What Is 80 Degrees Celsius In Fahrenheit
Kalali
Mar 21, 2025 · 5 min read
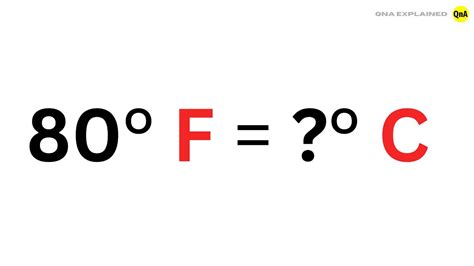
Table of Contents
What is 80 Degrees Celsius in Fahrenheit? A Comprehensive Guide
Knowing how to convert temperatures between Celsius and Fahrenheit is a valuable skill, whether you're checking a recipe, understanding a weather report, or simply satisfying your curiosity. This comprehensive guide will not only answer the question "What is 80 degrees Celsius in Fahrenheit?" but also delve into the intricacies of temperature conversion, explore the history behind these scales, and provide you with practical applications of this knowledge.
Understanding Celsius and Fahrenheit
Before we dive into the conversion, let's briefly understand the two scales:
Celsius (°C): The Metric System Standard
The Celsius scale, also known as the centigrade scale, is a metric system temperature scale named after Swedish astronomer Anders Celsius. Zero degrees Celsius (0°C) represents the freezing point of water, and 100 degrees Celsius (100°C) represents the boiling point of water at standard atmospheric pressure. This scale is widely used globally, especially in scientific contexts.
Fahrenheit (°F): The Imperial System Holdover
The Fahrenheit scale, named after German-Dutch physicist Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit, is part of the imperial system of measurement. It's primarily used in the United States and a few other countries. The freezing point of water is 32°F, and the boiling point is 212°F. The scale's origins are a bit more complex, involving a reference point based on a brine solution, but it's now defined relative to the Celsius scale.
Converting 80 Degrees Celsius to Fahrenheit
The formula for converting Celsius to Fahrenheit is:
°F = (°C × 9/5) + 32
Plugging in 80°C, we get:
°F = (80 × 9/5) + 32 = 144 + 32 = 176°F
Therefore, 80 degrees Celsius is equal to 176 degrees Fahrenheit.
Beyond the Conversion: Understanding the Relationship
While the formula provides a straightforward calculation, understanding the relationship between the two scales offers deeper insight. The difference in the numerical values arises from the different reference points and scale intervals. Fahrenheit has a smaller interval between degrees, which is why the Fahrenheit value is always numerically higher than the Celsius value at equivalent temperatures above 0°C.
Practical Applications of Temperature Conversion
Knowing how to convert between Celsius and Fahrenheit has numerous real-world applications:
Cooking and Baking:
Recipes often specify temperatures in either Celsius or Fahrenheit. Accurate temperature conversion is crucial for achieving the desired results in cooking and baking. Over or undercooking can significantly affect the texture, taste, and overall quality of your culinary creations. A simple temperature conversion can prevent culinary mishaps.
Meteorology and Weather Forecasting:
Weather reports may present temperatures in either scale depending on the region. Understanding the conversion allows you to accurately interpret weather forecasts, whether you're planning an outdoor activity or simply checking the daily weather. This is vital for accurate weather planning and preparedness.
Scientific Experiments and Research:
Many scientific experiments and research projects involve temperature control and measurement. Accurately converting temperatures is crucial for precise experimental results, ensuring data consistency, and facilitating comparisons across studies. This ensures data reliability and valid conclusions.
Healthcare and Medicine:
Body temperature is often measured in both Celsius and Fahrenheit, depending on the region and healthcare system. Converting between these scales is necessary for accurate diagnosis and treatment. Accurate temperature monitoring is crucial in various medical situations.
International Travel and Communication:
Traveling internationally often necessitates understanding different unit systems, including temperature scales. Knowing how to convert temperatures ensures smooth communication and understanding in various situations. This avoids confusion and misinterpretations.
The History of Temperature Scales: A Brief Overview
The development of temperature scales is a fascinating journey through scientific history. Both Celsius and Fahrenheit have their own unique stories:
Anders Celsius and the Centigrade Scale:
Anders Celsius, a Swedish astronomer, proposed a temperature scale in 1742. His original scale had 0° representing the boiling point of water and 100° representing the freezing point. This was later reversed to the scale we know today. Celsius's scale is based on the readily observable properties of water, making it simple and intuitive to understand.
Gabriel Fahrenheit and His Scale:
Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit, a German-Dutch physicist, developed his scale around 1724. His original scale had 0° representing the temperature of a freezing mixture of ice, water, and ammonium chloride, and 100° approximately representing the average human body temperature. While seemingly arbitrary, the Fahrenheit scale gained popularity, particularly in the English-speaking world.
Beyond Celsius and Fahrenheit: Other Temperature Scales
While Celsius and Fahrenheit are the most commonly used temperature scales, others exist, including:
-
Kelvin (K): The Kelvin scale is an absolute thermodynamic temperature scale. Zero Kelvin (0 K) represents absolute zero, the theoretical point where all molecular motion ceases. This scale is widely used in scientific research and engineering.
-
Rankine (°R): Similar to Kelvin, Rankine is an absolute scale, but it's based on the Fahrenheit degree. It's less commonly used than Kelvin.
These alternative scales highlight the various ways scientists and engineers have sought to quantify and understand temperature.
Tips for Accurate Temperature Conversion:
- Double-check your calculations: Errors in conversion can lead to significant problems, so always double-check your calculations, especially in critical applications.
- Use a reliable converter: Numerous online calculators and apps are available for quick and accurate temperature conversions. These tools can eliminate manual calculation errors.
- Understand the context: The context of the temperature measurement is crucial. For instance, the temperature of an oven might be significantly different from the ambient air temperature.
Conclusion: Mastering Temperature Conversions
The ability to convert between Celsius and Fahrenheit is a valuable skill applicable in various aspects of life, from everyday cooking to specialized scientific research. Understanding the underlying principles and historical context enhances the understanding of temperature measurement. By mastering this essential conversion, you gain a greater appreciation for the multifaceted world of temperature and measurement systems. Remember the formula, and use the resources available to ensure accuracy and efficiency in your temperature conversions. The more you practice, the easier and more intuitive this process will become. So, next time you encounter a temperature in Celsius or Fahrenheit, you'll be well-equipped to make the conversion swiftly and confidently.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Ounces Of Sour Cream Are In A Cup
Mar 28, 2025
-
Does A Catfish Have A Backbone
Mar 28, 2025
-
How Many Feet Are In 42 Inches
Mar 28, 2025
-
How Many Acres Is A Square Mile
Mar 28, 2025
-
15 Out Of 50 As A Percentage
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is 80 Degrees Celsius In Fahrenheit . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
