Lowest Common Factor Of 6 And 12
Kalali
Mar 09, 2025 · 5 min read
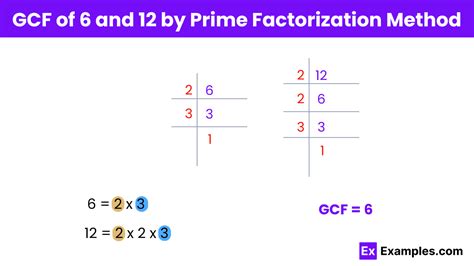
Table of Contents
Unveiling the Lowest Common Factor (LCF) of 6 and 12: A Deep Dive into Number Theory
Finding the lowest common factor (LCF) might seem like a simple arithmetic task, but understanding the underlying principles unlocks a deeper appreciation of number theory and its applications. This article delves into the concept of LCF, specifically focusing on the numbers 6 and 12, demonstrating various methods to determine the LCF, and exploring its significance in mathematics and beyond. We'll also touch upon related concepts like greatest common divisor (GCD) and least common multiple (LCM) to provide a comprehensive understanding.
Understanding Factors and the Concept of LCF
Before diving into the specifics of finding the LCF of 6 and 12, let's establish a clear understanding of fundamental terms.
Factors: Factors of a number are whole numbers that divide the number exactly without leaving any remainder. For example, the factors of 6 are 1, 2, 3, and 6. The factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12.
Common Factors: Common factors are the numbers that are factors of two or more numbers. Looking at 6 and 12, the common factors are 1, 2, 3, and 6.
Lowest Common Factor (LCF): The lowest common factor (LCF), also known as the greatest common divisor (GCD), is the largest of the common factors. It's the biggest number that divides both numbers without leaving a remainder.
Why use LCF/GCD instead of just "common factor"? Specifying "lowest" or "greatest" provides a single, definitive answer when dealing with multiple common factors. This is crucial for many mathematical operations and problem-solving.
Determining the LCF of 6 and 12: Multiple Approaches
Now, let's explore different ways to find the LCF (or GCD) of 6 and 12.
1. Listing Factors Method
This is a straightforward method, particularly useful for smaller numbers:
-
List the factors of each number:
- Factors of 6: 1, 2, 3, 6
- Factors of 12: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 12
-
Identify the common factors: The common factors of 6 and 12 are 1, 2, 3, and 6.
-
Determine the LCF: The largest of these common factors is 6. Therefore, the LCF of 6 and 12 is 6.
2. Prime Factorization Method
This method is more efficient for larger numbers:
-
Find the prime factorization of each number:
- 6 = 2 x 3
- 12 = 2 x 2 x 3 = 2² x 3
-
Identify common prime factors: Both numbers share a '2' and a '3' as prime factors.
-
Calculate the LCF: Multiply the common prime factors raised to their lowest power. In this case, it's 2¹ x 3¹ = 6. The LCF of 6 and 12 is 6.
3. Euclidean Algorithm
The Euclidean Algorithm is a highly efficient method for finding the GCD (LCF) of two numbers, especially large ones. It's based on repeated application of the division algorithm:
-
Divide the larger number by the smaller number: 12 ÷ 6 = 2 with a remainder of 0.
-
If the remainder is 0, the smaller number (6 in this case) is the GCD (LCF).
Therefore, the LCF of 6 and 12 is 6. If the remainder wasn't 0, you'd continue the process by replacing the larger number with the smaller number and the smaller number with the remainder, and repeat the division until the remainder becomes 0.
The Significance of LCF (GCD)
The LCF (or GCD) has significant applications in various areas of mathematics and beyond:
-
Simplifying Fractions: Finding the GCD allows us to simplify fractions to their lowest terms. For example, the fraction 12/6 simplifies to 2/1 (or simply 2) because the GCD of 12 and 6 is 6.
-
Solving Diophantine Equations: These equations involve finding integer solutions. The GCD plays a crucial role in determining whether solutions exist and in finding them.
-
Modular Arithmetic: The GCD is fundamental in modular arithmetic, a branch of number theory with applications in cryptography and computer science.
-
Geometry: The GCD can be used to determine the greatest common measure of lengths in geometrical problems.
-
Music Theory: The GCD is used in understanding musical intervals and harmonies.
Relation to Least Common Multiple (LCM)
The LCF and the least common multiple (LCM) are closely related. The LCM is the smallest number that is a multiple of both numbers. For 6 and 12:
- Multiples of 6: 6, 12, 18, 24, 30...
- Multiples of 12: 12, 24, 36, 48...
The smallest common multiple is 12. There's a useful relationship between the LCF (GCD) and LCM:
LCM(a, b) x GCD(a, b) = a x b
For 6 and 12:
LCM(6, 12) x GCD(6, 12) = 6 x 12 12 x 6 = 72
This relationship is a valuable tool for efficiently calculating either the LCM or GCD if you already know the other.
Expanding the Concept: LCF of Larger Numbers
The methods discussed above can be applied to larger numbers. Let's consider finding the LCF of 24 and 36:
Prime Factorization Method:
- 24 = 2³ x 3
- 36 = 2² x 3²
Common prime factors are 2² and 3¹. Therefore, the LCF (GCD) of 24 and 36 is 2² x 3 = 12.
Euclidean Algorithm:
- 36 ÷ 24 = 1 remainder 12
- 24 ÷ 12 = 2 remainder 0
The LCF (GCD) is 12.
Conclusion: The Power of Understanding LCF
The seemingly simple concept of the lowest common factor (LCF) or greatest common divisor (GCD) reveals a rich mathematical depth. Understanding the different methods for calculating the LCF, its significance in various mathematical fields, and its relationship with the LCM provides a solid foundation for further exploration in number theory and its practical applications. Whether you're simplifying fractions, solving equations, or exploring more advanced mathematical concepts, the ability to find the LCF is a fundamental skill that proves invaluable. This deep dive into the LCF of 6 and 12 serves as a stepping stone to mastering this crucial concept and unlocking a deeper appreciation for the beauty and power of mathematics.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
40 Oz Of Water Is How Many Cups
Jul 18, 2025
-
How Many Eighths In A Quarter Pound
Jul 18, 2025
-
Can The Sine Of An Angle Ever Equal 2
Jul 18, 2025
-
How Many Months Is A Hundred Days
Jul 18, 2025
-
Mother And I Or Mother And Me
Jul 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Lowest Common Factor Of 6 And 12 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.