What Is The Difference Between Polygenic Traits And Multiple Alleles
Kalali
Mar 17, 2025 · 6 min read
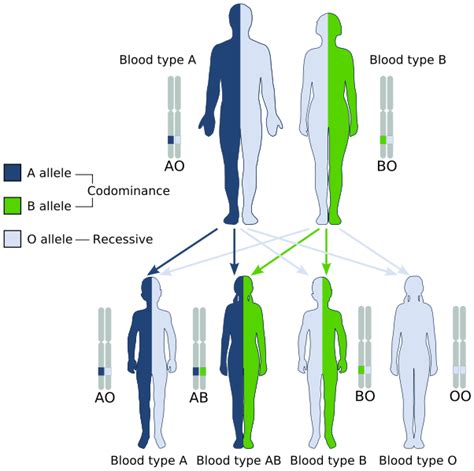
Table of Contents
What's the Difference Between Polygenic Traits and Multiple Alleles?
Understanding the mechanisms of inheritance is fundamental to grasping the diversity of life. While both polygenic traits and multiple alleles contribute to this complexity, they operate on different levels. This article delves deep into the distinctions between these two concepts, explaining them clearly and providing illustrative examples. We'll explore how they impact phenotypic variation and their significance in genetics.
Polygenic Traits: The Sum of Many Genes
Polygenic traits, unlike simple Mendelian traits governed by a single gene, are influenced by multiple genes, each contributing a small, additive effect to the overall phenotype. Think of it as a collaborative effort where many genes work together to shape a characteristic. This collaborative inheritance results in a continuous distribution of phenotypes, rather than discrete categories.
Characteristics of Polygenic Traits
- Quantitative Traits: These traits are measurable and often show continuous variation. Examples include height, weight, skin color, and intelligence.
- Environmental Influence: The environment plays a significant role in modifying the expression of polygenic traits. For instance, nutrition impacts height, and sun exposure affects skin color.
- Bell Curve Distribution: When the phenotypic values of a polygenic trait are plotted, they typically follow a bell-shaped curve (normal distribution). This indicates that most individuals fall near the average, with fewer individuals at the extremes.
- Additive Effects: Each gene involved contributes a small, quantifiable amount to the overall phenotype. The combined effects of all the genes determine the final outcome.
- Lack of Simple Dominance: Unlike simple Mendelian inheritance with clear dominant and recessive alleles, there's no simple dominance relationship among the genes influencing polygenic traits.
Examples of Polygenic Traits
- Human Height: Height is a classic example, influenced by numerous genes related to bone growth, hormone production, and overall body proportions. Environmental factors like nutrition also play a crucial role.
- Skin Color: Skin pigmentation is determined by the combined action of several genes controlling melanin production. Different alleles at these genes contribute varying amounts of melanin, resulting in a range of skin tones.
- Weight: Body weight is influenced by many genes related to metabolism, appetite regulation, and energy expenditure. Diet and exercise are significant environmental factors.
- Intelligence: While still a complex and debated topic, intelligence is believed to be a polygenic trait, involving numerous genes that contribute to cognitive abilities.
Understanding the Genetic Basis of Polygenic Traits
The genetic architecture of polygenic traits is complex and often involves:
- Quantitative Trait Loci (QTLs): These are regions of the genome that contain genes contributing to the variation of a quantitative trait. Identifying and characterizing QTLs is a major challenge in genetics.
- Gene-Gene Interactions (Epistasis): The effects of one gene on a polygenic trait can be modified by the presence or absence of other genes. This interaction complicates the analysis and prediction of phenotypes.
- Gene-Environment Interactions: The interaction between genes and environmental factors significantly impacts the expression of polygenic traits. This makes it challenging to pinpoint the exact contribution of each gene.
Multiple Alleles: Beyond Simple Dominance and Recessiveness
Multiple alleles refer to the existence of more than two alleles for a single gene within a population. While an individual can only possess two alleles (one from each parent), multiple alleles expand the range of possible genotypes and phenotypes. This contrasts with Mendelian inheritance, which typically considers only two alleles (dominant and recessive) for a gene.
Characteristics of Multiple Alleles
- More than Two Alleles: The key characteristic is the presence of more than two alternative forms of a gene within a population.
- Hierarchical Dominance: The dominance relationships between multiple alleles are often hierarchical, with some alleles showing dominance over others, while some may exhibit codominance or incomplete dominance.
- Increased Phenotypic Variation: Multiple alleles significantly increase the genetic diversity within a population and lead to a wider range of phenotypes.
- Blood Group System as an Example: The ABO blood group system is a classic example. Three alleles (IA, IB, and i) determine blood type, resulting in four possible phenotypes (A, B, AB, and O).
Examples of Multiple Alleles
- ABO Blood Group System: This system demonstrates hierarchical dominance. IA and IB are codominant (both expressed in AB blood type), while i is recessive to both IA and IB.
- Coat Color in Rabbits: Multiple alleles influence coat color in rabbits, resulting in a diverse range of colors and patterns.
- Human HLA System: The Human Leukocyte Antigen (HLA) system involves numerous alleles that play a crucial role in the immune system. The high level of polymorphism in the HLA genes contributes to the diversity of immune responses.
- CFTR Gene (Cystic Fibrosis): While cystic fibrosis is primarily associated with a recessive allele, multiple alleles exist within the CFTR gene, leading to varying disease severities.
Understanding the Genetic Basis of Multiple Alleles
Multiple alleles arise through mutations in a gene. Different mutations can lead to different alleles, each with its unique effect on gene function and phenotype. The accumulation of these mutations over time expands the allelic diversity within a population.
Key Differences Between Polygenic Traits and Multiple Alleles
| Feature | Polygenic Traits | Multiple Alleles |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Genes | Multiple genes involved | Single gene with multiple alleles |
| Inheritance | Additive effects of multiple genes | Different dominance relationships among alleles |
| Phenotype | Continuous variation, often bell curve distribution | Discrete phenotypes, but more varied than with two alleles |
| Environmental Influence | Significant environmental impact | Usually less significant environmental impact |
| Examples | Height, weight, skin color, intelligence | ABO blood group, coat color in rabbits |
The Interplay of Polygenic Traits and Multiple Alleles
While distinct, polygenic traits and multiple alleles can interact to shape phenotypic variation. A polygenic trait might involve genes each with multiple alleles, further increasing the complexity of the trait. For instance, the genes involved in determining human height may each have multiple alleles, each contributing slightly different effects on growth. This interaction dramatically expands the range of possible phenotypes.
Conclusion
Polygenic traits and multiple alleles are fundamental concepts in genetics that explain the vast diversity observed in living organisms. While they operate at different levels (multiple genes vs. multiple alleles of a single gene), they both contribute significantly to phenotypic variation. Understanding these concepts is crucial for comprehending the intricacies of inheritance and the genetic basis of complex traits, paving the way for advancements in fields like medicine, agriculture, and evolutionary biology. Further research into the genetic architecture of polygenic traits and the functional effects of multiple alleles continues to unveil the complexity and beauty of the genetic world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
A Black Hole Projected Into A 4d Universe
May 31, 2025
-
How To Wire A Three Phase Electric Motor
May 31, 2025
-
How To Get Oil Spots Off Driveway
May 31, 2025
-
How To Repair Basement Walls Crumbling
May 31, 2025
-
How Long Is A Rotation In Star Wars
May 31, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Difference Between Polygenic Traits And Multiple Alleles . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.