What Is 4 As A Fraction
Kalali
Apr 04, 2025 · 5 min read
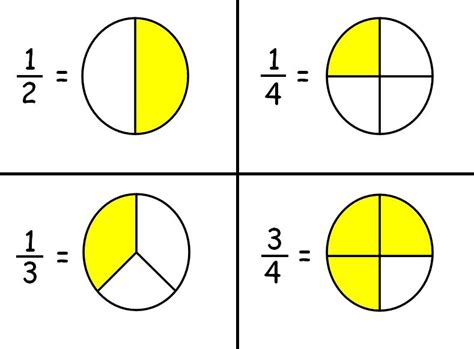
Table of Contents
What is 4 as a Fraction? A Comprehensive Guide
The seemingly simple question, "What is 4 as a fraction?" opens a door to a deeper understanding of fractions, their representation, and their versatility in mathematics. While it might seem trivial at first glance, exploring this question allows us to delve into fundamental mathematical concepts and their practical applications. This comprehensive guide will explore various ways to represent 4 as a fraction, highlighting the underlying principles and showcasing its importance in different contexts.
Understanding Fractions: A Quick Recap
Before we dive into representing 4 as a fraction, let's refresh our understanding of fractions. A fraction is a part of a whole. It's represented by two numbers: a numerator (the top number) and a denominator (the bottom number). The numerator indicates how many parts we have, while the denominator indicates how many equal parts the whole is divided into. For example, in the fraction 3/4, the numerator (3) represents three parts, and the denominator (4) indicates that the whole is divided into four equal parts.
Key Concepts
- Numerator: The top number representing the number of parts.
- Denominator: The bottom number representing the total number of equal parts the whole is divided into.
- Proper Fraction: A fraction where the numerator is smaller than the denominator (e.g., 1/2, 3/4).
- Improper Fraction: A fraction where the numerator is greater than or equal to the denominator (e.g., 5/4, 6/3).
- Mixed Number: A combination of a whole number and a proper fraction (e.g., 1 1/2).
Representing 4 as a Fraction: Multiple Perspectives
The integer 4 can be expressed as a fraction in infinitely many ways. The key is understanding that the fraction represents the same quantity as the whole number 4. This flexibility allows us to choose the representation most suitable for a given mathematical operation or problem.
The Simplest Form: 4/1
The most straightforward way to represent 4 as a fraction is 4/1. Here, the numerator (4) represents the whole number, and the denominator (1) signifies that the whole is divided into one equal part. This is equivalent to saying that we have four whole units. This form is considered the simplest and most commonly used representation of 4 as a fraction.
Equivalent Fractions: Expanding the Possibilities
The beauty of fractions lies in the concept of equivalent fractions. Equivalent fractions represent the same value, even though their numerators and denominators differ. We can create infinitely many equivalent fractions for 4 by multiplying both the numerator and the denominator by the same number. For example:
- 8/2: Multiplying both 4 and 1 by 2.
- 12/3: Multiplying both 4 and 1 by 3.
- 16/4: Multiplying both 4 and 1 by 4.
- 20/5: Multiplying both 4 and 1 by 5.
And so on... Each of these fractions simplifies back to 4/1, demonstrating their equivalence to the whole number 4.
Improper Fractions: A Different Perspective
While 4/1 is the simplest form, we can also represent 4 as an improper fraction. An improper fraction has a numerator larger than or equal to its denominator. We can express 4 as:
- 8/2: Four wholes divided into two equal halves each.
- 12/3: Four wholes divided into three equal thirds each.
- 16/4: Four wholes divided into four equal quarters each.
These improper fractions all simplify to 4, reinforcing the concept of equivalent fractions and the different ways to visualize the same quantity.
The Significance of Representing 4 as a Fraction
While expressing 4 as a fraction might seem unnecessary in simple calculations, its significance becomes clear when dealing with more complex mathematical operations and problem-solving.
Working with Fractions in Calculations
When working with fractions, consistency is key. Expressing whole numbers as fractions allows us to perform calculations smoothly and consistently, avoiding the need to handle whole numbers separately. For example, in adding or subtracting fractions, it's crucial to have a common denominator.
Problem Solving and Real-World Applications
The concept of representing whole numbers as fractions becomes crucial in many real-world applications. Consider:
- Measurement: Imagine dividing a 4-meter length of rope into equal parts. You might need to represent 4 meters as a fraction (e.g., 8/2 meters) for a specific calculation.
- Cooking: A recipe might require 4 cups of flour, but the measurement tool might only provide fractions of cups. Understanding how to represent 4 as a fraction becomes essential for accurate measurement.
- Division Problems: Often, division problems result in fractions. The ability to convert whole numbers into fractions allows for consistent problem-solving.
Advanced Mathematical Concepts
The representation of whole numbers as fractions lays a foundation for understanding more complex mathematical concepts such as:
- Algebra: Solving algebraic equations often involves working with fractions. Representing whole numbers as fractions ensures smooth transitions between different mathematical operations.
- Calculus: The concept of limits, derivatives, and integrals involves a significant amount of fraction manipulation. Understanding how to express whole numbers as fractions aids in the mastery of these core calculus concepts.
Conclusion: The Versatility of Fractional Representation
The question, "What is 4 as a fraction?" isn't simply about a single answer; it's a gateway to understanding the versatility and flexibility of fractions in mathematics. While 4/1 is the most basic representation, the ability to express 4 as an infinite number of equivalent fractions showcases the richness and power of fractional representation. This understanding allows for smooth integration of whole numbers into complex calculations, effective problem-solving in various contexts, and a solid foundation for tackling advanced mathematical concepts. The seemingly simple act of representing 4 as a fraction underscores the fundamental importance of understanding fractions as a cornerstone of mathematical literacy. The ability to easily convert whole numbers into fractions, and vice versa, enhances mathematical skills and problem-solving capabilities significantly.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Percentage Is 2 Out Of 6
Apr 04, 2025
-
25 Cm Is What In Inches
Apr 04, 2025
-
How Do River Systems Watersheds And Divides Interact
Apr 04, 2025
-
How To Find The Linear Function Of A Table
Apr 04, 2025
-
What Percent Is 2 Out Of 3
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is 4 As A Fraction . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
