Least Common Multiple Of 3 And 5
Kalali
Mar 18, 2025 · 5 min read
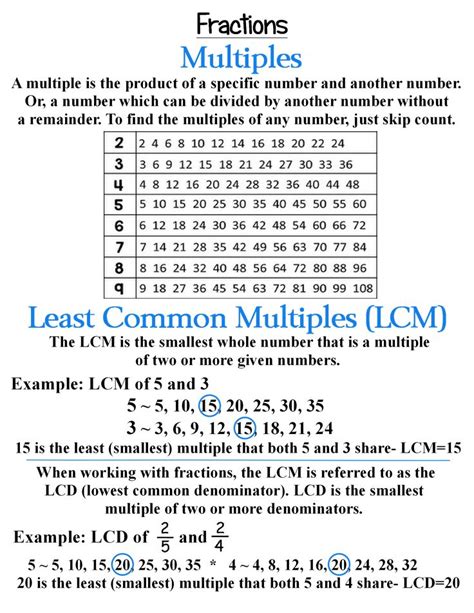
Table of Contents
Unveiling the Least Common Multiple: A Deep Dive into LCM(3, 5) and its Applications
The concept of the least common multiple (LCM) is a fundamental building block in mathematics, particularly within number theory and its various applications. Understanding LCM is crucial for solving a wide range of problems, from scheduling tasks to simplifying fractions and even tackling advanced mathematical concepts. This article will delve deep into the least common multiple of 3 and 5, exploring its calculation, properties, and practical relevance. We'll also touch upon broader applications of LCM and its relationship to other mathematical concepts like the greatest common divisor (GCD).
What is the Least Common Multiple (LCM)?
The least common multiple (LCM) of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the integers. In simpler terms, it's the smallest number that contains all the given numbers as factors. For example, the LCM of 2 and 3 is 6 because 6 is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by both 2 and 3.
Calculating LCM(3, 5)
Calculating the LCM of 3 and 5 can be done using several methods. Let's explore the most common ones:
Method 1: Listing Multiples
This method involves listing the multiples of each number until we find the smallest multiple common to both.
- Multiples of 3: 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21...
- Multiples of 5: 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30...
The smallest multiple that appears in both lists is 15. Therefore, LCM(3, 5) = 15.
Method 2: Prime Factorization
This method is particularly useful for larger numbers. It involves finding the prime factorization of each number and then constructing the LCM from the highest powers of each prime factor present.
- Prime factorization of 3: 3 = 3¹
- Prime factorization of 5: 5 = 5¹
Since 3 and 5 are prime numbers, their prime factorizations are simply themselves. To find the LCM, we take the highest power of each prime factor: 3¹ and 5¹. Multiplying these together gives us: 3¹ * 5¹ = 15. Therefore, LCM(3, 5) = 15.
Method 3: Using the Formula (LCM and GCD Relationship)
There's a fundamental relationship between the LCM and the greatest common divisor (GCD) of two numbers, 'a' and 'b':
LCM(a, b) * GCD(a, b) = a * b
Since 3 and 5 are co-prime (meaning their GCD is 1), we can simplify the formula:
LCM(3, 5) = 3 * 5 / GCD(3, 5) = 15 / 1 = 15
This method highlights the interconnectedness of LCM and GCD, a valuable concept in number theory.
Applications of LCM
The LCM has a wide array of applications across various fields:
1. Scheduling and Time Management
Imagine you have two machines. One completes a cycle every 3 minutes, and the other every 5 minutes. To find out when both machines will complete a cycle simultaneously, we need to find the LCM(3, 5) = 15. Both machines will complete a cycle at the same time after 15 minutes. This concept is crucial for scheduling tasks, coordinating events, and optimizing processes.
2. Fraction Operations
LCM plays a vital role in adding and subtracting fractions with different denominators. To add fractions like 1/3 and 1/5, we need to find a common denominator, which is the LCM of the denominators. In this case, LCM(3, 5) = 15. We then rewrite the fractions with the common denominator:
(1/3) * (5/5) = 5/15 (1/5) * (3/3) = 3/15
Now, we can add the fractions easily: 5/15 + 3/15 = 8/15.
3. Modular Arithmetic and Cryptography
LCM is fundamental in modular arithmetic, a branch of number theory with significant applications in cryptography. Understanding LCM helps in solving congruences and other modular arithmetic problems. These concepts are the bedrock of many modern encryption algorithms that secure online transactions and sensitive data.
4. Music Theory
Interestingly, LCM finds applications even in music theory. Finding the LCM of the durations of different musical notes helps in determining when musical phrases will align, which is crucial for creating harmonious and rhythmic compositions.
5. Engineering and Construction
In engineering and construction projects, LCM helps in aligning components with different repeating cycles or patterns. This is important for optimizing designs and ensuring proper functionality.
6. Computer Science and Algorithm Design
LCM concepts are frequently used in algorithms related to scheduling, resource allocation, and process synchronization within operating systems and other computer applications.
Beyond LCM(3, 5): Expanding the Concept
While this article focuses on LCM(3, 5), the concept readily extends to finding the LCM of more than two numbers. For example, finding the LCM of 3, 5, and 7 involves the same principles. We can use the prime factorization method or listing multiples, though the latter becomes more complex with more numbers. The prime factorization approach remains the most efficient method for larger sets of numbers.
Conclusion: The Power of the Least Common Multiple
The least common multiple, seemingly a simple concept, underlies many important applications across various fields. Understanding its calculation and properties unlocks a deeper appreciation for its role in solving problems ranging from simple fraction addition to complex cryptographic algorithms. This article has explored the LCM(3, 5) as a stepping stone to grasping the broader implications of LCM in mathematics and beyond, highlighting its importance as a core mathematical tool. By appreciating the power of the LCM, we gain a stronger foundation for tackling more complex mathematical challenges and better understanding the world around us. The simplicity of LCM(3,5) belies its profound significance within the broader landscape of mathematics and its applications in diverse fields. From simple scheduling problems to intricate cryptographic systems, LCM plays a critical, often unseen, role in shaping our world. Its elegance and utility are a testament to the power and beauty of fundamental mathematical concepts.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
In What Episode Of Bleach Does Ichigo Ask Orihime Out
Jul 13, 2025
-
How Much Is 4 Oz Chocolate Chips
Jul 13, 2025
-
How Many Times Does 9 Go Into 70
Jul 13, 2025
-
4 Pics 1 Word Cheat 8 Letters
Jul 13, 2025
-
220 Kilometers Per Hour To Miles Per Hour
Jul 13, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Least Common Multiple Of 3 And 5 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.