What Is A 26 Out Of 40
Kalali
Jul 20, 2025 · 5 min read
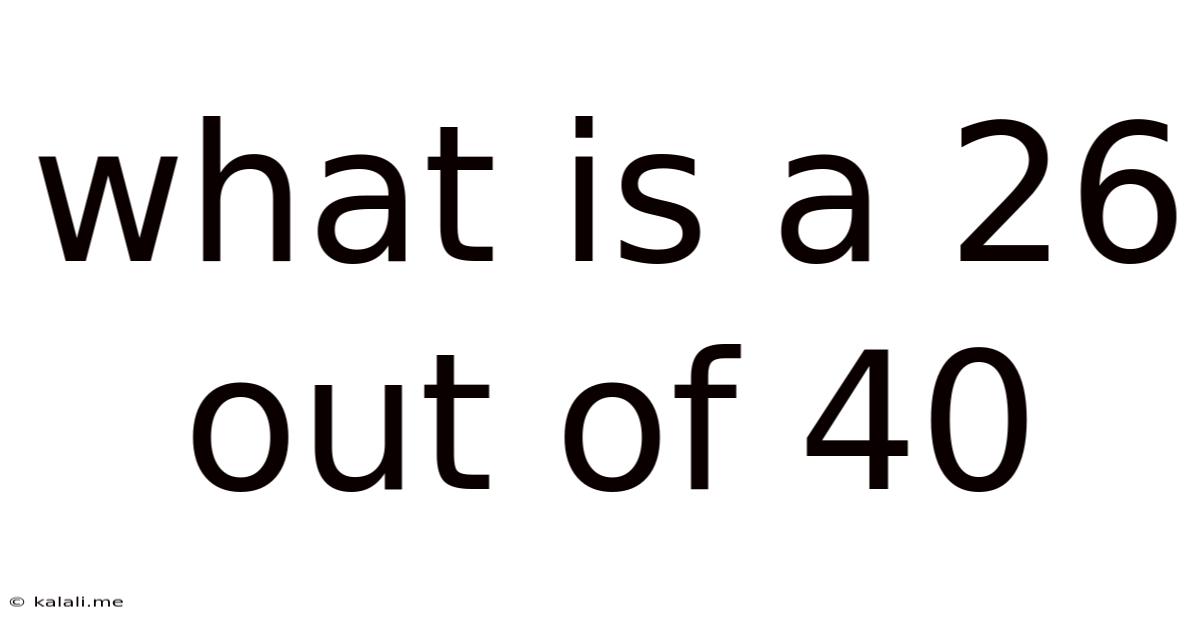
Table of Contents
What is a 26 out of 40? Deconstructing Scores, Understanding Percentages, and Contextualizing Results
A score of 26 out of 40 might seem straightforward at first glance – a simple numerical representation of performance. However, the true meaning of this score hinges heavily on context. Understanding its significance requires delving deeper than just the raw numbers. This article will explore the various aspects of interpreting a 26 out of 40 score, examining its percentage equivalent, contextual factors influencing its meaning, and the broader implications for different scenarios.
Understanding the Basics: Percentage Calculation and Interpretation
The first step in understanding a 26 out of 40 score is converting it into a percentage. This provides a standardized measure allowing for easier comparison across different scales. The calculation is straightforward:
(Score / Total Score) * 100% = Percentage Score
In this case: (26 / 40) * 100% = 65%
A 26 out of 40 translates to a 65% score. This seemingly simple calculation reveals a crucial piece of information: the performance lies above the average (50%). However, whether 65% represents good, bad, or average performance critically depends on the context.
Context is King: The Importance of Considering the Specific Situation
The interpretation of a 65% (or 26 out of 40) score dramatically shifts depending on the context. Several crucial factors must be considered:
-
The nature of the assessment: Was it a quiz, a major exam, a project evaluation, a survey response, or something else entirely? A 65% on a simple pop quiz might be acceptable, while the same score on a crucial final exam could be significantly concerning.
