What Is The Empirical Formula Of Glucose C6h12o6
Kalali
Mar 18, 2025 · 5 min read
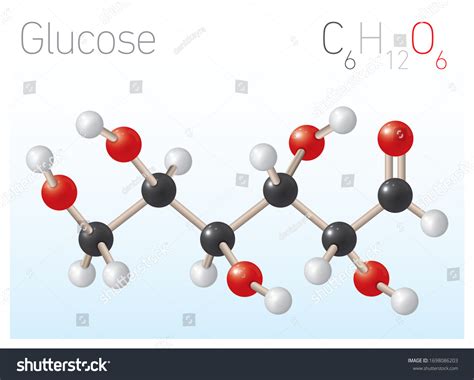
Table of Contents
- What Is The Empirical Formula Of Glucose C6h12o6
- Table of Contents
- What is the Empirical Formula of Glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆)? Understanding Molecular and Empirical Formulas
- Understanding Molecular and Empirical Formulas
- Determining the Empirical Formula of Glucose
- Significance of Empirical Formula Determination
- Glucose: A Deeper Dive into its Properties and Importance
- Properties of Glucose
- Importance of Glucose in Biological Systems
- Beyond Glucose: Empirical Formulas in Other Compounds
- Conclusion: The Importance of Both Empirical and Molecular Formulas
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
What is the Empirical Formula of Glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆)? Understanding Molecular and Empirical Formulas
Glucose, a simple sugar crucial for energy in living organisms, has the molecular formula C₆H₁₂O₆. But what about its empirical formula? This article delves deep into understanding the difference between molecular and empirical formulas, specifically focusing on glucose, and explores the broader implications of these concepts in chemistry.
Understanding Molecular and Empirical Formulas
Before we determine the empirical formula of glucose, let's clarify the distinction between molecular and empirical formulas.
Molecular Formula: This formula represents the actual number of atoms of each element present in one molecule of a compound. For glucose, the molecular formula, C₆H₁₂O₆, explicitly states that each molecule contains six carbon atoms, twelve hydrogen atoms, and six oxygen atoms.
Empirical Formula: This formula represents the simplest whole-number ratio of atoms of each element in a compound. It's the most reduced form of the molecular formula. It shows the relative proportions of the elements, not the exact number of atoms in a molecule.
Determining the Empirical Formula of Glucose
To find the empirical formula of glucose, we need to simplify the molecular formula (C₆H₁₂O₆) to its simplest whole-number ratio. We can do this by finding the greatest common divisor (GCD) of the subscripts.
In glucose's molecular formula:
- Carbon (C) has a subscript of 6
- Hydrogen (H) has a subscript of 12
- Oxygen (O) has a subscript of 6
The GCD of 6, 12, and 6 is 6. Dividing each subscript by the GCD (6), we get:
- Carbon: 6/6 = 1
- Hydrogen: 12/6 = 2
- Oxygen: 6/6 = 1
Therefore, the empirical formula of glucose is CH₂O. This signifies that for every carbon atom, there are two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom.
Significance of Empirical Formula Determination
Determining the empirical formula is a crucial step in various chemical analyses. It's often the first step in identifying an unknown compound. Here's why:
-
Simplified Representation: The empirical formula provides a simplified representation of the compound's composition, making it easier to understand the relative proportions of elements.
-
Elemental Analysis: Techniques like combustion analysis provide the mass percentages of elements in a compound. This data is then used to calculate the empirical formula. Knowing the empirical formula is the first step towards finding the molecular formula. The molecular formula can then be determined by other means, like mass spectrometry.
-
Understanding Chemical Reactions: Empirical formulas help in understanding the stoichiometry of chemical reactions involving the compound. They provide the molar ratios of reactants and products, which are vital for balancing chemical equations and performing stoichiometric calculations.
