What Is 11/16 As A Decimal
Kalali
Mar 20, 2025 · 5 min read
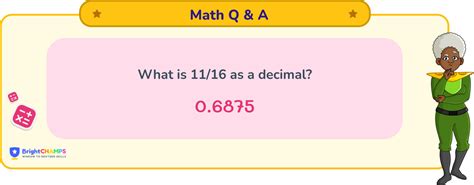
Table of Contents
What is 11/16 as a Decimal? A Comprehensive Guide
Converting fractions to decimals is a fundamental skill in mathematics with widespread applications in various fields. This comprehensive guide delves deep into the process of converting the fraction 11/16 into its decimal equivalent, exploring different methods and providing a detailed explanation to solidify your understanding. We'll also touch upon the broader context of fraction-to-decimal conversion, highlighting its importance and practical uses.
Understanding Fractions and Decimals
Before we dive into the conversion of 11/16, let's refresh our understanding of fractions and decimals.
Fractions: A fraction represents a part of a whole. It's expressed as a ratio of two numbers, the numerator (top number) and the denominator (bottom number). The denominator indicates the total number of equal parts the whole is divided into, while the numerator indicates how many of those parts are being considered.
Decimals: A decimal is another way of representing a part of a whole. It uses a base-10 system, where the digits to the right of the decimal point represent tenths, hundredths, thousandths, and so on.
The conversion between fractions and decimals is essentially about expressing the same quantity using different notations.
Method 1: Long Division
The most straightforward method for converting a fraction to a decimal is through long division. To convert 11/16 to a decimal, we divide the numerator (11) by the denominator (16):
-
Set up the long division: Write 11 as the dividend and 16 as the divisor. Since 11 is smaller than 16, we add a decimal point to 11 and add zeros as needed.
-
Perform the division: 16 goes into 11 zero times, so we add a zero to 11 making it 110. 16 goes into 110 six times (16 x 6 = 96). Subtract 96 from 110, leaving 14.
-
Continue the process: Add another zero to 14 making it 140. 16 goes into 140 eight times (16 x 8 = 128). Subtract 128 from 140, leaving 12.
-
Repeat as needed: Continue adding zeros and dividing until you reach a remainder of 0 or a repeating pattern. In this case, we continue:
- Add a zero to 12 making it 120. 16 goes into 120 seven times (16 x 7 = 112). Subtract 112 from 120, leaving 8.
- Add a zero to 8 making it 80. 16 goes into 80 five times (16 x 5 = 80). Subtract 80 from 80, leaving 0.
-
Result: The long division yields 0.6875. Therefore, 11/16 as a decimal is 0.6875.
Method 2: Using Equivalent Fractions
Another approach involves finding an equivalent fraction with a denominator that's a power of 10 (10, 100, 1000, etc.). While this method isn't always feasible, it can be simpler in certain cases. Unfortunately, 16 doesn't easily convert to a power of 10. The prime factorization of 16 is 2<sup>4</sup>, and powers of 10 only contain the prime factors 2 and 5. Therefore, this method is less practical for 11/16.
Method 3: Calculator
The simplest and quickest method is to use a calculator. Simply enter 11 ÷ 16 and the calculator will display the decimal equivalent, 0.6875.
Practical Applications of Fraction-to-Decimal Conversion
The conversion of fractions to decimals is essential in various fields:
-
Engineering and Technology: Precise measurements and calculations often require decimal representation.
-
Finance: Dealing with percentages, interest rates, and currency conversions frequently involves decimal values.
-
Science: Scientific data analysis and reporting frequently utilize decimals for accuracy.
-
Everyday Life: Calculating discounts, tips, and proportions often necessitates the conversion of fractions to decimals.
Understanding Repeating and Terminating Decimals
When converting fractions to decimals, you'll encounter two types of decimals:
-
Terminating decimals: These decimals have a finite number of digits after the decimal point, such as 0.6875 (the decimal equivalent of 11/16).
-
Repeating decimals: These decimals have a pattern of digits that repeats infinitely, such as 1/3 = 0.3333... The repeating pattern is often indicated with a bar over the repeating digits (e.g., 0.3̅).
The decimal representation of 11/16 is a terminating decimal because the division process ends with a remainder of 0. This is because the denominator (16) only contains the prime factor 2, and fractions with denominators containing only powers of 2 and/or 5 always result in terminating decimals.
Beyond 11/16: Generalizing Fraction-to-Decimal Conversion
The methods described above can be applied to any fraction. The key is to understand the relationship between the numerator and denominator and to choose the most efficient method based on the specific fraction.
Fractions with denominators that are powers of 10: These are the easiest to convert. Simply move the decimal point accordingly. For example, 3/10 = 0.3, and 27/100 = 0.27.
Fractions with denominators that are factors of powers of 10: These can sometimes be converted to equivalent fractions with denominators that are powers of 10.
Fractions with other denominators: Long division is the most reliable method for converting these fractions to decimals.
Troubleshooting Common Mistakes
-
Incorrect placement of the decimal point: Pay close attention to the placement of the decimal point in both the dividend and the quotient during long division.
-
Rounding errors: When dealing with repeating decimals, it's important to specify the level of accuracy required and round appropriately.
-
Computational errors: Carefully check your calculations during long division to avoid errors.
Conclusion
Converting the fraction 11/16 to its decimal equivalent (0.6875) is a straightforward process that can be accomplished through long division, or more simply with a calculator. Understanding the different methods and the underlying concepts of fractions and decimals is crucial for mastering this skill and applying it effectively in various contexts. This comprehensive guide provides a solid foundation for understanding and performing fraction-to-decimal conversions, equipping you with the knowledge to tackle similar problems confidently. Remember to practice regularly to solidify your understanding and improve your speed and accuracy.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Long Is 25cm In Inches
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Is 120 C In F
Mar 28, 2025
-
Los Hongos Produsesn Su Propio Alimento
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Is 2 25 As A Fraction
Mar 28, 2025
-
350 Miles Is How Many Kilometers
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is 11/16 As A Decimal . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