-
The difficulty of the assessment: Was the test exceptionally challenging or unusually easy? A 65% on a notoriously difficult exam might indicate a strong performance compared to a 65% on a straightforward assessment. The distribution of scores amongst other participants also provides valuable context. If most students scored significantly lower, a 65% might be considered excellent. Conversely, a low 65% suggests room for improvement.
-
The grading system: Different institutions and educators utilize varied grading systems. A 65% might be considered a passing grade in one system, but a failing grade in another. Understanding the specific grading rubric is crucial for accurate interpretation.
-
Individual goals and expectations: Personal goals play a pivotal role. If an individual aimed for a higher score (e.g., 80% or above), a 65% might be considered disappointing, even if it's technically a passing grade. Conversely, someone aiming for a passing grade would likely be satisfied.
-
Areas of strength and weakness: A comprehensive analysis of the assessment should also include an evaluation of the specific areas where the individual excelled and where they fell short. This provides valuable insights for future improvement. For example, in a science exam, the student might have scored well in biology but poorly in chemistry. This granular analysis is crucial for targeted study strategies.
-
Comparison with previous performance: Tracking progress over time provides another layer of context. A 65% might be considered an improvement if it represents a significant increase from previous scores. Conversely, it could be a decline if it represents a decrease from previous performance.
Examples in Different Contexts:
Let's consider different scenarios to illustrate the contextual importance of a 26 out of 40 score:
-
Academic Setting: In a high school history exam, a 65% might be a satisfactory grade, particularly if the exam was challenging. However, in a university-level mathematics exam, the same score might be considered subpar and require significant improvement.
-
Professional Setting: In a workplace performance review, a 65% rating on a specific skill might suggest areas needing development, even if it's technically above average. The feedback accompanying such a score is crucial for improvement.
-
Survey Results: If a survey question receives a 65% positive response, it indicates a generally favorable opinion, but not overwhelming support. A deeper analysis of respondent demographics might reveal further insights.
-
Sports and Competitions: In many competitive scenarios, a 65% performance might be far from satisfactory. Athletes often strive for much higher levels of achievement, and a score of this nature could prompt intense training to improve performance.
-
Product Testing: In product testing, a 65% success rate might represent a significant problem. Depending on the product and its function, even a small margin of error can be unacceptable.
Beyond the Numbers: Qualitative Aspects and Feedback
While the numerical score is important, it's not the only factor to consider. Qualitative aspects, such as feedback from instructors or evaluators, provide valuable insights into the areas where improvement is needed. Constructive criticism and specific suggestions for improvement are far more valuable than just a numerical score. This feedback allows for a deeper understanding of strengths and weaknesses, leading to more effective learning strategies.
Strategies for Improvement (If Applicable):
If a 26 out of 40 score represents a performance that needs improvement, several strategies can be employed:
-
Identify areas of weakness: A careful analysis of the assessment should highlight areas where the individual struggled. This targeted approach allows for focused study and practice.
-
Seek additional help: If specific concepts are causing difficulties, seeking help from teachers, tutors, or peers can be invaluable.
-
Develop better study habits: Effective study techniques, time management, and consistent effort are crucial for academic success.
-
Adjust learning strategies: If the current learning approach isn't working, it might be time to experiment with different methods. Learning styles vary significantly, and finding a suitable method is essential.
-
Practice and repetition: Consistent practice and repetition are key to mastering concepts and improving performance.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, a 26 out of 40 score, or its percentage equivalent of 65%, lacks inherent meaning without context. Its interpretation depends heavily on the specific assessment, its difficulty, the grading system, individual goals, and accompanying feedback. Focusing solely on the numerical value is insufficient; a deeper understanding of the surrounding circumstances is crucial for accurate interpretation and effective improvement strategies. Remember to always consider the complete picture, including qualitative feedback and personal goals, to gain a truly meaningful understanding of the score. The numerical score is just a data point; the context provides the narrative.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Quarts Are In 10 Pounds
Jul 20, 2025
-
8pm To 4am Is How Many Hours
Jul 20, 2025
-
Whats The Average Height For A 6th Grade Boy
Jul 20, 2025
-
How Many Books In The Bible Named After Women
Jul 20, 2025
-
How Many Grains Of Rice Are In A Cup
Jul 20, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is A 26 Out Of 40 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.