What Is Another Name For Condensation Reaction
Kalali
Mar 12, 2025 · 5 min read
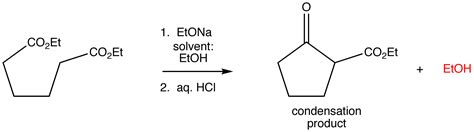
Table of Contents
What is Another Name for Condensation Reaction? A Comprehensive Guide
Condensation reactions are fundamental processes in chemistry, playing crucial roles in the synthesis of numerous compounds, from simple polymers to complex biomolecules. Understanding these reactions is essential for anyone studying organic chemistry, biochemistry, or materials science. While the term "condensation reaction" is widely used, it's not the only name for this type of chemical transformation. This article will explore the various synonyms and related terms associated with condensation reactions, clarifying the nuances between them and providing a comprehensive overview of their mechanisms and applications.
Understanding Condensation Reactions: The Basics
Before diving into alternative names, let's establish a firm understanding of what constitutes a condensation reaction. At its core, a condensation reaction is a process where two molecules combine to form a larger molecule, with the simultaneous elimination of a small molecule, often water (H₂O), but also including ammonia (NH₃), methanol (CH₃OH), hydrogen sulfide (H₂S), or hydrogen chloride (HCl). This process is essentially the reverse of a hydrolysis reaction.
Key Characteristics of Condensation Reactions:
- Combination of two molecules: Two smaller molecules react to form a larger one.
- Elimination of a small molecule: A byproduct, such as water, is released during the reaction.
- Formation of a new bond: A new covalent bond is formed between the reacting molecules.
- Often catalyzed: Many condensation reactions require a catalyst to proceed efficiently.
Alternative Names for Condensation Reactions: A Detailed Exploration
The term "condensation reaction" is a general descriptor, and depending on the specific context and the molecules involved, several alternative names can be used. These names often highlight a specific aspect of the reaction or the type of molecules involved.
1. Dehydration Reaction
This is perhaps the most common synonym for condensation reaction, particularly when water is the small molecule eliminated. A dehydration reaction explicitly emphasizes the removal of water. This term is frequently used in organic chemistry, especially when discussing the formation of esters from carboxylic acids and alcohols, or the formation of amides from carboxylic acids and amines. For instance, the synthesis of an ester involves the dehydration of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol, forming an ester linkage and releasing water.
Example: The formation of a peptide bond between two amino acids is a dehydration reaction, where water is eliminated to form a peptide linkage.
2. Polymerization
While not strictly interchangeable, condensation reactions are a key subset of polymerization reactions. Polymerization refers to the process of linking many small molecules (monomers) together to form a large chain-like molecule (polymer). Condensation polymerization is a specific type of polymerization where the monomers link together through the elimination of a small molecule. Many important polymers, including nylon and polyester, are produced via condensation polymerization.
Example: The synthesis of nylon involves the condensation polymerization of diamines and diacids, with water as the byproduct.
3. Esterification
This term specifically refers to a condensation reaction between a carboxylic acid and an alcohol to form an ester. Esterification is a well-known and widely used reaction in organic chemistry, with esters having various applications, including fragrances, flavors, and solvents. This is a specific example of a dehydration condensation reaction where water is removed.
4. Amide Formation
Similarly to esterification, amide formation specifically refers to a condensation reaction between a carboxylic acid and an amine to form an amide. Amide bonds are crucial in the structure of proteins and peptides, where amino acids are linked together through amide bonds (peptide bonds) via a condensation reaction.
5. Glycosidic Bond Formation
In the context of carbohydrate chemistry, the formation of a glycosidic bond is a condensation reaction where two monosaccharides link together to form a disaccharide or polysaccharide. This reaction typically involves the elimination of a water molecule.
6. Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution
This is a more mechanistic term that describes the condensation reactions involving acyl groups (e.g., in carboxylic acids, esters, and amides). Nucleophilic acyl substitution involves a nucleophile attacking the carbonyl carbon of an acyl group, leading to the formation of a new bond and the elimination of a leaving group (often resulting in a condensation reaction).
Distinguishing Condensation from Other Reactions
It's important to distinguish condensation reactions from other reaction types that might appear similar. For instance:
- Addition reactions: These involve the combination of two or more molecules to form a larger molecule without the elimination of a small molecule.
- Substitution reactions: These involve the replacement of one atom or group of atoms by another.
- Elimination reactions: These involve the removal of atoms or groups from a molecule to form a double bond.
While these reactions can sometimes be related to condensation reactions or occur in conjunction with them, the defining characteristic of a condensation reaction is the simultaneous combination of two molecules and elimination of a smaller molecule.
Applications of Condensation Reactions
Condensation reactions are ubiquitous in chemistry and biology, with applications spanning diverse fields:
- Polymer chemistry: Synthesis of numerous synthetic polymers (nylon, polyester, polycarbonates, etc.) relies heavily on condensation polymerization.
- Biochemistry: Formation of peptide bonds in proteins, glycosidic bonds in carbohydrates, and ester bonds in lipids are all crucial condensation reactions.
- Organic synthesis: Condensation reactions are employed to synthesize a vast array of organic compounds, including esters, amides, ketones, and many more.
- Materials science: Condensation reactions are used in the synthesis of various materials, including resins, adhesives, and coatings.
Conclusion
While "condensation reaction" is a widely accepted term, it's helpful to understand its numerous synonyms and related terms, such as dehydration reaction, polymerization, esterification, and amide formation. Each term highlights a specific aspect or context of this fundamental chemical process. The ability to recognize and understand these variations is essential for a comprehensive grasp of chemical reactions and their diverse applications across various scientific disciplines. Understanding the nuances between these terms allows for clearer communication and a deeper appreciation for the remarkable versatility of condensation reactions in the world around us. Further research into specific examples of condensation reactions, such as the detailed mechanisms of esterification or the various types of polymerization, will solidify your understanding of these crucial chemical transformations. Remember to consult textbooks and reputable online resources for more in-depth information and examples.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Cups Are In 24 Ounces
Mar 13, 2025
-
What Is 163 Cm In Feet
Mar 13, 2025
-
How Many Feet Is 59 In
Mar 13, 2025
-
How Tall Is 40 Inches In Feet
Mar 13, 2025
-
48 In Is How Many Feet
Mar 13, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is Another Name For Condensation Reaction . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
