What Is An Answer To A Division Problem Called
Kalali
Mar 13, 2025 · 6 min read
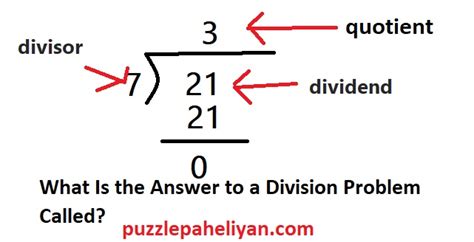
Table of Contents
What is an Answer to a Division Problem Called? A Deep Dive into Quotients and Remainders
The simple question, "What is an answer to a division problem called?" might seem straightforward, but it opens the door to a fascinating exploration of mathematical concepts. The answer isn't just a single word; it depends on the context and the type of division. Let's delve into the intricacies of division, exploring the terminology, different types of division, and the practical applications of understanding these concepts.
Understanding the Fundamentals of Division
Division is one of the four basic arithmetic operations, alongside addition, subtraction, and multiplication. It's essentially the process of splitting a quantity into equal parts or groups. We use division to determine how many times one number (the divisor) goes into another number (the dividend). The result of this process has specific names, depending on the nature of the division.
The Key Players: Dividend, Divisor, and Quotient
Before we get to the answer to our main question, let's define the key terms involved in a division problem:
- Dividend: This is the number being divided. It's the total quantity you're splitting up.
- Divisor: This is the number you're dividing by. It represents the size of each group or the number of parts you're splitting the dividend into.
- Quotient: This is the main answer to a division problem. It represents the number of times the divisor goes into the dividend completely. This is often referred to as the whole number result of the division.
Let's illustrate with a simple example: 12 ÷ 3 = 4.
In this case:
- 12 is the dividend.
- 3 is the divisor.
- 4 is the quotient.
So, to answer the core question directly: the main answer to a division problem is called the quotient.
Beyond the Quotient: Introducing the Remainder
However, not all division problems result in a whole number quotient. When the dividend isn't perfectly divisible by the divisor, we have a remainder.
- Remainder: This is the amount left over after dividing the dividend as completely as possible by the divisor. It's always smaller than the divisor.
Let's look at an example where a remainder appears: 14 ÷ 3 = 4 with a remainder of 2.
Here:
- 14 is the dividend.
- 3 is the divisor.
- 4 is the quotient.
- 2 is the remainder.
Understanding the remainder is crucial in many real-world applications. For example, if you're dividing 14 candies among 3 children, each child gets 4 candies (the quotient), and you have 2 candies left over (the remainder).
Different Types of Division and Their Results
The terminology and the interpretation of the results can vary slightly depending on the type of division being performed:
1. Whole Number Division
This is the simplest form of division, where we're only interested in the whole number quotient and the remainder. We might express the result as "4 remainder 2" or using the modulo operator (%) in programming, which returns only the remainder.
2. Decimal Division
In decimal division, we continue the division process beyond the whole number quotient to obtain a decimal result. The remainder is incorporated into the decimal part of the quotient. For example, 14 ÷ 3 = 4.666... (a repeating decimal). In this case, we don't explicitly mention the remainder; it's implicitly included in the decimal part of the quotient.
3. Fractional Division
This is similar to decimal division, but the result is expressed as a fraction. The remainder becomes the numerator, and the divisor remains the denominator. So, 14 ÷ 3 = 4 ⅔ (four and two-thirds). Again, the remainder is integrated into the final answer.
The Importance of Understanding Quotients and Remainders
The ability to understand and interpret quotients and remainders is essential in numerous fields:
1. Everyday Life
From splitting a bill evenly among friends to calculating the number of items needed for a project, division is pervasive in daily life. Understanding the remainder helps in making practical decisions—like buying extra items to ensure everyone gets their share.
2. Engineering and Design
Engineers use division extensively in calculations related to scaling, proportions, and resource allocation. The remainder often indicates adjustments needed to optimize designs or resource utilization.
3. Computer Science
In computer programming, the modulo operator (%) plays a significant role in various algorithms, including those for cryptography, data structures, and game development. It provides the remainder, which is crucial for controlling program flow and performing specific operations.
4. Finance and Accounting
Division is fundamental in financial calculations, such as calculating interest rates, profits, and losses. Understanding the remainder can be important for accurately determining fractional amounts or discrepancies.
5. Mathematics and Science
Division forms the foundation of many mathematical concepts, including fractions, decimals, ratios, and proportions. It’s essential in scientific calculations, data analysis, and statistical modeling. Understanding remainders is vital for accurate measurements and calculations, particularly in physics and chemistry.
Advanced Concepts Related to Division
Let's briefly touch upon more complex mathematical concepts related to division:
1. Long Division
This is a method used for performing division with larger numbers, systematically breaking down the problem into smaller, manageable steps. It explicitly shows the quotient and the remainder at each step.
2. Synthetic Division
This is a shortcut method for polynomial division. It simplifies the process of dividing polynomials, focusing on the coefficients and producing the quotient and remainder efficiently.
3. Euclidean Division
This is a fundamental concept in number theory, establishing that for any two integers, 'a' (the dividend) and 'b' (the divisor), there exist unique integers 'q' (the quotient) and 'r' (the remainder) such that a = bq + r, and 0 ≤ r < |b|. This forms the basis for many algorithms in number theory and cryptography.
4. Modular Arithmetic
This branch of number theory focuses on remainders, utilizing the modulo operator extensively. It has applications in cryptography, computer science, and other areas where cyclic patterns are important.
Conclusion: More Than Just a Number
The answer to "What is an answer to a division problem called?" is more nuanced than a simple "quotient." While the quotient represents the main result, the remainder provides crucial additional information, especially when the division isn't exact. Understanding both the quotient and the remainder, and knowing how to interpret them in different contexts, is essential for effective problem-solving across various disciplines. From everyday tasks to advanced mathematical concepts, mastering division and its components is a cornerstone of numeracy and critical thinking. The depth and breadth of this seemingly simple mathematical operation highlight its fundamental role in our understanding of the world around us.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Quarts In 2 5 Gallons
Mar 13, 2025
-
What Is The Average Height For A 14 Year Old
Mar 13, 2025
-
60 Ml Equals How Many Ounces
Mar 13, 2025
-
68 5 Inches To Feet And Inches
Mar 13, 2025
-
2 Gallons Is How Many Quarts
Mar 13, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is An Answer To A Division Problem Called . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
