Números Primos Del 1 Al 100
Kalali
Mar 19, 2025 · 5 min read
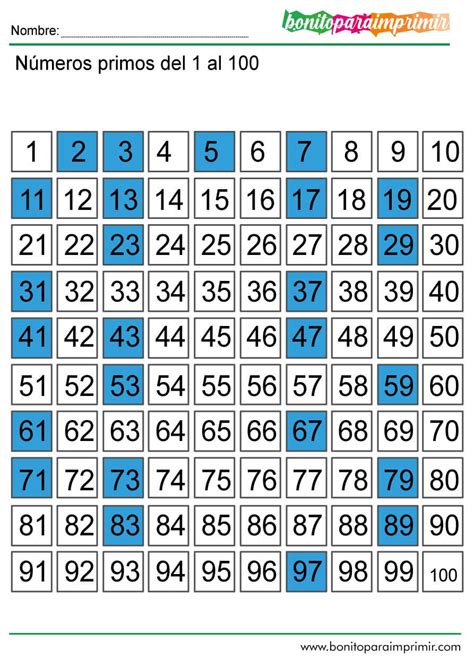
Table of Contents
Prime Numbers from 1 to 100: A Comprehensive Guide
Prime numbers, the building blocks of arithmetic, hold a unique fascination for mathematicians and number enthusiasts alike. This comprehensive guide delves into the prime numbers between 1 and 100, exploring their properties, distribution, and significance in mathematics and beyond. We'll uncover methods for identifying primes, examine their fascinating patterns, and touch upon some of the unsolved mysteries surrounding these fundamental numbers.
What are Prime Numbers?
A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that has no positive divisors other than 1 and itself. In simpler terms, it's a number that can only be divided evenly by 1 and itself. For example, 7 is a prime number because it's only divisible by 1 and 7. Conversely, 6 is not a prime number because it's divisible by 1, 2, 3, and 6. The number 1 is considered neither prime nor composite.
Understanding prime numbers is crucial for grasping fundamental concepts in number theory, cryptography, and computer science. Their seemingly random distribution yet underlying order has captivated mathematicians for centuries, leading to countless research papers and unsolved problems.
Identifying Prime Numbers from 1 to 100
Manually identifying prime numbers can be time-consuming for larger ranges, but for numbers up to 100, a systematic approach is manageable. Here's a breakdown of the process, along with the list of prime numbers:
The Sieve of Eratosthenes: This ancient algorithm provides an efficient method for finding all prime numbers up to a specified integer. The steps are as follows:
- List the numbers: Write down all the numbers from 2 to 100.
- Mark the first prime: 2 is the first prime number. Circle it.
- Eliminate multiples: Cross out all multiples of 2 (4, 6, 8, etc.).
- Find the next prime: The next uncrossed number is 3. Circle it.
- Eliminate multiples: Cross out all multiples of 3 (6, 9, 12, etc.). Note that some multiples will already be crossed out.
- Repeat: Continue this process, finding the next uncrossed number and eliminating its multiples. You only need to check up to the square root of 100 (approximately 10), as any larger number's multiples will have already been crossed out.
By following these steps, you'll be left with only the prime numbers.
List of Prime Numbers from 1 to 100:
2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37, 41, 43, 47, 53, 59, 61, 67, 71, 73, 79, 83, 89, 97
This list represents all the numbers between 1 and 100 that are divisible only by 1 and themselves. Notice their irregular spacing; there's no simple pattern predicting the next prime number.
Properties and Patterns of Prime Numbers
While the distribution of prime numbers appears unpredictable at first glance, several interesting properties and patterns emerge upon closer examination:
- Infinitude of Primes: Euclid proved that there are infinitely many prime numbers. This fundamental theorem highlights the unending nature of these fundamental building blocks of arithmetic.
- Prime Number Theorem: This theorem provides an approximation for the number of primes less than a given number. While it doesn't give an exact count, it offers valuable insight into their distribution.
- Twin Primes: Twin primes are pairs of prime numbers that differ by 2 (e.g., 3 and 5, 11 and 13, 17 and 19). The existence of infinitely many twin primes is a famous unsolved problem in number theory – the Twin Prime Conjecture.
- Prime Gaps: The difference between consecutive prime numbers is known as a prime gap. The study of prime gaps reveals fascinating insights into the irregular distribution of primes. Some prime gaps are small, while others can be surprisingly large.
- Distribution: While primes appear randomly distributed, the Prime Number Theorem suggests a tendency towards decreasing density as numbers increase. Larger numbers generally have a lower probability of being prime.
The Significance of Prime Numbers
Prime numbers are far more than just abstract mathematical concepts; they hold significant practical applications:
- Cryptography: The foundation of modern cryptography relies heavily on the difficulty of factoring large numbers into their prime components. Algorithms like RSA encryption leverage this property to secure online communication and data transmission.
- Hashing: Prime numbers play a vital role in hash functions, which are used in various computing applications, including data storage and retrieval.
- Computer Science: Prime numbers are used in various algorithms and data structures to optimize performance and efficiency.
- Number Theory: Prime numbers are fundamental objects of study in number theory, driving research in numerous unsolved problems and theoretical breakthroughs.
Unsolved Mysteries Surrounding Prime Numbers
Despite centuries of study, prime numbers continue to hold captivating unsolved mysteries:
- Riemann Hypothesis: This is arguably the most important unsolved problem in mathematics. It relates to the distribution of prime numbers and has profound implications for number theory and other fields.
- Goldbach's Conjecture: This conjecture states that every even integer greater than 2 can be expressed as the sum of two primes. While extensively tested, it remains unproven.
- Twin Prime Conjecture: As mentioned earlier, this conjecture proposes that there are infinitely many pairs of twin primes. Its proof or disproof would significantly advance our understanding of prime number distribution.
Conclusion: The Enduring Allure of Prime Numbers
The exploration of prime numbers from 1 to 100 provides a compelling glimpse into the fascinating world of number theory. From their fundamental definition to their significant applications in cryptography and computer science, these numbers reveal a blend of order and randomness that continues to inspire research and fascination. The unsolved mysteries surrounding primes underscore their enduring allure and the wealth of knowledge yet to be discovered within their seemingly simple structure. While we've explored the primes up to 100, the journey into the world of prime numbers is far from over – each larger number presents a new challenge and a potential revelation within this captivating field of mathematics. The seemingly simple question of "what is a prime number?" opens the door to a universe of mathematical depth and enduring intrigue.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
7 Out Of 24 As A Percentage
Mar 19, 2025
-
109 Inches Is How Many Feet
Mar 19, 2025
-
Round 136 To The Nearest Ten
Mar 19, 2025
-
2 3 4 Inch To Mm
Mar 19, 2025
-
Which Layer Of The Earth Has The Lowest Density
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Números Primos Del 1 Al 100 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
