What Is Degree In Math Algebraic Expression
Kalali
Mar 22, 2025 · 6 min read
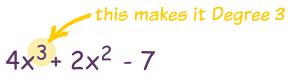
Table of Contents
What is a Degree in a Math Algebraic Expression? A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the degree of an algebraic expression is fundamental to mastering algebra. It's a seemingly simple concept, yet its implications extend far beyond basic algebraic manipulation, influencing how we solve equations, analyze polynomials, and even delve into advanced mathematical fields. This comprehensive guide will break down the concept of the degree of an algebraic expression, providing clear explanations, practical examples, and insights into its significance.
Defining Algebraic Expressions and Their Components
Before we dive into the degree, let's solidify our understanding of algebraic expressions. An algebraic expression is a mathematical phrase that combines numbers, variables, and operators (like +, -, ×, ÷). Variables are often represented by letters like x, y, or z, representing unknown quantities. For example, 3x + 2y - 5 is an algebraic expression.
The components of an algebraic expression are crucial for determining its degree:
- Constants: These are fixed numerical values, like 2, -5, or π.
- Variables: These represent unknown values, usually denoted by letters.
- Terms: A term is a single number, a variable, or a product of numbers and variables. In the expression
3x + 2y - 5,3x,2y, and-5are individual terms. - Coefficients: The numerical factor of a term is its coefficient. In
3x, the coefficient is 3. - Exponents: Exponents indicate the power to which a variable is raised. In
x², the exponent is 2.
Understanding the Degree of a Term
The degree of a term is the sum of the exponents of its variables. Let's illustrate this with some examples:
- Term:
x³Degree: 3 (exponent of x is 3) - Term:
5xy²Degree: 3 (exponent of x is 1, exponent of y is 2; 1 + 2 = 3) - Term:
-7a²bc⁴Degree: 7 (exponent of a is 2, exponent of b is 1, exponent of c is 4; 2 + 1 + 4 = 7) - Term:
8Degree: 0 (a constant term has a degree of 0) - Term:
-2xDegree: 1 (exponent of x is 1)
Important Note: The degree of a term does not include the exponents of constants. Constants do not affect the degree.
Determining the Degree of an Algebraic Expression
The degree of an entire algebraic expression is determined by the highest degree among its individual terms. Consider these examples:
-
Expression:
2x³ + 5x - 7- Term
2x³has a degree of 3. - Term
5xhas a degree of 1. - Term
-7has a degree of 0. - Therefore, the degree of the expression is 3.
- Term
-
Expression:
4xy² + 3x²y - 6xyz- Term
4xy²has a degree of 3. - Term
3x²yhas a degree of 3. - Term
-6xyzhas a degree of 3. - Therefore, the degree of the expression is 3.
- Term
-
Expression:
8a⁴b³ - 5a²b⁵ + 2ab - 1- Term
8a⁴b³has a degree of 7. - Term
-5a²b⁵has a degree of 7. - Term
2abhas a degree of 2. - Term
-1has a degree of 0. - Therefore, the degree of the expression is 7.
- Term
Special Cases and Considerations
Several scenarios require careful attention when determining the degree:
-
Expressions with multiple variables: As shown above, add the exponents of all variables in each term to find the degree of that term. The highest degree among the terms determines the overall degree of the expression.
-
Zero degree: An algebraic expression consisting solely of a constant (e.g., 5, -10) has a degree of 0.
-
Expressions with only one variable: Find the highest exponent of the variable present in the expression. This is the degree of the expression.
-
Polynomials: Polynomials are algebraic expressions where the exponents of the variables are non-negative integers. The degree of a polynomial is the highest degree of its terms. Classifying polynomials by degree (linear, quadratic, cubic, etc.) is a common practice in algebra.
The Significance of the Degree in Algebra and Beyond
The degree of an algebraic expression plays a vital role in several algebraic concepts and applications:
-
Polynomial Classification: The degree of a polynomial dictates its classification (e.g., linear, quadratic, cubic, quartic, quintic). This classification helps us understand the behavior of the polynomial, its graph, and the number of roots it might have.
-
Solving Equations: Knowing the degree of a polynomial equation provides insights into the number of possible solutions. For example, a quadratic equation (degree 2) will have at most two solutions.
-
Graphing Polynomials: The degree of a polynomial significantly influences the shape and characteristics of its graph. Higher-degree polynomials exhibit more complex curves and turning points.
-
Calculus: The degree of a polynomial is crucial in calculus, particularly in differentiation and integration. The derivative of a polynomial reduces its degree by one.
-
Linear Algebra: In linear algebra, the degree of polynomials is relevant in studying vector spaces and polynomial rings.
-
Abstract Algebra: Degree concepts extend to more advanced abstract algebra, influencing topics like field extensions and algebraic geometry.
Practical Applications and Examples
Let's explore some practical scenarios where understanding the degree of an algebraic expression is vital:
Scenario 1: Finding the Roots of a Polynomial Equation
Consider the equation x³ - 6x² + 11x - 6 = 0. This is a cubic equation (degree 3), meaning it can have at most three real roots. Solving this equation (e.g., using factoring or numerical methods) would reveal these roots.
Scenario 2: Graphing a Polynomial Function
Consider the function f(x) = x⁴ - 2x² + 1. This is a quartic polynomial (degree 4). Its graph will have at most three turning points, showing a more complex curve than a linear or quadratic function.
Scenario 3: Analyzing the Behavior of a Polynomial
Consider the polynomial g(x) = -2x⁵ + 5x³ - x. This is a quintic polynomial (degree 5). Its end behavior will be different from lower-degree polynomials. As x approaches positive infinity, g(x) will approach negative infinity, and vice versa.
Scenario 4: Simplifying Algebraic Expressions
Understanding the degree can help in simplifying expressions. By combining like terms, we can reduce the degree or even completely eliminate certain terms.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Concepts
The concept of degree expands beyond simple algebraic expressions. In advanced mathematics, you'll encounter:
-
Degree of a polynomial in several variables: This extends the concept to polynomials with multiple variables.
-
Degree of a rational function: This deals with functions expressed as ratios of polynomials. The degree is determined by the difference between the degrees of the numerator and denominator.
-
Degree of a differential equation: This refers to the highest order of the derivative appearing in the equation.
-
Degree of a form: In multilinear algebra, forms are multilinear functions. The degree of a form is the number of arguments it takes.
-
Degree of a field extension: This is a concept in abstract algebra concerning the dimension of a field extension.
Conclusion
The degree of an algebraic expression, while seemingly a simple concept, is a cornerstone of algebra and extends its influence into numerous advanced mathematical fields. Mastering this fundamental concept is crucial for success in algebra, calculus, and beyond. Its applications are wide-ranging, from solving equations to understanding the behavior of polynomial functions and even delving into the intricacies of abstract algebra. By understanding the degree of an algebraic expression, we gain a powerful tool for analyzing and manipulating mathematical objects and unlocking a deeper understanding of the mathematical world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Eighths In A Quarter Pound
Jul 18, 2025
-
Can The Sine Of An Angle Ever Equal 2
Jul 18, 2025
-
How Many Months Is A Hundred Days
Jul 18, 2025
-
Mother And I Or Mother And Me
Jul 18, 2025
-
How Many Oz In One Water Bottle
Jul 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is Degree In Math Algebraic Expression . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.