-
Isomers and Polymeric Structures: Many compounds share the same empirical formula but have different molecular formulas and structures. For instance, several sugars have the same empirical formula (CH₂O) but differ in their molecular formulas and arrangement of atoms. This illustrates how the molecular formula provides more comprehensive information than the empirical formula. This is especially true for polymers where empirical formulas represent the repeating unit.
Glucose: A Deeper Dive into its Properties and Importance
Glucose, with its molecular formula C₆H₁₂O₆, is a crucial monosaccharide, a simple sugar. Let's explore some key aspects of this vital biomolecule:
Properties of Glucose
-
Solubility: Glucose is highly soluble in water due to its numerous hydroxyl (-OH) groups, which can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules.
-
Crystalline Structure: Pure glucose exists as a white, crystalline solid.
-
Optical Isomerism: Glucose exhibits optical isomerism, existing as D-glucose and L-glucose. D-glucose is the naturally occurring form and the primary source of energy for living organisms.
-
Reducing Sugar: Glucose is a reducing sugar, meaning it can donate electrons to other molecules. This property is crucial in various biochemical reactions.
Importance of Glucose in Biological Systems
Glucose plays a pivotal role in various biological processes:
-
Cellular Respiration: Glucose is the primary fuel source for cellular respiration, the process that generates ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the energy currency of cells.
-
Glycolysis: Glucose undergoes glycolysis, a metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose into pyruvate, producing a small amount of ATP and NADH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide).
-
Gluconeogenesis: The liver can synthesize glucose from non-carbohydrate sources like amino acids and glycerol in a process called gluconeogenesis.
-
Glycogen Storage: Excess glucose is stored as glycogen, a polysaccharide, in the liver and muscles for later use.
-
Photosynthesis: In plants, glucose is synthesized during photosynthesis using sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water.
Beyond Glucose: Empirical Formulas in Other Compounds
The concept of empirical formulas extends beyond glucose and is applicable to numerous compounds. Let's consider a few examples:
-
Water (H₂O): The empirical formula and molecular formula of water are the same, indicating that the simplest ratio of hydrogen to oxygen atoms is also the actual ratio in a water molecule.
-
Hydrogen Peroxide (H₂O₂): The molecular formula is H₂O₂, while the empirical formula is HO. This highlights the difference between the actual composition and the simplest ratio.
-
Acetylene (C₂H₂): The empirical formula is CH, signifying a 1:1 ratio of carbon to hydrogen, whereas the molecular formula indicates two carbon atoms and two hydrogen atoms per molecule.
-
Benzene (C₆H₆): The empirical formula is CH, indicating a 1:1 ratio of carbon to hydrogen, while the molecular formula, C₆H₆, reflects the actual number of atoms in a benzene molecule.
Conclusion: The Importance of Both Empirical and Molecular Formulas
In summary, while the empirical formula of glucose is CH₂O, its molecular formula, C₆H₁₂O₆, provides a more complete picture of the molecule's actual composition. Understanding both types of formulas is essential for comprehending the chemical properties, reactions, and biological significance of glucose and other compounds. The empirical formula serves as a valuable tool in elemental analysis and provides a simplified representation of a compound's composition, while the molecular formula offers a detailed description of its atomic makeup. Together, they contribute significantly to our understanding of chemical structures and reactions. Further research into the synthesis and reactions of glucose, and other compounds, relies heavily on the precise understanding of both empirical and molecular formulas. The accurate determination of these formulas, using established analytical techniques, allows us to predict and interpret the chemical behaviour of compounds with increased accuracy. The importance of both empirical and molecular formulas is undeniable in the pursuit of chemical knowledge and applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Percentage Of 40 Is 25
Mar 19, 2025
-
How Many Acute Angles Are In An Acute Triangle
Mar 19, 2025
-
How Much Is 35 Degrees Celsius In Fahrenheit
Mar 19, 2025
-
28 Is What Percent Of 50
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Percentage Of 50 Is 5
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Empirical Formula Of Glucose C6h12o6 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
