What Is More 7 840 Square Feet Or 0.25 Acres
Kalali
Jul 21, 2025 · 5 min read
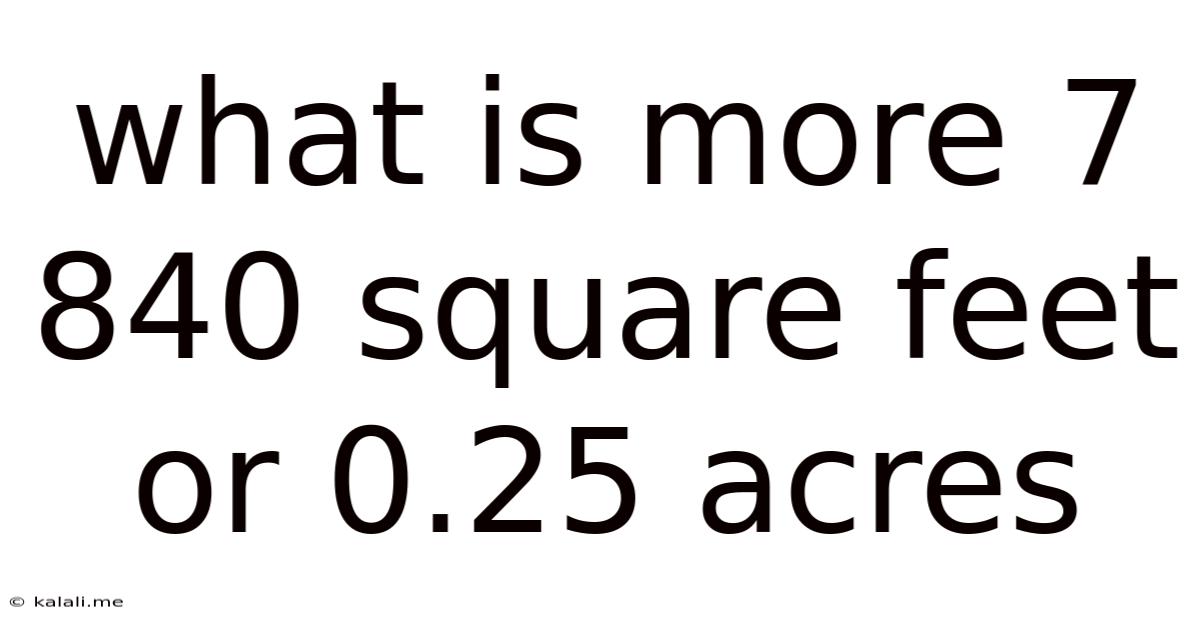
Table of Contents
What's Bigger: 7,840 Square Feet or 0.25 Acres? Understanding Land Area Measurement
Deciding whether 7,840 square feet or 0.25 acres is larger often arises when comparing property sizes, planning construction projects, or simply understanding land measurements. While seemingly straightforward, the conversion between square feet and acres can be confusing. This article dives deep into understanding these measurements, provides a definitive answer, and explores the practical implications of this comparison. Understanding the difference is crucial for making informed decisions regarding real estate, landscaping, construction, and more.
Understanding Square Feet and Acres: A Fundamental Comparison
Square feet (sq ft or ft²) measure area using a square with sides of one foot each. It's a common unit for measuring smaller areas, such as rooms, houses, or smaller lots.
Acres, on the other hand, are a larger unit of land measurement. One acre is equal to 43,560 square feet. It's traditionally used for measuring larger areas, such as agricultural land, large residential lots, or commercial properties. The origin of the acre is rooted in historical land surveying practices, making it a somewhat less intuitive unit compared to the easily visualized square foot.
The Conversion: 7,840 Square Feet to Acres
To determine which is larger, we need to convert one unit to the other. Let's convert 7,840 square feet into acres:
7,840 sq ft / 43,560 sq ft/acre ≈ 0.18 acres
This calculation shows that 7,840 square feet is equivalent to approximately 0.18 acres.
The Verdict: 0.25 Acres is Larger
Therefore, 0.25 acres is significantly larger than 7,840 square feet. The difference is substantial enough to have a meaningful impact on the size and potential uses of the land.
