What Is The Average Atomic Mass Of Titanium
Kalali
Apr 02, 2025 · 5 min read
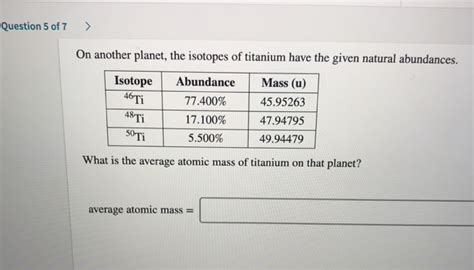
Table of Contents
What is the Average Atomic Mass of Titanium? A Deep Dive into Isotopes and Atomic Weight
Titanium, a lustrous transition metal with remarkable strength and corrosion resistance, finds extensive applications in various industries, from aerospace to biomedical engineering. Understanding its properties, including its average atomic mass, is crucial for its effective utilization. This article delves deep into the concept of average atomic mass, focusing specifically on titanium, exploring its isotopes, abundance, and the calculation behind its weighted average atomic mass.
Understanding Atomic Mass and Isotopes
Before we delve into the specifics of titanium, let's establish a foundational understanding of atomic mass and isotopes. The atomic mass of an element refers to the total mass of protons and neutrons within the nucleus of an atom. It's expressed in atomic mass units (amu), where 1 amu is approximately 1/12 the mass of a carbon-12 atom.
However, a single element rarely exists as a single type of atom. Instead, it typically consists of a mixture of isotopes. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that possess the same number of protons (defining the element) but differ in the number of neutrons. This difference in neutron count leads to variations in their atomic mass. For instance, carbon has two prominent isotopes: carbon-12 (⁶¹²C) and carbon-14 (⁶¹⁴C).
Titanium's Isotopes: A Closer Look
Titanium (Ti), with its atomic number 22 (meaning 22 protons), exhibits five naturally occurring stable isotopes:
- ⁴⁶Ti: This isotope comprises a relatively small percentage of naturally occurring titanium. Its nucleus contains 22 protons and 24 neutrons.
- ⁴⁷Ti: Another less abundant isotope, ⁴⁷Ti, possesses 22 protons and 25 neutrons.
- ⁴⁸Ti: This is the most abundant isotope of titanium, making up a significant portion of its natural composition. It consists of 22 protons and 26 neutrons.
- ⁴⁹Ti: A moderately abundant isotope, ⁴⁹Ti contains 22 protons and 27 neutrons.
- ⁵⁰Ti: Like ⁴⁶Ti, this isotope is present in a smaller percentage in naturally occurring titanium. It possesses 22 protons and 28 neutrons.
The variations in neutron numbers among these isotopes affect their individual atomic masses. However, what we typically refer to as the atomic mass of titanium is a weighted average of the masses of these isotopes, considering their relative abundance in nature.
Calculating the Average Atomic Mass of Titanium
The average atomic mass isn't simply the average of the mass numbers of the isotopes. Instead, it's a weighted average, taking into account the relative abundance of each isotope. The formula for calculating this weighted average is:
Average Atomic Mass = Σ (Isotope Mass x Isotope Abundance)
Where:
- Isotope Mass: The mass of a specific isotope in amu.
- Isotope Abundance: The percentage abundance of that isotope in nature, expressed as a decimal (e.g., 75% = 0.75).
- Σ: Represents the sum of all isotopes.
Let's apply this to titanium. The exact isotopic abundances can vary slightly depending on the source of the titanium sample, but we can use commonly accepted values for this calculation. We'll use the following approximate abundances:
| Isotope | Mass (amu) | Abundance (%) | Abundance (decimal) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ⁴⁶Ti | 45.95263 | 8.0 | 0.08 |
| ⁴⁷Ti | 46.95176 | 7.3 | 0.073 |
| ⁴⁸Ti | 47.94795 | 73.8 | 0.738 |
| ⁴⁹Ti | 48.94787 | 5.5 | 0.055 |
| ⁵⁰Ti | 49.94479 | 5.4 | 0.054 |
Now, let's perform the calculation:
Average Atomic Mass = (45.95263 amu * 0.08) + (46.95176 amu * 0.073) + (47.94795 amu * 0.738) + (48.94787 amu * 0.055) + (49.94479 amu * 0.054)
Average Atomic Mass ≈ 3.67621 amu + 3.42923 amu + 35.36613 amu + 2.69213 amu + 2.69706 amu
Average Atomic Mass ≈ 47.85 amu
This calculated value of approximately 47.85 amu is consistent with the average atomic mass of titanium reported on the periodic table. It's essential to remember that minor variations in the reported average atomic mass are possible due to differing sample compositions and measurement techniques.
The Significance of Average Atomic Mass in Titanium Applications
The average atomic mass of titanium plays a vital role in various applications:
-
Material Science: Understanding the average atomic mass is crucial for calculating the density of titanium and predicting its behavior in different alloys. This is particularly important in aerospace engineering where lightweight, high-strength materials are essential.
-
Nuclear Physics: Knowledge of isotopic abundances and atomic masses is crucial in nuclear research and applications involving titanium isotopes, such as in nuclear medicine or nuclear reactor technology.
-
Chemical Calculations: Accurate atomic mass values are fundamental for stoichiometric calculations in chemical reactions involving titanium compounds. This is essential in various chemical processes and manufacturing applications.
-
Geochemistry: The isotopic composition of titanium can be used as a tracer in geological processes, providing insights into the formation and evolution of rocks and minerals. The average atomic mass is a valuable parameter in these analyses.
Beyond the Average: Isotopic Variations and Their Implications
While the average atomic mass provides a useful average value, it's crucial to understand that natural titanium consists of a mixture of isotopes. These variations can have subtle but important implications:
-
Isotopic Fractionation: Different processes, like evaporation or chemical reactions, can fractionate titanium isotopes, leading to variations in the isotopic ratios within specific materials. These variations can be used to trace the origins of materials or understand the processes that formed them.
-
Nuclear Applications: Specific titanium isotopes might exhibit different nuclear properties and could be used in targeted applications. For instance, certain isotopes might be more suitable for specific nuclear reactions or medical applications.
-
Material Properties: While the average atomic mass provides a general understanding, the presence of specific isotopes can subtly influence the overall physical and chemical properties of titanium materials.
Conclusion
The average atomic mass of titanium, approximately 47.85 amu, is a crucial parameter reflecting the weighted average of its five naturally occurring isotopes and their relative abundances. This value is fundamental to various applications in material science, chemical calculations, nuclear research, and geochemistry. Understanding the intricacies of titanium's isotopic composition, beyond just the average atomic mass, is key to unlocking its full potential and exploiting its unique properties across a range of scientific and technological fields. The subtle variations in isotopic abundances and their implications remain an area of ongoing research and provide deeper insights into the behaviour and applications of this versatile metal.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Feet In 12 Inches
Apr 03, 2025
-
What Is 20 Percent Of 140
Apr 03, 2025
-
What Is The Waste Product Of Photosynthesis
Apr 03, 2025
-
Cuanto Es 33 Pies En Metros
Apr 03, 2025
-
How Many Ounces In 60 Ml
Apr 03, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Average Atomic Mass Of Titanium . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
