What Is 2 3 2 3 In Cups
Kalali
Aug 24, 2025 · 6 min read
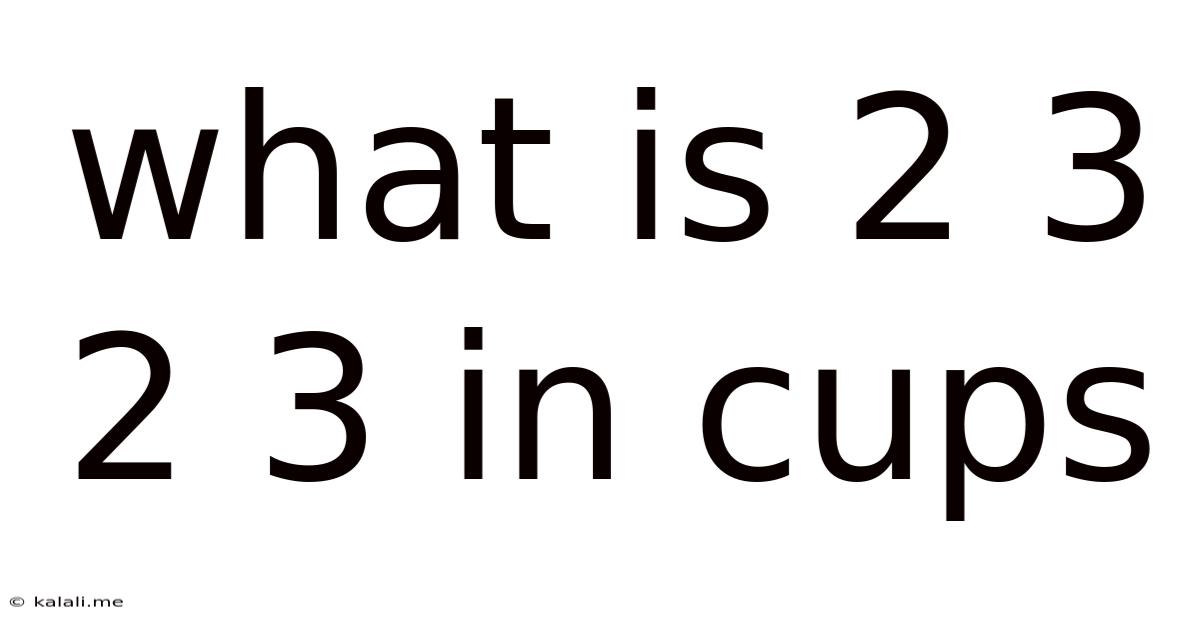
Table of Contents
Decoding "2 3 2 3 in Cups": A Comprehensive Guide to Baking Ratios
Are you staring at a baking recipe that mysteriously calls for "2 3 2 3 in cups"? This cryptic instruction, often found in older recipes or those adapted from metric measurements, leaves many bakers scratching their heads. This article will demystify this common baking ratio, explaining what it means, how to convert it into usable measurements, and ultimately, how to confidently tackle recipes using this unconventional notation. We'll also delve into the underlying principles of baking ratios and explore variations to help you become a more adaptable and skilled baker.
What Does 2 3 2 3 in Cups Actually Mean?
The "2 3 2 3 in cups" notation typically refers to a ratio of dry ingredients commonly used in cakes, muffins, quick breads, and other baked goods. It represents a proportion, not precise amounts. The numbers represent the relative amounts of four key ingredients:
- 2: Usually refers to 2 cups of flour. This is the base ingredient, providing structure to the baked good.
- 3: Typically represents 3 cups of sugar. Sugar contributes sweetness, moisture, and browning.
- 2: This often denotes 2 cups of liquid (usually milk, buttermilk, or water). Liquid provides moisture and helps activate the leavening agents.
- 3: This typically refers to 3 cups of other ingredients (e.g., dry ingredients like oats or cocoa powder). This category is the most variable and adaptable.
Understanding the Importance of Ratios in Baking
Before we dive into conversions, let's understand why ratios are crucial in baking. Unlike cooking, where minor adjustments to ingredient amounts often have minimal impact, baking is a precise science. The ratio of ingredients directly affects the texture, moisture, and overall outcome of your baked goods. Using a consistent ratio allows for:
- Predictability: Once you understand a ratio, you can easily scale it up or down to bake larger or smaller batches.
- Consistency: Sticking to the ratio helps ensure your baked goods turn out consistently, regardless of the batch size.
- Flexibility: Understanding the underlying principles allows you to adapt and experiment with variations and substitutions.