Visualizing the Difference: Practical Implications
The difference between 0.18 acres and 0.25 acres might not seem vast on paper, but the practical implications can be significant, particularly when considering the following:
-
Building Potential: A 0.25-acre lot generally allows for a larger house and more extensive landscaping compared to a lot measuring 7,840 square feet. Building codes and zoning regulations often dictate minimum lot sizes for specific building types. The larger lot offers more flexibility in design and construction.
-
Landscaping and Outdoor Space: The extra space on a 0.25-acre lot allows for a more extensive garden, larger pool, more extensive hardscaping (patios, walkways), or simply more open green space. The increased area provides greater opportunities for outdoor living and recreation.
-
Privacy: A larger lot naturally provides greater privacy from neighbors compared to a smaller lot. This is especially important in densely populated areas. The extra space acts as a buffer zone, reducing the feeling of being overlooked or cramped.
-
Resale Value: Generally, larger lots command a higher resale value in the real estate market. Buyers often prefer more space, particularly in areas where land is scarce. The larger lot represents a more valuable asset.
-
Utilities and Infrastructure: While often not directly proportional, the size of the lot can influence utility costs and infrastructure considerations. Larger lots might require longer utility lines or more extensive drainage systems, impacting upfront costs.
Beyond the Numbers: Factors Influencing Land Value
While the sheer size of the land is a crucial factor, several other elements significantly impact its value and desirability:
-
Location: A 0.25-acre lot in a desirable, high-demand neighborhood will be considerably more valuable than a similar-sized lot in a less desirable area. Factors like proximity to schools, amenities, and transportation greatly influence property values.
-
Topography: The slope, drainage, and overall terrain of the land can affect its usability and development potential. A flat, level lot is generally more desirable and easier to build on than a steeply sloped or uneven lot.
-
Zoning Regulations: Local zoning laws dictate how the land can be used. Restrictions on building height, setbacks, and allowable uses can significantly impact the value and development potential of the property.
-
Soil Conditions: The quality of the soil can be crucial for landscaping, foundation stability, and overall development. Poor soil conditions might require additional costs for remediation or site preparation.
-
Utilities Availability: The availability of essential utilities like water, electricity, sewer, and gas significantly influences a lot's value. Properties with readily available utilities are generally more attractive to buyers.
-
Environmental Factors: The presence of protected wetlands, endangered species, or other environmental concerns can significantly affect the usability and value of the land. These factors often impose development restrictions or require mitigation efforts.
-
Views and Aesthetics: Properties with attractive views, such as mountain vistas or waterfront access, often command premium prices, irrespective of the lot's square footage. The aesthetic appeal of the land adds value beyond its mere size.
Real-World Examples: Comparing Property Sizes
To solidify the understanding, let's consider a few hypothetical scenarios:
-
Scenario 1: Suburban Residential Lot: A 0.25-acre lot is common in suburban areas and typically provides enough space for a sizable house, a garage, and a sizeable garden. A 7,840 sq ft lot, on the other hand, may be considered a smaller lot, possibly suited for a townhome or smaller single-family house with limited landscaping options.
-
Scenario 2: Rural Property: In rural settings, 0.25 acres might be viewed as a relatively small parcel, suitable for a smaller cabin or a building lot with limited agricultural potential. However, it's still significantly larger than 7,840 sq ft.
-
Scenario 3: Commercial Development: For commercial purposes, both 0.25 acres and 7,840 sq ft are likely insufficient for large-scale developments. However, 0.25 acres could accommodate a smaller retail space or office building, while 7,840 sq ft might only suit a very small commercial structure or part of a larger development.
Conclusion: Understanding the Bigger Picture
While the mathematical conversion clearly demonstrates that 0.25 acres is larger than 7,840 square feet, the practical implications extend beyond simple numbers. The size of the land is a crucial factor, but it's essential to consider location, zoning, topography, and other factors to fully assess a property's value and suitability for its intended purpose. Understanding both square footage and acreage, along with their associated implications, empowers informed decision-making in real estate and land-related ventures. Always consult with professionals, such as real estate agents, surveyors, and architects, to obtain comprehensive and tailored advice when making significant land-related decisions.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Situation Shows A Constant Rate Of Change Apex
Jul 21, 2025
-
You Have A Way About You Meaning
Jul 21, 2025
-
How Many Hours Are In 50 Years
Jul 21, 2025
-
How Many Cups Are In 12 Oz Of Chocolate Chips
Jul 21, 2025
-
How Many Square Feet In 819 Arces
Jul 21, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is More 7 840 Square Feet Or 0.25 Acres . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.