One Of The Physical Properties Of Bases Is That They-
Kalali
Mar 27, 2025 · 6 min read
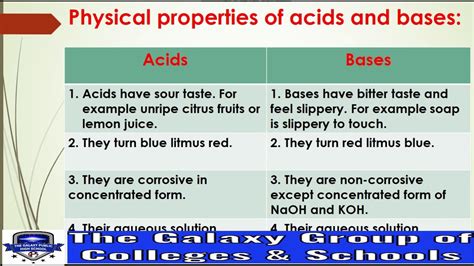
Table of Contents
One of the Physical Properties of Bases is That They… Feel Slippery! Exploring the Tactile and Chemical Nature of Bases
One of the most easily recognizable, albeit somewhat surprising, physical properties of bases is that they feel slippery or soapy to the touch. This seemingly simple observation opens a door to a fascinating world of chemistry, exploring the interactions between bases, water, and the proteins on our skin. Let's delve deeper into this tactile characteristic and unravel the underlying chemical mechanisms.
The Slippery Sensation: More Than Just a Feeling
The slippery feeling associated with bases isn't a mere illusion; it's a direct consequence of a chemical reaction occurring at the interface between the base and the skin's surface. It's not the base itself that's slippery, but rather the product of its interaction with the water and lipids present on our skin.
Understanding the Role of Water
Water plays a crucial role in this phenomenon. Bases, especially strong ones, readily react with water in a process called hydrolysis. This reaction produces hydroxide ions (OH⁻), which are responsible for the characteristic properties of bases. These hydroxide ions don't simply sit idly; they actively participate in altering the surface chemistry of our skin.
The Chemistry of Skin: Proteins and Lipids
Our skin is a complex organ composed of several layers. The outermost layer, the stratum corneum, is primarily composed of dead skin cells containing proteins like keratin and lipids. These lipids form a protective barrier, helping to retain moisture and prevent the entry of harmful substances. It's this lipid layer that is significantly impacted by the presence of bases.
Hydrolysis and Saponification: The Key Reactions
The hydroxide ions generated by the base's hydrolysis react with the lipids in our skin. This reaction is a type of saponification, a process that's central to soap-making. Saponification involves the breakdown of fats and oils (lipids) into glycerol and fatty acid salts (soaps).
The fatty acid salts are surfactants. Surfactants are amphiphilic molecules, meaning they have both hydrophilic (water-loving) and hydrophobic (water-fearing) regions. This dual nature allows them to reduce the surface tension of water, creating the slippery feeling we associate with bases. The hydrophilic head interacts with water, while the hydrophobic tail interacts with the oils and lipids on our skin. This interaction disrupts the normal lipid organization, leading to the characteristic slipperiness.
Beyond the Slip: Other Physical Properties of Bases
While the slippery feel is a common and readily observable property, it's just one aspect of the broader physical characteristics of bases. Several other physical properties help distinguish bases from acids and contribute to their diverse applications.
1. Taste: Bitter and Caustic
Bases generally taste bitter, quite unlike the sour taste of acids. However, it's crucial to emphasize that tasting bases should never be attempted. Many bases are highly corrosive and can cause severe damage to the mouth, throat, and esophagus. This bitterness is a chemical characteristic and not a reliable way to identify bases.
2. Conductivity: Electrically Conductive
Like acids, bases can conduct electricity when dissolved in water. This conductivity stems from the presence of ions in the solution. The hydroxide ions (OH⁻) and the counterions (cations) from the base carry electric charge, enabling the solution to conduct electricity. The strength of the conductivity is directly related to the concentration of ions in the solution—strong bases, producing higher concentrations of ions, are better conductors.
3. pH: High pH Values
Bases have a pH greater than 7, a direct measure of their hydroxide ion concentration. The pH scale is logarithmic, meaning that a change of one pH unit represents a tenfold change in hydroxide ion concentration. Strong bases have a high pH (close to 14), while weak bases have a pH closer to 7. The pH value is a crucial parameter used to quantify the basicity of a solution.
4. Color Change with Indicators: pH Indicators
Bases cause distinct color changes in various pH indicators. pH indicators are substances that change color depending on the pH of the solution. This color change provides a visual way to determine the basicity of a solution without relying on sophisticated equipment. Litmus paper, for instance, turns blue in the presence of bases. Other indicators like phenolphthalein and methyl orange exhibit different color changes at specific pH ranges, allowing for precise pH determination.
5. Reaction with Acids: Neutralization Reactions
One of the defining chemical reactions of bases is their reaction with acids. This reaction, called neutralization, produces water and a salt. The reaction is exothermic, meaning it releases heat. The heat generated can vary depending on the strength of the acid and base involved. The neutralization reaction is crucial in various applications, including industrial processes and controlling pH in different systems.
Safety Precautions when Handling Bases
It's paramount to reiterate that many bases are corrosive and can cause serious harm if handled improperly. Always follow these safety precautions:
- Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE): This includes gloves, eye protection, and lab coats.
- Work in a well-ventilated area: Some bases release harmful vapors.
- Handle bases carefully: Avoid spills and direct contact with skin and eyes.
- Neutralize spills immediately: Use a weak acid, such as dilute acetic acid, to neutralize spills of strong bases.
- Dispose of bases properly: Follow all local regulations for the disposal of chemical waste.
Examples of Bases and their Applications
Bases are ubiquitous in our daily lives and are essential in numerous industrial processes. Here are a few examples:
-
Sodium hydroxide (NaOH): Also known as lye or caustic soda, it's used in soap making, paper production, and drain cleaners. Its high corrosiveness necessitates careful handling.
-
Potassium hydroxide (KOH): Similar to sodium hydroxide, it's used in various applications, including soap making and the production of fertilizers.
-
Calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)₂): Also known as slaked lime, it's used in construction (mortar and plaster), water treatment, and agriculture.
-
Ammonia (NH₃): A weak base, it's found in household cleaners and is also used in the production of fertilizers. It's crucial to note that ammonia gas is highly irritating and toxic.
-
Baking soda (sodium bicarbonate, NaHCO₃): A weak base commonly used in baking and as an antacid. Its relatively mild nature makes it safe for household use.
Conclusion: The Slippery Truth about Bases
The slippery feel of bases is a fascinating manifestation of their chemical reactivity. This tactile experience, coupled with their other physical and chemical properties, highlights the importance of understanding bases' behavior. From their role in everyday products to their industrial applications, bases are integral to our world. Always remember to handle bases with care, using appropriate safety precautions to prevent injuries. The more we understand their properties, the better we can harness their beneficial qualities while mitigating their potential risks. Further exploration into the specific types of bases and their applications will only deepen our appreciation for their crucial role in various aspects of our lives. The seemingly simple observation of slipperiness unveils a complex and intricate world of chemical interactions, underscoring the fascinating interplay between chemistry and our everyday experiences.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
150 Ml Equals How Many Cups
Mar 30, 2025
-
How Many Cups Are 5 Quarts
Mar 30, 2025
-
How Many Cups Is 32 Ox
Mar 30, 2025
-
How Big Is 22 Cm In Inches
Mar 30, 2025
-
What Is 52 Inches In Centimeters
Mar 30, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about One Of The Physical Properties Of Bases Is That They- . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
