Least Common Multiple Of 14 And 8
Kalali
Mar 10, 2025 · 5 min read
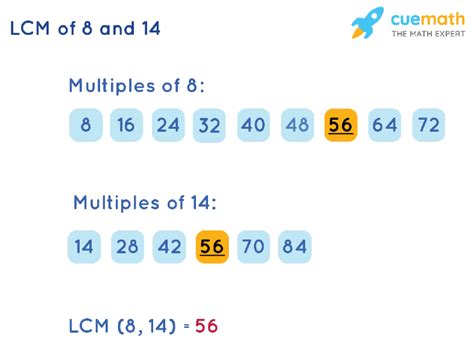
Table of Contents
Finding the Least Common Multiple (LCM) of 14 and 8: A Comprehensive Guide
The least common multiple (LCM) is a fundamental concept in number theory with applications across various fields, from scheduling problems to musical harmony. This article delves deep into calculating the LCM of 14 and 8, exploring multiple methods and illustrating the underlying principles. We'll go beyond a simple answer and unpack the theoretical underpinnings to provide a robust understanding of this important mathematical concept.
Understanding Least Common Multiples
Before we tackle the specific problem of finding the LCM of 14 and 8, let's define the term precisely. The least common multiple (LCM) of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the integers. In simpler terms, it's the smallest number that contains all the numbers as factors.
For instance, let's consider the numbers 2 and 3. Multiples of 2 are 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16... and multiples of 3 are 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18... The common multiples of 2 and 3 are 6, 12, 18, and so on. The least common multiple is 6.
Method 1: Listing Multiples
The most straightforward approach, especially for smaller numbers like 14 and 8, is to list the multiples of each number until you find the smallest common multiple.
Multiples of 14: 14, 28, 42, 56, 70, 84, 98, 112, ...
Multiples of 8: 8, 16, 24, 32, 40, 48, 56, 64, 72, 80, 88, 96, 112, ...
By examining both lists, we can see that the smallest number present in both sequences is 56. Therefore, the LCM(14, 8) = 56. This method is effective for smaller numbers but becomes increasingly cumbersome as the numbers get larger.
Method 2: Prime Factorization
A more efficient and general method utilizes prime factorization. This method is particularly useful for larger numbers where listing multiples becomes impractical.
Step 1: Find the prime factorization of each number.
- 14: The prime factorization of 14 is 2 x 7.
- 8: The prime factorization of 8 is 2 x 2 x 2 = 2³.
Step 2: Identify the highest power of each prime factor present in either factorization.
Both factorizations contain the prime factor 2. The highest power of 2 is 2³ = 8. The prime factor 7 appears only in the factorization of 14, with a power of 1.
Step 3: Multiply the highest powers of all prime factors together.
LCM(14, 8) = 2³ x 7 = 8 x 7 = 56
This method offers a systematic and efficient way to calculate the LCM, regardless of the size of the numbers involved.
Method 3: Using the Greatest Common Divisor (GCD)
There's a powerful relationship between the LCM and the greatest common divisor (GCD) of two numbers. The GCD is the largest number that divides both numbers without leaving a remainder. The formula connecting LCM and GCD is:
LCM(a, b) = (a x b) / GCD(a, b)
Step 1: Find the GCD of 14 and 8.
We can use the Euclidean algorithm to find the GCD:
- 14 = 1 x 8 + 6
- 8 = 1 x 6 + 2
- 6 = 3 x 2 + 0
The last non-zero remainder is 2, so GCD(14, 8) = 2.
Step 2: Apply the formula.
LCM(14, 8) = (14 x 8) / 2 = 112 / 2 = 56
This method demonstrates the elegant connection between LCM and GCD, providing another efficient route to the solution.
Applications of LCM
The LCM has numerous applications in various fields:
-
Scheduling: Imagine two buses departing from the same station at different intervals. The LCM helps determine when they will depart simultaneously again. For example, if one bus departs every 14 minutes and the other every 8 minutes, they will depart together again after 56 minutes.
-
Music: In music theory, the LCM helps determine the least common denominator for musical intervals, allowing musicians to harmonize different rhythms.
-
Fractions: When adding or subtracting fractions with different denominators, finding the LCM of the denominators is crucial to find a common denominator.
-
Modular Arithmetic: LCM plays a crucial role in solving problems in modular arithmetic, a branch of number theory with wide applications in cryptography and computer science.
-
Gear Ratios: In engineering, LCM helps in calculating gear ratios to achieve desired speeds and torques.
Extending to More Than Two Numbers
The methods described above can be extended to find the LCM of more than two numbers. For prime factorization, simply include all prime factors from all the numbers and take the highest power of each. For the GCD-based method, you would iteratively apply the GCD and LCM calculations.
For example, to find the LCM of 14, 8, and 6:
-
Prime Factorization:
- 14 = 2 x 7
- 8 = 2³
- 6 = 2 x 3 The highest powers are 2³, 3, and 7. LCM(14, 8, 6) = 2³ x 3 x 7 = 8 x 3 x 7 = 168
-
Iterative GCD/LCM:
- First, find LCM(14, 8) = 56 (as shown before)
- Then, find LCM(56, 6) = (56 x 6) / GCD(56, 6)
- GCD(56, 6) = 2
- LCM(56, 6) = (56 x 6) / 2 = 168
Conclusion: Mastering LCM Calculations
Understanding the least common multiple is essential for various mathematical applications. This article has explored three distinct methods for calculating the LCM, highlighting their strengths and weaknesses. Whether you use the straightforward method of listing multiples, the efficient prime factorization approach, or the elegant GCD-based method, understanding the underlying principles will empower you to tackle LCM problems with confidence, regardless of the complexity. Remember that the choice of method often depends on the numbers involved and the tools available. For smaller numbers, listing multiples might suffice; for larger numbers, prime factorization or the GCD method is significantly more efficient. The key takeaway is to grasp the concept of LCM and its practical significance across diverse mathematical and real-world scenarios.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Grams In A Teaspoon Of Cinnamon
Jul 18, 2025
-
How Long To Heat Water In Microwave
Jul 18, 2025
-
40 Oz Of Water Is How Many Cups
Jul 18, 2025
-
How Many Eighths In A Quarter Pound
Jul 18, 2025
-
Can The Sine Of An Angle Ever Equal 2
Jul 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Least Common Multiple Of 14 And 8 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.