Converting "2 3 2 3" into Usable Measurements: A Step-by-Step Guide
The first step is to determine the total number of units in the ratio: 2 + 3 + 2 + 3 = 10. This means the ratio is expressed as parts of ten. Now, let’s say you want to bake a cake using this ratio, but want to adjust it to a smaller size. Let's make a half-batch, so we will divide by two:
-
Decide on Your Desired Batch Size: Let's make a half-batch to keep it manageable. This means dividing each number by 2.
-
Calculate Individual Ingredient Amounts:
- Flour: 2 cups / 2 = 1 cup
- Sugar: 3 cups / 2 = 1.5 cups
- Liquid: 2 cups / 2 = 1 cup
- Other: 3 cups / 2 = 1.5 cups
-
Substitute "Other" Ingredients: Now, you need to decide what ingredients make up the "Other" 1.5 cups. This is where creativity and understanding your recipe come in. This could be:
- Example 1 (Cake): 1 cup all-purpose flour and 0.5 cup cocoa powder (or other flavorings)
- Example 2 (Muffin): 1 cup rolled oats and 0.5 cup chopped nuts or chocolate chips.
- Example 3 (Quick Bread): 0.75 cup chopped dried fruit and 0.75 cup whole wheat flour.
Scaling the Ratio: Making Larger or Smaller Batches
This ratio is easily scalable. Suppose you wanted to double the recipe:
- Flour: 2 cups * 2 = 4 cups
- Sugar: 3 cups * 2 = 6 cups
- Liquid: 2 cups * 2 = 4 cups
- Other: 3 cups * 2 = 6 cups
You can apply the same principle to create larger or smaller batches. Just multiply or divide each component of the ratio by the desired scaling factor.
Variations and Substitutions within the "2 3 2 3" Ratio
The beauty of understanding the ratio is the flexibility it offers. While the basic ratio provides a good starting point, you can adapt it to suit your preferences and available ingredients. Consider these variations:
-
Reducing Sugar: If you prefer a less sweet cake, you can reduce the sugar portion slightly. For instance, you could try a 2:2.5:2:3 ratio. However, remember that sugar plays a vital role in moisture and texture, so don't reduce it too drastically.
-
Adding Whole Wheat Flour: You can partially replace all-purpose flour with whole wheat flour to increase fiber content. Start with a 50/50 mix. Keep in mind that whole wheat flour is denser, so you may need to adjust the liquid slightly.
-
Using Different Liquids: Experiment with different liquids such as buttermilk, milk, yogurt, or even apple sauce (if baking a fruit cake). This changes the flavor and moisture level of the final product. Remember to adjust the baking time accordingly, as some liquids bake differently.
-
Incorporating Flavorings: This is where you can really get creative! The "Other" ingredient category provides ample opportunity to add extracts (vanilla, almond), spices (cinnamon, nutmeg), zest (lemon, orange), or cocoa powder.
Troubleshooting Common Issues When Using Ratios
Even with a clear ratio, some issues might arise. Here's how to troubleshoot:
-
Dry Cake: This often indicates insufficient liquid. Add a tablespoon or two of liquid at a time, mixing well, until the desired consistency is reached.
-
Sticky Cake: This might be due to too much liquid or sugar. Next time, reduce the liquid slightly or decrease the sugar amount.
-
Tough Cake: This usually points to overmixing. Mix only until the ingredients are just combined to maintain a tender crumb.
-
Uneven Baking: Ensure your oven is properly preheated and that the cake is baked until a toothpick inserted in the center comes out clean.
Beyond "2 3 2 3": Exploring Other Baking Ratios
While "2 3 2 3" is common, many other baking ratios exist, each suited to specific types of baked goods. Understanding the underlying principles allows you to adapt to these variations. For example:
-
The 1:2:1 Ratio: This simpler ratio is often used for very basic cakes and muffins and consists of equal parts flour and liquid, with double the amount of sugar.
-
The 1:1:1 Ratio: This ratio is common in muffins, indicating equal parts of flour, sugar, and liquid.
Conclusion: Mastering Baking Ratios for Consistent Success
Understanding the "2 3 2 3 in cups" ratio, and the principles of baking ratios in general, empowers you to become a more confident and creative baker. By mastering these concepts, you can successfully adapt recipes, create your own variations, and consistently achieve delicious results. Remember to start with a small batch to test the ratio, adjust as needed based on the results, and don't be afraid to experiment to find your perfect balance. Baking is a journey, and understanding ratios is a crucial step towards mastery.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Acres In A Quarter Of Land
Aug 24, 2025
-
Is 81 A Prime Number Or A Composite Number
Aug 24, 2025
-
Why Did Pastor Charles Stanley Get Divorced
Aug 24, 2025
-
How Many Ml Are In A 2 Liter Bottle
Aug 24, 2025
-
How Many Ounces Are In 3 5 Pounds
Aug 24, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is 2 3 2 3 In Cups . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.