Solving Equations Using The Distributive Property
Kalali
Mar 21, 2025 · 6 min read
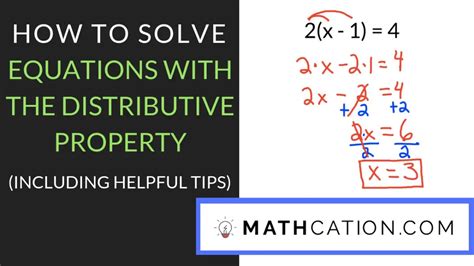
Table of Contents
Solving Equations Using the Distributive Property: A Comprehensive Guide
The distributive property is a fundamental concept in algebra that simplifies complex equations and opens doors to solving a wide range of mathematical problems. Mastering this property is crucial for anyone looking to build a strong foundation in algebra and beyond. This comprehensive guide will delve into the distributive property, exploring its applications in solving equations, providing step-by-step examples, and offering tips and tricks to enhance your understanding.
Understanding the Distributive Property
The distributive property states that multiplying a sum by a number is the same as multiplying each addend by the number and then adding the products. Mathematically, it's represented as:
a(b + c) = ab + ac
Where 'a', 'b', and 'c' can represent numbers, variables, or expressions. The property works equally well for subtraction:
a(b - c) = ab - ac
This seemingly simple concept is the key to unlocking numerous algebraic solutions. It allows us to break down complex expressions into simpler, manageable parts, making equation solving significantly easier.
Applying the Distributive Property to Solve Equations
The distributive property is most often used when parentheses are present in an equation. These parentheses group terms, and the distributive property helps us to remove them, allowing us to proceed with solving the equation.
Let's explore several examples demonstrating different scenarios and complexities:
Example 1: Basic Application
Solve the equation: 3(x + 2) = 15
Step 1: Distribute the 3:
3(x) + 3(2) = 15
This simplifies to:
3x + 6 = 15
Step 2: Isolate the variable term:
Subtract 6 from both sides of the equation:
3x + 6 - 6 = 15 - 6
3x = 9
Step 3: Solve for x:
Divide both sides by 3:
3x / 3 = 9 / 3
x = 3
Example 2: Incorporating Subtraction
Solve the equation: 2(y - 5) = 8
Step 1: Distribute the 2:
2(y) - 2(5) = 8
This simplifies to:
2y - 10 = 8
Step 2: Isolate the variable term:
Add 10 to both sides:
2y - 10 + 10 = 8 + 10
2y = 18
Step 3: Solve for y:
Divide both sides by 2:
2y / 2 = 18 / 2
y = 9
Example 3: Distributing a Negative Number
Solve the equation: -4(z + 3) = 20
Step 1: Distribute the -4:
-4(z) + (-4)(3) = 20
This simplifies to:
-4z - 12 = 20
Step 2: Isolate the variable term:
Add 12 to both sides:
-4z - 12 + 12 = 20 + 12
-4z = 32
Step 3: Solve for z:
Divide both sides by -4:
-4z / -4 = 32 / -4
z = -8
Remember, when distributing a negative number, the signs of the terms inside the parentheses change.
Example 4: Equations with Variables on Both Sides
Solve the equation: 5(x + 1) = 2x + 17
Step 1: Distribute the 5:
5(x) + 5(1) = 2x + 17
5x + 5 = 2x + 17
Step 2: Combine like terms:
Subtract 2x from both sides:
5x - 2x + 5 = 2x - 2x + 17
3x + 5 = 17
Step 3: Isolate the variable term:
Subtract 5 from both sides:
3x + 5 - 5 = 17 - 5
3x = 12
Step 4: Solve for x:
Divide both sides by 3:
3x / 3 = 12 / 3
x = 4
Example 5: Equations with Fractions
Solve the equation: 1/2(2x + 6) = 5
Step 1: Distribute the 1/2:
(1/2)(2x) + (1/2)(6) = 5
x + 3 = 5
Step 2: Isolate the variable term:
Subtract 3 from both sides:
x + 3 - 3 = 5 - 3
x = 2
These examples showcase the versatility of the distributive property in solving various equation types. The key is to systematically apply the property to eliminate parentheses, then proceed with standard equation-solving techniques.
Beyond Basic Applications: Advanced Scenarios
The distributive property isn't limited to simple equations. It finds application in more complex scenarios:
Factoring Expressions
The distributive property is also used in reverse, a process called factoring. This allows us to rewrite expressions in a more concise form. For example, the expression 3x + 6 can be factored as 3(x + 2), using the distributive property in reverse. Factoring is a crucial skill in simplifying expressions and solving quadratic equations.
Solving Inequalities
The distributive property works exactly the same way with inequalities. Remember to maintain the inequality symbol throughout the solution process. For example, solving 2(x + 3) > 8 follows the same steps as solving the equivalent equation, but the solution will be an inequality (e.g., x > 1).
Working with Polynomials
The distributive property is essential when working with polynomials, expressions with multiple terms. For instance, expanding (x + 2)(x + 3) requires distributing each term in the first parenthesis to each term in the second parenthesis. This results in a quadratic expression that can be further simplified.
Real-World Applications
The distributive property isn't confined to the realm of theoretical mathematics. It finds practical application in various real-world scenarios, including:
- Calculating area and volume: Finding the area of a complex shape often involves breaking it down into simpler shapes, using the distributive property to calculate individual areas and then summing them.
- Financial calculations: Calculating compound interest or determining the total cost of items after sales tax often involves applying the distributive property.
- Physics and engineering: Many physics and engineering problems rely on solving equations, and the distributive property provides a crucial tool for simplifying those equations.
Tips and Tricks for Success
- Practice makes perfect: The more you practice using the distributive property, the more comfortable and proficient you will become. Work through a variety of examples, focusing on different scenarios and complexities.
- Check your work: After solving an equation, substitute your solution back into the original equation to verify that it's correct. This will help identify any mistakes you might have made.
- Focus on understanding, not memorization: Don't just memorize the formula; understand the underlying principle. This understanding will help you apply the distributive property correctly in various contexts.
- Break down complex problems: When faced with a complex equation, break it down into smaller, more manageable parts. This will make the problem easier to solve.
- Utilize online resources: Numerous online resources, including videos, tutorials, and practice problems, can help you further develop your understanding of the distributive property.
Conclusion
The distributive property is a cornerstone of algebra, enabling us to simplify expressions and solve equations efficiently. By understanding its applications and practicing regularly, you'll strengthen your mathematical skills and build a solid foundation for more advanced mathematical concepts. Mastering the distributive property isn't just about solving equations; it's about developing a deeper understanding of mathematical relationships and problem-solving techniques that are applicable across many disciplines. Continue practicing, explore different problems, and you’ll soon find yourself confidently tackling even the most complex algebraic equations.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Acres Is A Square Mile
Mar 28, 2025
-
15 Out Of 50 As A Percentage
Mar 28, 2025
-
How Many Inches In 8 Cm
Mar 28, 2025
-
How To Find Slope Of Vector
Mar 28, 2025
-
How Tall Is 163cm In Feet
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Solving Equations Using The Distributive Property . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
