Is Sugar A Pure Substance Or Mixture
Kalali
Mar 10, 2025 · 6 min read
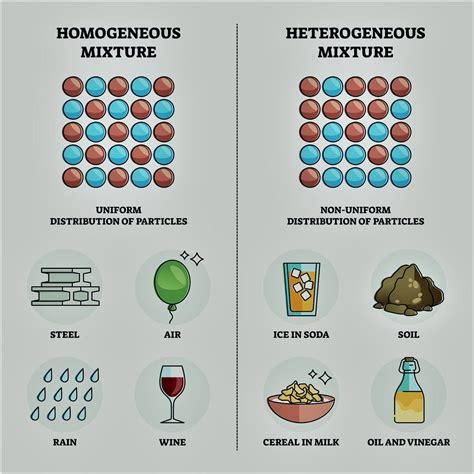
Table of Contents
Is Sugar a Pure Substance or a Mixture? Delving into the Chemistry of Sucrose
The seemingly simple question, "Is sugar a pure substance or a mixture?", opens a fascinating door into the world of chemistry and the properties of matter. While everyday usage might lead us to think of sugar as a single, uniform entity, a closer examination reveals a more nuanced reality. This article will explore the definition of pure substances and mixtures, delve into the chemical composition of sugar (primarily sucrose), and ultimately answer the question definitively, while also exploring related concepts.
Understanding Pure Substances and Mixtures
Before we can classify sugar, we need to clearly understand the fundamental difference between pure substances and mixtures.
Pure Substances: The Building Blocks of Matter
A pure substance is a form of matter that has a constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. This means that no matter where you find it, a pure substance will always have the same chemical makeup and will exhibit the same physical and chemical characteristics. Pure substances can be further divided into two categories:
-
Elements: These are the fundamental building blocks of matter, consisting of only one type of atom. Examples include oxygen (O), hydrogen (H), and gold (Au). Elements cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means.
-
Compounds: These are substances formed by the chemical combination of two or more elements in fixed proportions. The properties of a compound are distinct from the properties of its constituent elements. A classic example is water (H₂O), where hydrogen and oxygen combine to form a substance with very different properties than either element alone. Compounds can be broken down into simpler substances through chemical reactions.
Mixtures: A Blend of Substances
In contrast to pure substances, a mixture is a combination of two or more substances that are not chemically bonded. The components of a mixture retain their individual properties and can be separated by physical methods, such as filtration, distillation, or evaporation. Mixtures can be further categorized into:
-
Homogeneous Mixtures: These mixtures have a uniform composition throughout. This means that the different components are evenly distributed and indistinguishable to the naked eye. Examples include saltwater, air, and sugar dissolved in water (a sugar solution).
-
Heterogeneous Mixtures: These mixtures have a non-uniform composition. The different components are visibly distinguishable and are not evenly distributed. Examples include sand and water, oil and water, and a salad.
The Chemical Composition of Sugar: Primarily Sucrose
Table sugar, the kind we commonly use in our kitchens, is primarily composed of sucrose. Sucrose is a disaccharide, meaning it's a type of sugar composed of two monosaccharides: glucose and fructose. These monosaccharides are chemically bonded together.
The Molecular Structure of Sucrose
Sucrose has a specific molecular formula: C₁₂H₂₂O₁₁. This formula indicates that each molecule of sucrose contains 12 carbon atoms, 22 hydrogen atoms, and 11 oxygen atoms. This precise and consistent ratio is a key characteristic of a pure substance. The arrangement of these atoms within the molecule is also fixed, contributing to sucrose's unique properties.
Refining Sugar: From Cane to Crystalline Sweetness
The process of obtaining refined table sugar from sugarcane or sugar beets involves several steps, including extraction, purification, and crystallization. While impurities are removed during this process, the goal is to isolate the sucrose, making the final product as close to pure sucrose as possible. However, even refined sugar is not 100% pure sucrose. Trace amounts of other substances might remain, but these are generally insignificant.
Is Sugar a Pure Substance or a Mixture? The Answer
Given the information above, we can now definitively answer the question: refined table sugar is considered a pure substance, specifically a compound. While it's not 100% pure sucrose due to the potential presence of minute impurities, the overwhelming majority of its composition is sucrose, and it exhibits the consistent chemical composition and properties expected of a pure substance.
The crucial factor is that the glucose and fructose molecules are chemically bonded to form sucrose. If the sugar were a mixture, the glucose and fructose would exist separately and could be separated using physical methods. This is not the case. The chemical bond between glucose and fructose requires chemical processes to break.
Exploring Different Types of Sugar
It's important to note that different types of sugar exist, and their classification as pure substances or mixtures can vary:
-
Brown Sugar: Contains sucrose as its primary component, but it also includes molasses, which is a complex mixture of various substances. Therefore, brown sugar is a mixture.
-
Raw Sugar: This less-refined sugar also contains impurities like molasses, making it a mixture.
-
Honey: A complex mixture of various sugars (glucose, fructose, etc.), water, and other compounds.
-
Maple Syrup: Similar to honey, a complex mixture containing various sugars and other substances.
These examples highlight the importance of specifying the type of sugar when discussing its classification. When referring to "sugar" without further clarification, it generally implies refined table sugar, which is a pure substance.
Practical Implications and Further Considerations
The classification of sugar as a pure substance has several practical implications:
-
Food Science and Nutrition: Understanding the precise chemical composition of sucrose is crucial in food science, enabling controlled applications and precise nutritional analysis.
-
Industrial Applications: Sucrose's consistent properties make it essential in numerous industries, including pharmaceuticals, textiles, and cosmetics.
-
Chemical Reactions: The predictable behavior of sucrose in chemical reactions is essential for various chemical processes.
Beyond Sucrose: Other Sugars
While sucrose is the most common type of sugar we encounter, other sugars exist. These include:
-
Glucose: A simple sugar (monosaccharide), found in fruits and honey. It's a pure substance.
-
Fructose: Another simple sugar (monosaccharide), found naturally in fruits. It's a pure substance.
-
Lactose: A disaccharide found in milk, composed of glucose and galactose. It's a pure substance.
The classification of these individual sugars, like sucrose, depends on their chemical purity and the absence of other significant substances.
Conclusion: A Deeper Understanding of Sugar's Nature
In conclusion, while the initial question seems simple, understanding whether sugar is a pure substance or a mixture requires a deep dive into chemistry. While different types of sugar can be mixtures due to the presence of impurities or other sugars, refined table sugar, composed primarily of sucrose, is best classified as a pure substance, specifically a compound. This distinction is critical for various applications and underscores the importance of understanding the chemical nature of everyday substances. The consistent chemical composition and predictable behavior of sucrose make it a vital component in various industrial and scientific contexts. However, remember to always specify the type of sugar when discussing its classification, as impurities can transform its nature from a pure substance to a mixture.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many 16 9 Oz Bottles Make A Half Gallon
Jun 30, 2025
-
How Many Times Does 3 Go Into 24
Jun 30, 2025
-
What Year Was I Born If Im 15
Jun 30, 2025
-
What Is The Easter Bunny Favorite Color
Jun 30, 2025
-
How Much Is 100 Gallons Of Diesel
Jun 30, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is Sugar A Pure Substance Or Mixture . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.