Is Supports Combustion A Physical Or Chemical Property
Kalali
Mar 11, 2025 · 5 min read
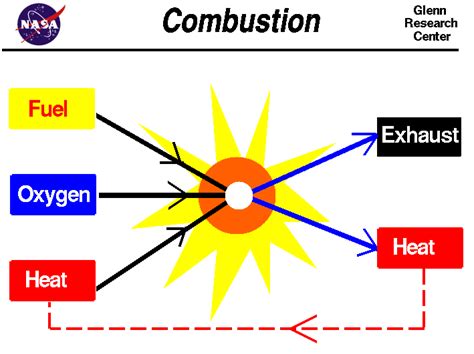
Table of Contents
Is Supporting Combustion a Physical or Chemical Property? A Deep Dive
The question of whether supporting combustion is a physical or chemical property often sparks debate. Understanding the nuances requires exploring the fundamental definitions of both physical and chemical properties, the nature of combustion itself, and the role of substances that support this process. This detailed exploration will clarify the classification and provide a comprehensive understanding of the underlying principles.
Understanding Physical and Chemical Properties
Before diving into the core question, let's establish a firm understanding of the terms "physical property" and "chemical property."
Physical Properties
Physical properties are characteristics of a substance that can be observed or measured without changing the substance's chemical composition. These properties describe the substance's appearance, texture, and behavior under various conditions. Examples include:
- Color: The visual appearance of a substance.
- Density: Mass per unit volume.
- Melting point: Temperature at which a solid turns into a liquid.
- Boiling point: Temperature at which a liquid turns into a gas.
- Solubility: Ability to dissolve in a solvent.
- Conductivity: Ability to conduct electricity or heat.
- Hardness: Resistance to scratching or indentation.
- Malleability: Ability to be hammered into thin sheets.
- Ductility: Ability to be drawn into wires.
Crucially, observing a physical property does not alter the fundamental chemical structure of the material. A piece of gold remains gold, regardless of whether you measure its density, color, or malleability.
Chemical Properties
Chemical properties describe how a substance reacts or changes when interacting with other substances. Observing a chemical property always results in a change in the chemical composition of the substance. Examples include:
- Flammability: Ability to burn in the presence of oxygen.
- Reactivity with acids: How a substance interacts with acidic solutions.
- Toxicity: The degree to which a substance is poisonous.
- Stability: The tendency of a substance to decompose or react with other substances.
- Corrosion resistance: The ability of a substance to resist being corroded or degraded.
In a chemical reaction, the starting materials (reactants) are transformed into different substances (products) with different chemical properties. For example, burning wood (a chemical change) produces ash and gases, distinctly different from the original wood.
Combustion: A Chemical Process
Combustion is a rapid chemical reaction between a substance and an oxidant (usually oxygen) that produces heat and light. It's an exothermic process, meaning it releases energy. The key here is the chemical transformation involved. The fuel undergoes a chemical change, forming new compounds like carbon dioxide and water. This is not a mere physical rearrangement; the molecular structure of the fuel is fundamentally altered.
The Role of Substances Supporting Combustion
Substances that "support combustion" are those that provide the necessary oxidant for the reaction to occur. The most common is oxygen (O₂), but other oxidizing agents can also support combustion under specific conditions. These substances don't themselves burn; rather, they facilitate the burning of the fuel.
This is where the crucial distinction lies. The ability of a substance to support combustion (its oxidizing power) is a chemical property. It reflects the substance's inherent capacity to participate in a chemical reaction, specifically a redox reaction (reduction-oxidation) where the oxidant accepts electrons from the fuel. Oxygen's high electronegativity drives this process.
Think of it this way: oxygen doesn't merely "sit there" while a fuel burns. It actively participates in the reaction, forming chemical bonds with the fuel's atoms, leading to the formation of entirely new compounds. This inherent capacity to react chemically is the defining characteristic of a chemical property.
Why Supporting Combustion is a Chemical Property
Several reasons solidify the classification of supporting combustion as a chemical property:
-
Chemical Transformation: The process of combustion involves a chemical change, not merely a physical one. The fuel's chemical structure is altered, forming new substances with different properties. The oxidant, such as oxygen, also undergoes a chemical change, accepting electrons and transforming its chemical state.
-
Redox Reactions: Combustion is fundamentally a redox reaction. The fuel is oxidized (loses electrons), while the oxidant (like oxygen) is reduced (gains electrons). Redox reactions are inherently chemical processes involving changes in oxidation states.
-
Energy Transfer: The release of heat and light during combustion further emphasizes the chemical nature of the process. This energy transfer is a consequence of the rearrangement of chemical bonds, indicative of a chemical reaction.
-
Irreversibility: Once combustion is complete, it's typically difficult to revert the products back to the original reactants. This irreversibility underscores the significant chemical transformation that has occurred.
-
Observable Changes: The changes observed during combustion – production of heat, light, gases, and often new chemical compounds (like ash) – provide direct evidence of a chemical reaction.
Common Misconceptions
Some might argue that the presence of oxygen is a physical property, as we can measure the amount of oxygen present without chemically changing it. However, this is a misinterpretation. The ability of oxygen to support combustion – its role in the chemical reaction – is the key element. The presence of oxygen is a necessary condition, but it's the chemical interaction that defines it as a chemical property.
The focus should remain on the effect of the substance, not merely its presence. The presence of oxygen is a physical observation, but its capacity to cause a chemical change (combustion) is what determines its classification.
Conclusion: A Definitive Answer
In conclusion, the capacity of a substance to support combustion is unequivocally a chemical property. This is because it describes the substance's inherent ability to participate in a chemical reaction (combustion), leading to a change in the chemical composition of the reactants and the release of energy. It's the chemical interaction, the redox reaction, and the resulting transformation that define this property, not simply the presence of the substance. This clear understanding is crucial for various fields, including fire safety, materials science, and chemical engineering. The ability to correctly classify properties like supporting combustion underpins deeper comprehension of chemical processes and their implications. Understanding this fundamental concept enhances our ability to predict and control chemical reactions, contributing to safer and more efficient applications in countless domains.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Tablespoons In A Packet Of Hidden Valley Ranch
Jun 30, 2025
-
How Many Bunnies Are There In The World
Jun 30, 2025
-
How Is A Watch And Ruler Similar
Jun 30, 2025
-
How Many Liters Is In A Water Bottle
Jun 30, 2025
-
How Many Cups Of Milk Are In A Half Gallon
Jun 30, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is Supports Combustion A Physical Or Chemical Property . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.