mixtures can be homogeneous (uniform throughout, like saltwater) or heterogeneous (non-uniform, like sand and water). Mixtures can be separated into their components by physical means. Examples: Saltwater, air, soil.
The Chemical Composition of Sugar (Sucrose)
Table sugar, commonly known as sucrose, is a pure substance. It's a disaccharide, meaning it's composed of two simpler sugars, glucose and fructose, chemically bonded together. The chemical formula for sucrose is C₁₂H₂₂O₁₁. This precise formula highlights its consistent composition: every molecule of sucrose contains exactly 12 carbon atoms, 22 hydrogen atoms, and 11 oxygen atoms. This fixed ratio is the hallmark of a pure substance.
The Bond that Makes Sucrose a Pure Substance:
The glucose and fructose molecules in sucrose are joined through a glycosidic bond, a specific type of covalent bond. This covalent bond is a strong chemical bond, and it's not easily broken through simple physical processes. This strong bond ensures the consistent molecular structure of sucrose. You cannot physically separate glucose and fructose from sucrose without breaking this bond, which requires a chemical reaction, not a physical separation.
Refining Sugar: The Impurity Factor
While sucrose itself is a pure substance, the sugar we commonly use is not entirely pure in its raw form. Raw sugar, obtained directly from sugarcane or sugar beets, contains impurities like water, minerals, and other plant materials. The refining process aims to remove these impurities, ultimately yielding a purer form of sucrose. However, the refining process is a physical and chemical separation process to remove impurities, not a breakdown of the sucrose molecules themselves.
Important Note: The presence of impurities does not change the fundamental classification of sucrose as a pure substance. Even refined sugar contains trace amounts of other substances, but these are considered contaminants, not integral components of the sucrose itself. The sucrose molecules remain consistent and their properties remain the same.
Differentiating Sugar from Mixtures
Let's compare sugar to some examples of mixtures to further clarify its classification:
Sugar vs. Saltwater:
Saltwater is a homogenous mixture of sodium chloride (NaCl) and water (H₂O). The salt and water molecules are not chemically bonded but are interspersed. Saltwater's properties vary depending on the concentration of salt. One can easily separate the salt and water through evaporation, which is a physical process. Sugar, on the other hand, cannot be separated into glucose and fructose through physical means.
Sugar vs. Sand and Sugar:
A mixture of sand and sugar is a heterogeneous mixture. The components – sand and sugar – retain their individual identities and properties. Simple physical separation, like sieving, can easily separate the sand and sugar. Sugar, by contrast, has a uniform composition that cannot be broken down by physical separation.
Advanced Considerations: Isomers and Sugar
While sucrose is a pure substance, it's important to note the existence of isomers. Isomers are molecules with the same chemical formula but different structural arrangements. For example, glucose and fructose both have the chemical formula C₆H₁₂O₆ but differ in their molecular structure. They are distinct substances with different properties. However, the fact that sucrose is formed from these isomers doesn't change its status as a pure substance; the molecules themselves form a stable and uniform substance once bonded.
Practical Implications: Understanding the Purity of Sugar
Understanding the pure substance nature of sucrose has practical implications.
- Food Science: The consistent properties of sucrose are crucial in baking and other culinary applications. Predictable sweetness, solubility, and crystallization properties are dependent on the uniform composition of sucrose.
- Medicine: Sucrose is used in various pharmaceutical formulations. Its purity is essential for ensuring accurate drug dosage and avoiding adverse reactions.
- Industrial Applications: Sucrose's properties are used in various industrial processes, including the production of biofuels and other chemicals. Consistency is critical to achieving predictable outcomes.
Conclusion: Sugar - A Pure Substance, Despite Impurities
In conclusion, despite the presence of impurities in commercially available sugar, sucrose itself is unequivocally a pure substance. Its consistent chemical composition (C₁₂H₂₂O₁₁), the strong covalent bonds holding its molecules together, and its inability to be separated into its simpler components through physical processes firmly establish its classification as a pure substance. While the refining process is crucial for removing impurities, it doesn't alter the fundamental chemical nature of sucrose. Understanding the difference between a pure substance and a mixture and the nature of sugar's chemical makeup provides a more complete and insightful understanding of this fundamental molecule and its vast applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Are The Multiples Of 8
Mar 10, 2025
-
What Is 12 Out Of 15 As A Percentage
Mar 10, 2025
-
Is Odor A Physical Or Chemical Property
Mar 10, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple 5 And 6
Mar 10, 2025
-
What Is 2 5 In A Fraction
Mar 10, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is Sugar A Mixture Or Pure Substance . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
