What Is An Answer To A Division Problem
Kalali
Mar 19, 2025 · 5 min read
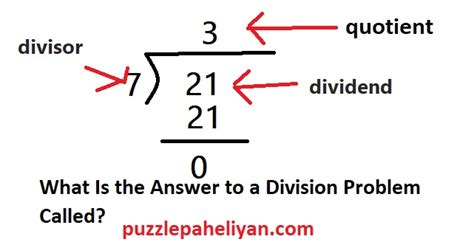
Table of Contents
What is an Answer to a Division Problem? Understanding Quotients, Remainders, and Their Real-World Applications
Division, one of the four fundamental arithmetic operations, plays a crucial role in numerous mathematical concepts and real-world scenarios. Understanding what constitutes the answer to a division problem goes beyond simply stating the result; it involves grasping the meaning of quotients, remainders, and their significance in various contexts. This comprehensive guide delves deep into the nature of division answers, exploring their interpretations, applications, and the crucial role they play in problem-solving.
Understanding the Components of a Division Problem
Before diving into the answer itself, let's establish a clear understanding of the components involved in a division problem. A typical division problem can be expressed as:
Dividend ÷ Divisor = Quotient + Remainder
- Dividend: This is the number being divided. It represents the total quantity being split or shared.
- Divisor: This is the number by which the dividend is divided. It represents the number of groups or the size of each group.
- Quotient: This is the primary result of the division, representing the number of times the divisor goes into the dividend evenly. It’s often described as the "whole number" part of the answer.
- Remainder: This is the amount left over after the division process is complete. It's the portion of the dividend that couldn't be evenly divided by the divisor. The remainder is always less than the divisor.
The Quotient: The Heart of the Division Answer
The quotient is undoubtedly the most important part of the answer to a division problem. It signifies the number of complete groups or units that can be formed from the dividend, given the size or number defined by the divisor.
Examples illustrating the quotient:
-
Example 1: If you have 20 cookies and want to divide them equally among 5 friends, the division problem is 20 ÷ 5 = 4. The quotient, 4, represents the number of cookies each friend receives.
-
Example 2: A factory produces 1000 widgets in a day. If they package them in boxes of 25 widgets each, the division is 1000 ÷ 25 = 40. The quotient, 40, indicates the number of boxes needed to package all the widgets.
The Remainder: The Leftover Piece
The remainder, though often overlooked, provides valuable information about the division process. It signifies the portion of the dividend that doesn't fit perfectly into the groups defined by the divisor.
Examples illustrating the remainder:
-
Example 1: You have 23 candies and want to divide them equally among 4 children. The division is 23 ÷ 4 = 5 with a remainder of 3. The quotient, 5, shows that each child gets 5 candies, and the remainder, 3, indicates there are 3 candies left over.
-
Example 2: A bus has a capacity of 50 passengers. If 157 people need to be transported, the division is 157 ÷ 50 = 3 with a remainder of 7. Three buses are needed, and 7 people will need to be accommodated on a fourth bus, or by other means.
Interpreting Remainders: Different Approaches
How you interpret the remainder depends entirely on the context of the problem. There are several ways to handle a remainder:
-
Discarding the Remainder: In some scenarios, the remainder can be ignored. For instance, if you're calculating the number of full boxes needed, you only consider the quotient.
-
Rounding Up: If the remainder represents a partial quantity that needs to be accounted for, you might round the quotient up to the nearest whole number. For example, if you need to buy enough buses to transport 157 people, even though the remainder is 7, you would need to round up to 4 buses.
-
Expressing as a Fraction or Decimal: The remainder can be expressed as a fraction or decimal. In the candy example (23 ÷ 4), the answer could be expressed as 5 ¾ or 5.75. This provides a more precise representation of the result.
Division with Zero: A Special Case
Division involving zero requires special consideration. The rules regarding division by zero and division of zero are fundamental:
-
Division by Zero (x ÷ 0): Division by zero is undefined. There's no meaningful result when you attempt to divide a number by zero. It's a mathematical impossibility.
-
Division of Zero (0 ÷ x, where x ≠ 0): Dividing zero by any non-zero number always results in zero.
Real-World Applications of Division and its Answers
Division is not merely an abstract mathematical concept; it's a fundamental tool used extensively in various aspects of everyday life and professional fields. Here are some examples:
-
Finance: Calculating unit costs, splitting bills, determining interest rates, and analyzing financial statements all involve division.
-
Engineering and Construction: Division is essential in tasks like calculating material quantities, determining dimensions, and distributing resources.
-
Cooking and Baking: Scaling recipes up or down, dividing ingredients proportionally, and calculating serving sizes all rely on division.
-
Data Analysis: Calculating averages, percentages, and rates of change frequently involve division operations.
-
Computer Science: Data processing, algorithm design, and memory management often utilize division for efficient resource allocation.
-
Sports: Calculating batting averages, earned run averages (ERA), and other statistical measures in sports rely heavily on division.
Advanced Division Concepts: Exploring Beyond the Basics
While the basic understanding of quotients and remainders forms the foundation of division, there are more advanced concepts to consider:
-
Long Division: This method provides a step-by-step approach to handling larger division problems, particularly those involving multi-digit numbers.
-
Synthetic Division: A more efficient algorithm for dividing polynomials, synthetic division simplifies the process significantly.
-
Division Algorithms: These are systematic procedures for performing division, applicable in various contexts, from simple arithmetic to complex number systems.
Conclusion: Mastering Division for Real-World Success
The answer to a division problem is more than just a single number; it's a comprehensive representation of the division process, encompassing the quotient and the remainder. Understanding these elements, their interpretations, and their varied applications is vital for problem-solving across a broad spectrum of disciplines. Whether it's splitting a bill, scaling a recipe, or analyzing complex datasets, the ability to perform and interpret division accurately is a valuable skill for navigating the complexities of the real world. Mastering division not only strengthens mathematical proficiency but equips individuals with the problem-solving skills necessary for success in numerous fields. By understanding the nuances of quotients, remainders, and their diverse interpretations, one can effectively tackle division problems and apply them confidently to real-world challenges.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 36 8 Degrees Celsius In Fahrenheit
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Percentage Of 8 Is 3
Mar 19, 2025
-
How Many Inches Is 104 Cm
Mar 19, 2025
-
How Many Grams Is In A Half Pound
Mar 19, 2025
-
Cuanto Es Un Kilometro En Millas
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is An Answer To A Division Problem . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
