Lowest Common Multiple Of 4 And 7
Kalali
Mar 10, 2025 · 5 min read
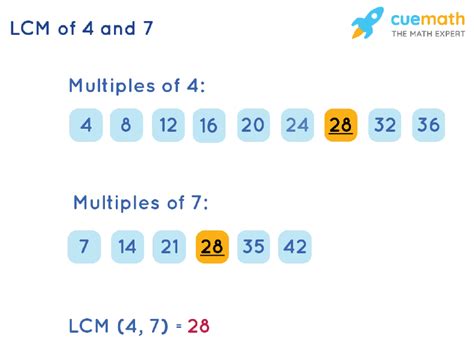
Table of Contents
Unveiling the Mysteries of the Lowest Common Multiple of 4 and 7
Finding the lowest common multiple (LCM) might seem like a simple arithmetic task, but understanding the underlying concepts and exploring different methods can unlock a deeper appreciation for number theory. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of calculating the LCM of 4 and 7, providing various approaches suitable for different mathematical backgrounds, and highlighting the significance of LCM in various applications.
Understanding the Fundamentals: What is LCM?
The Lowest Common Multiple (LCM) of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the integers without leaving a remainder. Think of it as the smallest number that contains all the integers as factors. It's a crucial concept in arithmetic and has far-reaching applications in areas like scheduling, fractions, and even music theory.
Prime Factorization: A Powerful Tool for Finding LCM
One of the most effective methods for determining the LCM is through prime factorization. This involves breaking down each number into its prime factors – numbers divisible only by 1 and themselves. Let's apply this method to find the LCM of 4 and 7:
Step-by-Step Prime Factorization for LCM(4, 7)
-
Prime Factorize 4: 4 = 2 x 2 = 2²
-
Prime Factorize 7: 7 is a prime number, so its prime factorization is simply 7.
-
Identify the Highest Power of Each Prime Factor: In this case, we have 2² and 7.
-
Multiply the Highest Powers: LCM(4, 7) = 2² x 7 = 4 x 7 = 28
Therefore, the lowest common multiple of 4 and 7 is 28.
This method works flawlessly for larger numbers as well. By breaking down the numbers into their prime components, we systematically identify the smallest number that encompasses all the factors.
The Listing Method: A Simpler Approach for Smaller Numbers
For smaller numbers like 4 and 7, the listing method provides a straightforward alternative. This involves listing the multiples of each number until a common multiple is found.
Listing Multiples of 4 and 7
- Multiples of 4: 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, 28, 32, 36...
- Multiples of 7: 7, 14, 21, 28, 35, 42...
The smallest number that appears in both lists is 28, confirming that the LCM(4, 7) = 28.
While this method is intuitive, it becomes less efficient as the numbers increase in size. The prime factorization method remains superior for larger numbers due to its systematic and efficient nature.
The Relationship Between LCM and GCD: The LCM-GCD Formula
The Greatest Common Divisor (GCD), also known as the Highest Common Factor (HCF), is the largest number that divides both integers without leaving a remainder. The LCM and GCD are intimately related through a powerful formula:
LCM(a, b) x GCD(a, b) = a x b
where 'a' and 'b' are the two integers.
Let's use this formula to find the LCM(4, 7):
-
Find the GCD(4, 7): The only common divisor of 4 and 7 is 1. Therefore, GCD(4, 7) = 1.
-
Apply the LCM-GCD Formula: LCM(4, 7) x GCD(4, 7) = 4 x 7
LCM(4, 7) x 1 = 28
LCM(4, 7) = 28
This formula offers an elegant and efficient way to find the LCM, especially when dealing with larger numbers where finding the GCD is relatively easier than directly calculating the LCM. The Euclidean algorithm is a particularly efficient method for calculating the GCD.
Applications of LCM: Where Does it Matter?
The LCM isn't merely an abstract mathematical concept; it finds practical applications in various fields:
1. Scheduling and Time Management
Imagine you have two tasks that repeat at different intervals: Task A repeats every 4 days, and Task B repeats every 7 days. To find when both tasks will coincide again, you need the LCM(4, 7). The LCM, 28, indicates that both tasks will coincide every 28 days.
2. Fraction Operations
Adding or subtracting fractions with different denominators requires finding the LCM of the denominators to create a common denominator. This simplifies the process and ensures accurate results.
3. Music Theory
The LCM plays a role in determining harmonic intervals and rhythmic patterns in music. Understanding the LCM of different note durations helps composers create harmonious and rhythmically consistent pieces.
4. Gear Ratios and Mechanical Engineering
In mechanical systems involving gears, the LCM helps determine the synchronization points of rotating components, ensuring smooth and efficient operation.
5. Project Management
LCM can be used to determine when multiple independent tasks, with different completion times, will all be completed. This can be particularly useful for optimizing project scheduling.
Exploring LCM in Different Number Systems
While our discussion has focused on the LCM in the context of integers, the concept can be extended to other number systems. The principles remain largely the same, although the methods for finding the LCM might differ.
Advanced Techniques for Finding LCM (for larger numbers)
For significantly larger numbers, manual prime factorization can become cumbersome. In these situations, algorithms and computational tools provide efficient solutions. These algorithms often leverage the relationship between the LCM and the GCD to expedite calculations.
Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of LCM
The seemingly simple task of finding the LCM of 4 and 7 serves as a gateway to understanding fundamental concepts in number theory. Through various methods – prime factorization, the listing method, and the LCM-GCD relationship – we've explored different approaches to calculating the LCM. Its applications extend far beyond the classroom, demonstrating its practical importance in various disciplines. Whether you're tackling scheduling problems, simplifying fractions, or delving deeper into mathematical theory, the understanding of the LCM provides a valuable tool for problem-solving and a deeper appreciation for the intricacies of numbers. Mastering the concept of LCM enhances your mathematical toolkit and opens doors to more advanced mathematical explorations.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is Half Of 1 4 Teaspoon
Jul 02, 2025
-
How Many Cups In A Pound Of Hamburger Meat
Jul 02, 2025
-
Imagery Or Figurative Language From Romeo And Juliet
Jul 02, 2025
-
What Is A Quarter Of A Million
Jul 02, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is True Concerning A Dao
Jul 02, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Lowest Common Multiple Of 4 And 7 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.