Side By Side Stem And Leaf Plot
Kalali
Apr 04, 2025 · 6 min read
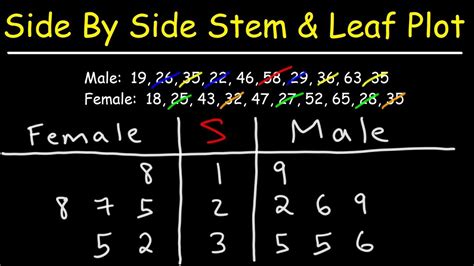
Table of Contents
Side-by-Side Stem and Leaf Plots: A Comprehensive Guide
Stem and leaf plots are a fantastic way to visualize and analyze data, particularly when dealing with smaller datasets. They offer a unique blend of visual representation and numerical detail, allowing for a quick grasp of data distribution, central tendency, and spread. This article dives deep into a powerful variation: the side-by-side stem and leaf plot, showcasing its capabilities and offering step-by-step instructions with examples. We'll explore its advantages, when to use it, and how to interpret the results effectively.
What is a Side-by-Side Stem and Leaf Plot?
A stem and leaf plot organizes data by separating each data point into a "stem" (the leading digit or digits) and a "leaf" (the trailing digit). A side-by-side stem and leaf plot extends this concept by comparing two or more datasets simultaneously on a single plot. This allows for direct visual comparison of the distribution, central tendency, and spread of different groups.
Imagine you're comparing the test scores of two classes. A side-by-side stem and leaf plot allows you to display the scores of both classes side-by-side, making it easy to identify which class performed better overall and how their scores are distributed. This direct visual comparison is a key advantage over creating separate plots for each dataset.
Advantages of Using Side-by-Side Stem and Leaf Plots
- Visual Comparison: The most significant advantage is the direct comparison of multiple datasets. This makes it easy to identify similarities and differences in data distribution.
- Data Retention: Unlike histograms or box plots, stem and leaf plots retain the original data values, offering a detailed view of the data points.
- Easy to Create: They're relatively simple to construct, making them a practical tool for quick data analysis.
- Clear Identification of Outliers: Outliers are easily identifiable as they appear as isolated values on the plot.
- Suitable for Smaller Datasets: Stem and leaf plots are most effective for datasets with a relatively small number of data points. While possible with larger datasets, they can become cumbersome to read.
When to Use a Side-by-Side Stem and Leaf Plot
Side-by-side stem and leaf plots are particularly useful when:
- Comparing two or more groups: The primary purpose is to compare the distribution of data across different groups or categories.
- Dataset size is relatively small: While technically possible for larger datasets, readability decreases as the number of data points increases.
- Detailed data representation is needed: The plot retains the original data values, unlike some other visualization methods.
- Quick analysis is required: They're easy and quick to construct, making them ideal for preliminary data exploration.
Steps to Create a Side-by-Side Stem and Leaf Plot
Let's illustrate the creation process with an example. Suppose we have the following test scores for two classes, Class A and Class B:
Class A: 78, 85, 92, 75, 88, 95, 82, 79, 90, 80
Class B: 80, 88, 90, 76, 85, 93, 82, 78, 86, 91
Step 1: Identify the Stems
The stems will be the tens digit of each score. In this case, the stems range from 7 to 9.
Step 2: Arrange the Data
Organize the data for each class, separating the stem and leaf for each score.
Class A:
- 7 | 8, 5, 9
- 8 | 5, 8, 2, 0
- 9 | 2, 5, 0
Class B:
- 7 | 6, 8
- 8 | 0, 8, 5, 2, 6
- 9 | 0, 3, 1
Step 3: Create the Side-by-Side Plot
Now, arrange the data in a side-by-side format, aligning the stems vertically. Use a key to indicate what the stems and leaves represent.
Class A Class B
Stem | Leaf Stem | Leaf
-----------------------------
7 | 5 8 9 7 | 6 8
8 | 0 2 5 8 8 | 0 2 5 6 8
9 | 0 2 5 9 | 0 1 3
Key: 7|8 represents 78
Interpreting a Side-by-Side Stem and Leaf Plot
Once the plot is created, interpretation is relatively straightforward. Observe the following aspects:
- Distribution: Compare the spread of the leaves for each class. A wider spread indicates greater variability.
- Central Tendency: Examine the clustering of leaves. The area with the most leaves suggests the approximate mean or median score for each class.
- Outliers: Identify any significantly isolated leaves. These represent outliers, values significantly different from the rest of the data.
- Comparison: Directly compare the distributions, central tendency, and spread of both classes. This allows for insightful conclusions regarding the relative performance of each class.
For example, by looking at the above plot, we can immediately see that Class A has a slightly higher proportion of scores in the 90s, suggesting potentially better overall performance than Class B, though the difference is not dramatic. Both classes have similar spreads.
Advanced Techniques and Considerations
While the basic side-by-side stem and leaf plot is straightforward, there are a few techniques to enhance its clarity and usefulness:
-
Split Stems: For datasets with many data points clustered within a narrow range, using split stems can improve the plot's readability. For instance, you could split the stem '8' into '80-84' and '85-89'. This allows for a more detailed view of the data's distribution within the stem.
-
Back-to-Back Stem and Leaf Plot: Another variation is the back-to-back stem and leaf plot, where the leaves for each group extend in opposite directions from a shared stem. This allows for a more compact representation, particularly useful for comparing two datasets.
-
Categorical Data: Side-by-side stem and leaf plots aren't ideally suited for categorical data. Other visualization techniques, such as bar charts or pie charts, are better suited for visualizing categorical data.
-
Data Transformation: If the data is heavily skewed or has a wide range, consider applying a transformation (like logarithmic transformation) before creating the plot. This can improve the readability and interpretation of the plot.
Conclusion
The side-by-side stem and leaf plot is a versatile and valuable tool for comparing and analyzing multiple datasets simultaneously. Its ability to retain individual data points while providing a visual representation of distribution makes it a powerful addition to any data analyst's toolkit. By understanding the advantages, steps involved in creation, and interpretation, you can effectively utilize this method to draw meaningful insights from your data. Remember to choose the appropriate visualization technique based on the characteristics of your data and the insights you aim to extract. Careful consideration of these factors ensures effective communication of your findings.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 185 Celsius In Fahrenheit
Apr 04, 2025
-
How Many Miles In 10 Kilometers
Apr 04, 2025
-
What Time Of Day Is Hottest
Apr 04, 2025
-
Does Sea Moss Have Vitamin B12
Apr 04, 2025
-
How Many Hours Is 330 Minutes
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Side By Side Stem And Leaf Plot . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
