The Normal Pacemaker Of The Heart Is The
Kalali
Mar 24, 2025 · 6 min read
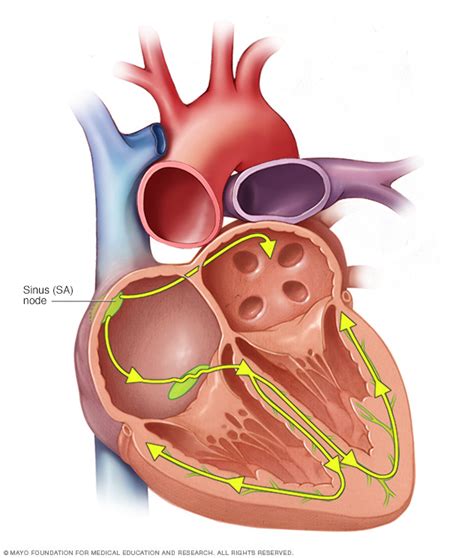
Table of Contents
The Normal Pacemaker of the Heart Is the Sinoatrial (SA) Node
The human heart, a remarkable organ, beats rhythmically throughout our lives, pumping blood to every corner of our body. This continuous, coordinated rhythm isn't accidental; it's orchestrated by a sophisticated internal electrical conduction system. At the heart of this system lies the sinoatrial (SA) node, the natural pacemaker of the heart. Understanding the SA node's function, its role in maintaining a healthy heartbeat, and potential disruptions to its activity is crucial for comprehending cardiovascular health.
Understanding the Sinoatrial (SA) Node: The Heart's Natural Pacemaker
The SA node, a small, specialized group of cells located in the right atrium near the superior vena cava, acts as the heart's primary pacemaker. Unlike other cardiac muscle cells, SA nodal cells possess unique properties that allow them to spontaneously generate electrical impulses. These impulses trigger the coordinated contractions of the heart muscle, enabling the heart to pump blood effectively.
The Unique Properties of SA Nodal Cells
Several key properties distinguish SA nodal cells from other cardiac cells:
-
Automaticity: This is the defining characteristic of SA nodal cells. They possess the ability to spontaneously depolarize and generate action potentials without external stimulation. This inherent rhythmicity is what drives the heart's rhythmic contractions.
-
Rhythmicity: SA nodal cells don't just generate impulses; they do so at a regular, rhythmic pace. This consistent rhythm is essential for maintaining a stable heart rate.
-
Conductivity: While the SA node initiates the heartbeat, it's equally important that the impulse spreads efficiently throughout the heart. SA nodal cells effectively conduct the electrical impulse to other parts of the cardiac conduction system.
-
Excitability: SA nodal cells are highly excitable, meaning they respond readily to stimuli. Although they spontaneously generate impulses, their inherent rhythm can be modulated by various factors like the autonomic nervous system and hormones.
The Cardiac Conduction System: A Symphony of Electrical Signals
The SA node is not the only player in the heart's electrical conduction system. It's part of a larger network that ensures the efficient and coordinated contraction of the heart chambers. This system comprises several key components:
-
Sinoatrial (SA) Node: The primary pacemaker, initiating the heartbeat.
-
Atrioventricular (AV) Node: Located between the atria and ventricles, the AV node acts as a gatekeeper, delaying the electrical impulse before it reaches the ventricles. This delay ensures that the atria contract and empty their blood into the ventricles before ventricular contraction begins.
-
Bundle of His: This specialized pathway conducts the impulse from the AV node to the ventricles.
-
Bundle Branches: The Bundle of His divides into right and left bundle branches, further conducting the impulse to the right and left ventricles.
-
Purkinje Fibers: These fibers rapidly distribute the impulse throughout the ventricular muscle, ensuring synchronous ventricular contraction.
The coordinated action of these components is essential for efficient blood pumping. Disruptions at any point in this pathway can lead to irregular heart rhythms, or arrhythmias.
Regulation of Heart Rate: The Autonomic Nervous System's Influence
The heart rate isn't fixed; it constantly adapts to meet the body's changing needs. The autonomic nervous system, comprising the sympathetic and parasympathetic branches, plays a critical role in regulating heart rate by influencing the SA node's activity.
Sympathetic Stimulation: Increasing Heart Rate
The sympathetic nervous system, associated with the "fight-or-flight" response, accelerates the heart rate. Sympathetic nerves release norepinephrine, a neurotransmitter that increases the rate of spontaneous depolarization in SA nodal cells. This leads to faster impulse generation and a higher heart rate. This increase is crucial during physical activity or stressful situations, when the body demands increased blood flow.
