Qualitative Data Can Be Measured Quantitatively. T F
Kalali
Mar 27, 2025 · 5 min read
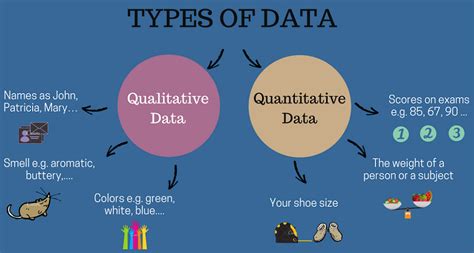
Table of Contents
Qualitative Data Can Be Measured Quantitatively: True or False?
The statement "Qualitative data can be measured quantitatively" is True, but with significant caveats. While seemingly paradoxical, qualitative and quantitative data aren't mutually exclusive categories. The crucial understanding lies in recognizing the methods used to analyze data, not the inherent nature of the data itself. Qualitative data, often perceived as descriptive and rich in context, can indeed be transformed and analyzed using quantitative methods, yielding valuable insights. However, the process requires careful consideration and methodological rigor to avoid misinterpretations and loss of nuanced information.
Understanding the Qualitative-Quantitative Divide
Before diving into the methods of quantifying qualitative data, let's clarify the fundamental differences between the two data types:
Qualitative Data: The Rich Tapestry of Description
Qualitative data is characterized by its descriptive nature. It captures the "why" and "how" behind phenomena, focusing on in-depth understanding of experiences, perspectives, and meanings. Examples include:
- Interviews: Open-ended questions allow participants to express their thoughts and feelings freely.
- Focus groups: Group discussions explore shared opinions and perspectives on a particular topic.
- Observations: Detailed accounts of behaviors and interactions in natural settings.
- Textual data: Documents, transcripts, diaries, and other written materials.
- Images and videos: Visual representations capturing events and contexts.
Qualitative data analysis emphasizes interpretation and identifying patterns, themes, and meanings within the rich textual or visual data.
Quantitative Data: The Precision of Numbers
Quantitative data, in contrast, is numerical and measurable. It focuses on quantifying observations and establishing relationships between variables. Examples include:
- Surveys with closed-ended questions: Providing numerical responses like ratings on a scale.
- Experiments: Measuring the impact of an independent variable on a dependent variable.
- Statistical analyses: Using numerical data to test hypotheses and draw conclusions.
Quantitative data analysis relies on statistical methods to identify trends, test hypotheses, and make predictions.
Bridging the Gap: Quantifying Qualitative Data
The key to understanding how qualitative data can be measured quantitatively lies in the process of quantification. This involves transforming descriptive, non-numerical data into numerical representations that can be subjected to statistical analysis. This isn't about losing the richness of the qualitative data; it's about adding another layer of analysis that reveals different patterns and insights. Several techniques facilitate this process:
1. Content Analysis: Counting and Categorizing
Content analysis is a widely used method for quantifying qualitative data. It involves systematically identifying, coding, and counting the occurrence of specific words, phrases, or themes within textual or visual data. This process requires:
- Defining a coding scheme: Creating a set of categories or codes that represent the key themes or concepts being investigated.
- Coding the data: Systematically assigning codes to units of analysis (e.g., sentences, paragraphs, or images) based on the coding scheme.
- Analyzing the coded data: Calculating the frequency of occurrence of each code and identifying relationships between codes.
Example: Imagine analyzing interview transcripts about customer satisfaction. A coding scheme might include categories such as "positive feedback," "negative feedback," and "neutral feedback." By counting the occurrences of each code, you can quantify the overall level of customer satisfaction.
2. Word Frequency Analysis: Unveiling Patterns in Language
Word frequency analysis leverages computational tools to determine the frequency of different words or phrases in a text corpus. This technique can reveal dominant themes, sentiments, and underlying patterns in the data. Software packages like NLTK (Natural Language Toolkit) and R offer functionalities for conducting word frequency analysis.
Example: Analyzing social media posts related to a brand. Word frequency analysis can reveal the most frequently mentioned aspects of the brand, identifying potential strengths and weaknesses in customer perception.
3. Sentiment Analysis: Gauging Emotional Tone
Sentiment analysis, also known as opinion mining, focuses on identifying and quantifying the emotional tone expressed in text data. This technique is often used to assess public opinion, customer sentiment, or brand reputation.
Example: Analyzing customer reviews on an e-commerce platform. Sentiment analysis can quantify the percentage of positive, negative, or neutral reviews, providing a numerical measure of overall customer satisfaction.
4. Network Analysis: Mapping Relationships
Network analysis is a powerful technique for visualizing and analyzing relationships between different entities within qualitative data. This approach is particularly useful when dealing with social networks, organizational structures, or knowledge domains.
Example: Analyzing interviews to understand the relationships between different stakeholders involved in a project. Network analysis can visualize the connections between individuals and identify key players in the network.
5. Thematic Analysis with Quantitative Measures
Even with purely qualitative thematic analysis, quantification can play a role. While the themes themselves are qualitative, the frequency with which those themes appear can be a quantitative measure of their significance or prevalence. For example, if the theme "lack of communication" appears in 70% of the interviews, it suggests a serious problem requiring attention.
Challenges and Considerations
While quantifying qualitative data offers valuable insights, it's crucial to acknowledge potential limitations and challenges:
- Loss of Nuance: Reducing rich qualitative data to numerical values can lead to a loss of context and subtle meanings.
- Subjectivity in Coding: The process of coding qualitative data involves interpretation and judgment, which can introduce bias and subjectivity. Inter-coder reliability checks are crucial to minimize this.
- Data Validity and Reliability: The validity and reliability of quantified qualitative data depend on the rigor of the data collection and analysis methods.
- Inappropriate Statistical Tests: Applying inappropriate statistical tests to quantified qualitative data can lead to misleading or incorrect conclusions.
Ethical Considerations
When quantifying qualitative data, ethical considerations are paramount. Researchers should ensure:
- Informed consent: Participants should be fully informed about the purpose of the study and how their data will be used.
- Data anonymity and confidentiality: Steps should be taken to protect the identity and privacy of participants.
- Transparency and replicability: The data collection and analysis methods should be clearly documented and replicable.
Conclusion: A Powerful Synergy
The ability to quantify qualitative data opens up exciting possibilities for researchers across various disciplines. By combining the strengths of both qualitative and quantitative approaches, researchers can gain a more comprehensive and nuanced understanding of complex phenomena. The process is not without its challenges, but when executed rigorously and ethically, the synergy between qualitative and quantitative methods can yield compelling insights that would be missed by relying on a single approach. The key takeaway is that the method of analysis dictates the classification, not the inherent nature of the data itself. Qualitative data, while rich in description, is amenable to quantitative analysis, unlocking a deeper understanding of the information contained within.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
8 Pints Is How Many Cups
Mar 30, 2025
-
30 Meters Is How Many Feet
Mar 30, 2025
-
What Is 30 Percent Of 800
Mar 30, 2025
-
How Many Liters Is 100 Ml
Mar 30, 2025
-
1 In 25 As A Percentage
Mar 30, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Qualitative Data Can Be Measured Quantitatively. T F . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
