What Is 4 To The Power Of 3
Kalali
Mar 20, 2025 · 5 min read
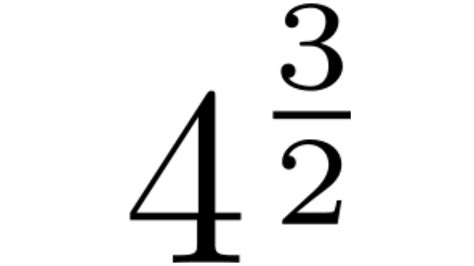
Table of Contents
What is 4 to the Power of 3? A Deep Dive into Exponents and Their Applications
Understanding exponents is fundamental to mathematics and numerous fields. This article will thoroughly explore the question, "What is 4 to the power of 3?", delving into the concept of exponentiation, its practical applications, and related mathematical principles. We'll go beyond a simple answer, providing a comprehensive understanding that will benefit students, professionals, and anyone curious about the power of exponents.
Understanding Exponents: A Foundation
Before we tackle 4 to the power of 3, let's establish a solid understanding of exponents. An exponent, also known as a power or index, indicates how many times a number (the base) is multiplied by itself. It's represented by a small number written slightly above and to the right of the base.
For example, in the expression 4³, the number 4 is the base, and the number 3 is the exponent. This means 4 is multiplied by itself three times: 4 x 4 x 4.
Key Terminology:
- Base: The number being multiplied. (In 4³, the base is 4)
- Exponent: The number indicating how many times the base is multiplied by itself. (In 4³, the exponent is 3)
- Power: The entire expression, including the base and exponent. (4³ is the power)
Calculating 4 to the Power of 3
Now, let's address the core question: What is 4 to the power of 3?
4³ = 4 x 4 x 4 = 64
Therefore, 4 to the power of 3 is 64. This simple calculation demonstrates the core concept of exponentiation.
Expanding the Concept: Exponents Beyond 3
While we've focused on 4³, understanding exponents requires exploring various scenarios:
Exponents of 0 and 1:
- Any number raised to the power of 1 is itself: x¹ = x. For example, 4¹ = 4.
- Any non-zero number raised to the power of 0 is 1: x⁰ = 1 (where x ≠ 0). For example, 4⁰ = 1. The case of 0⁰ is undefined and a subject of ongoing mathematical debate.
Negative Exponents:
Negative exponents represent the reciprocal of the base raised to the positive exponent:
x⁻ⁿ = 1 / xⁿ
For example, 4⁻² = 1 / 4² = 1 / (4 x 4) = 1/16
Fractional Exponents (Roots):
Fractional exponents represent roots. For example, a fractional exponent of 1/2 represents the square root, 1/3 represents the cube root, and so on.
x^(m/n) = ⁿ√xᵐ
For example, 4^(1/2) = √4 = 2 (the square root of 4 is 2) 4^(2/3) = ∛4² = ∛16 ≈ 2.52
Applications of Exponents: Real-World Examples
Exponents are not just abstract mathematical concepts; they have wide-ranging applications in various fields:
Science and Engineering:
- Growth and Decay: Exponents are crucial in modeling exponential growth (e.g., population growth, compound interest) and exponential decay (e.g., radioactive decay, drug metabolism).
- Physics: Many physical phenomena, such as the intensity of light or sound, are described using exponential functions.
- Chemistry: Chemical reactions and concentrations often involve exponential relationships.
Finance and Economics:
- Compound Interest: The power of compound interest, where interest earned also earns interest, is described using exponential functions. The formula for compound interest is A = P(1 + r/n)^(nt), where A is the final amount, P is the principal, r is the annual interest rate, n is the number of times interest is compounded per year, and t is the number of years.
- Economic Growth: Economic models often use exponential functions to represent economic growth or inflation.
Computer Science:
- Big O Notation: Exponents are used in Big O notation to describe the efficiency of algorithms. For example, an O(n²) algorithm has a runtime that grows quadratically with the input size.
- Binary Numbers: The binary number system, fundamental to computers, uses powers of 2.
Everyday Life:
While less obvious, exponents are present in everyday situations:
- Recipe Scaling: Doubling or tripling a recipe involves multiplying ingredients by 2 or 3, essentially raising the quantities to the power of 2 or 3.
- Geometric Progression: Patterns like the number of squares on a chessboard (1, 4, 9, 16,...) follow a geometric progression, illustrating the concept of squares (powers of 2).
Beyond 4 to the Power of 3: Exploring Further
This in-depth exploration of 4³ opens doors to a deeper understanding of exponents and their applications. Exploring more complex scenarios, including:
Higher Powers and Larger Bases:
Calculating higher powers (e.g., 4⁵, 4¹⁰) demonstrates the rapid growth associated with exponents. Similarly, examining larger bases (e.g., 10³, 100³) illustrates the scale of exponential growth.
Working with Variables:
Understanding how exponents work with variables (e.g., x³, (2x)², (x+y)²) is crucial for algebra and more advanced mathematical concepts.
Logarithms:
Logarithms are the inverse of exponents. They provide a way to solve equations involving exponents, allowing for a better understanding of exponential relationships.
Exponential Functions and their Graphs:
Visualizing exponential functions through graphing helps understand their growth patterns and properties.
Conclusion: The Significance of 4 to the Power of 3 and Beyond
While the answer to "What is 4 to the power of 3?" is simply 64, this article has expanded on that simple calculation to provide a robust understanding of exponents. From their fundamental principles to their diverse applications in various fields, exponents are a cornerstone of mathematics and scientific inquiry. Mastering this fundamental concept opens doors to a deeper comprehension of the world around us, paving the way for further exploration of more complex mathematical ideas and their practical uses. The seemingly simple question of 4 cubed becomes a gateway to a world of mathematical possibilities and real-world applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is Ten Feet In Meters
May 09, 2025
-
What Percentage Is 5 Out Of 15
May 09, 2025
-
How To Find Molarity From Titration
May 09, 2025
-
What Is The Square Root Of 244
May 09, 2025
-
What Is The Prime Factorization Of 75
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is 4 To The Power Of 3 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.