Parasympathetic Stimulation: Decreasing Heart Rate
The parasympathetic nervous system, associated with the "rest-and-digest" response, slows the heart rate. The vagus nerve, the primary parasympathetic nerve to the heart, releases acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that slows down the rate of spontaneous depolarization in SA nodal cells. This results in a slower impulse generation and a lower heart rate. This reduction conserves energy during rest.
Electrocardiogram (ECG): A Window into the Heart's Electrical Activity
The electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a valuable diagnostic tool used to assess the heart's electrical activity. It provides a graphical representation of the electrical impulses generated by the heart, allowing clinicians to identify irregularities in the heart's rhythm and conduction. Analyzing the ECG can reveal whether the SA node is functioning correctly and if other components of the cardiac conduction system are performing optimally. Key features of a normal ECG reflect the normal function of the SA node and the rest of the conduction system.
Conditions Affecting the SA Node: Bradycardia and Tachycardia
While the SA node is typically a reliable pacemaker, its function can be compromised by various conditions, leading to abnormal heart rhythms.
Bradycardia: Slow Heart Rate
Bradycardia refers to a slow heart rate, typically below 60 beats per minute. Several factors can cause bradycardia, including:
-
SA node dysfunction: The SA node may not generate impulses at the normal rate due to disease, aging, or medication side effects.
-
Increased parasympathetic activity: Excessive vagal tone can slow down the heart rate.
-
Underlying heart conditions: Certain heart diseases can impair the SA node's function.
Bradycardia can cause symptoms such as dizziness, fatigue, and shortness of breath. In severe cases, it can lead to fainting or even cardiac arrest.
Tachycardia: Fast Heart Rate
Tachycardia is characterized by a rapid heart rate, usually above 100 beats per minute. Several causes can lead to tachycardia, including:
-
SA node dysfunction: The SA node may generate impulses at an abnormally fast rate.
-
Increased sympathetic activity: Excessive sympathetic stimulation, due to stress or other factors, can accelerate the heart rate.
-
Ectopic pacemakers: Other areas of the heart may take over as the pacemaker, leading to rapid, irregular heartbeats.
Tachycardia can cause palpitations, shortness of breath, chest pain, and dizziness.
Maintaining a Healthy Heart: Lifestyle Choices and Medical Interventions
Maintaining a healthy heart is crucial for overall well-being. Lifestyle choices significantly impact heart health:
-
Regular Exercise: Physical activity strengthens the heart muscle and improves cardiovascular function.
-
Balanced Diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains supports cardiovascular health.
-
Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the strain on the heart.
-
Stress Management: Chronic stress can negatively impact the heart; techniques like yoga or meditation can help manage stress.
-
Avoiding Smoking and Excessive Alcohol Consumption: These habits damage the cardiovascular system.
In cases of SA node dysfunction, medical interventions may be necessary. These can include:
-
Medication: Drugs can help regulate heart rate and rhythm.
-
Pacemaker Implantation: A pacemaker is a small electronic device implanted under the skin to regulate the heart rate in cases of bradycardia. This device electrically stimulates the heart to maintain a normal rhythm.
Conclusion: The SA Node – A Vital Component of Cardiovascular Health
The sinoatrial node, the heart's natural pacemaker, plays a critical role in maintaining a healthy heartbeat. Its unique properties of automaticity, rhythmicity, conductivity, and excitability enable the heart to pump blood efficiently. The SA node's function is intricately regulated by the autonomic nervous system and influenced by various factors, including lifestyle choices and underlying medical conditions. Understanding the SA node's role in the cardiac conduction system is crucial for diagnosing and managing various heart rhythm disorders, emphasizing the importance of maintaining cardiovascular health through a healthy lifestyle and appropriate medical interventions when necessary. Regular checkups and awareness of potential symptoms are key to early detection and intervention, ensuring optimal heart health and overall well-being.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Cuanto Es El 7 Por Ciento De 1000
May 09, 2025
-
What Type Of Symmetry Do Platyhelminthes Have
May 09, 2025
-
Convert 58 Degrees Fahrenheit To Celsius
May 09, 2025
-
65 Cm In Inches And Feet
May 09, 2025
-
How Much Is 20 Of 300
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Normal Pacemaker Of The Heart Is The . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.