What Is The Lcm For 18 And 24
Kalali
Mar 10, 2025 · 5 min read
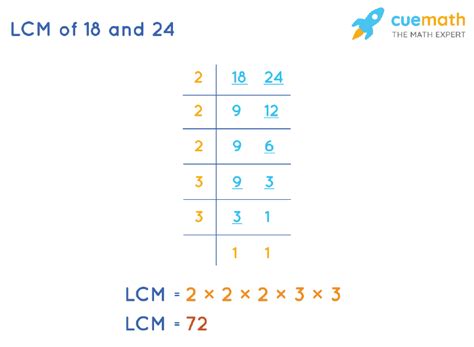
Table of Contents
What is the LCM for 18 and 24? A Deep Dive into Least Common Multiples
Finding the least common multiple (LCM) is a fundamental concept in mathematics, crucial for various applications, from simplifying fractions to solving complex problems in algebra and beyond. This comprehensive guide will not only answer the question, "What is the LCM for 18 and 24?" but also explore the various methods for calculating LCMs, providing a robust understanding of the concept itself. We'll delve into the theoretical underpinnings, practical applications, and even explore some related mathematical concepts.
Understanding Least Common Multiples (LCM)
The least common multiple (LCM) of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the integers. In simpler terms, it's the smallest number that contains all the numbers as factors. Understanding LCMs is essential in various mathematical operations and real-world scenarios. For instance, it plays a crucial role in adding or subtracting fractions with different denominators, determining the least common denominator (LCD).
Why is LCM important?
-
Fraction Operations: LCM is the key to finding a common denominator when adding or subtracting fractions. Without it, accurately combining fractions becomes impossible.
-
Scheduling and Timing: Imagine two buses arrive at a stop at different intervals. The LCM helps determine when both buses will arrive at the stop simultaneously again.
-
Modular Arithmetic: LCM finds applications in various areas of modular arithmetic, a branch of mathematics dealing with remainders.
-
Pattern Recognition: Identifying repeating patterns, like in tiling or musical rhythms, often relies on finding LCMs of involved intervals.
Methods for Calculating LCM
Several methods exist for calculating the LCM, each offering unique advantages depending on the numbers involved and the level of mathematical understanding. Let's explore three common approaches:
1. Listing Multiples Method
This is the most straightforward method, particularly suitable for smaller numbers. It involves listing the multiples of each number until a common multiple is found. The smallest common multiple is the LCM.
Example: Finding the LCM of 18 and 24
- Multiples of 18: 18, 36, 54, 72, 90, 108, 126, 144, 162, 180…
- Multiples of 24: 24, 48, 72, 96, 120, 144, 168, 192, 216, 240…
Observing the lists, we see that 72 is the smallest number appearing in both lists. Therefore, the LCM(18, 24) = 72.
This method is simple but can become cumbersome with larger numbers.
2. Prime Factorization Method
The prime factorization method is a more efficient approach, especially for larger numbers. It involves finding the prime factorization of each number and then constructing the LCM using the highest powers of each prime factor present.
Example: Finding the LCM of 18 and 24 using prime factorization
- Prime factorization of 18: 2 x 3²
- Prime factorization of 24: 2³ x 3
To find the LCM, we take the highest power of each prime factor present in either factorization:
- Highest power of 2: 2³ = 8
- Highest power of 3: 3² = 9
Therefore, LCM(18, 24) = 2³ x 3² = 8 x 9 = 72
This method is generally faster and more efficient for larger numbers compared to the listing multiples method.
3. Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) Method
The greatest common divisor (GCD) method leverages the relationship between LCM and GCD. The product of the LCM and GCD of two numbers is equal to the product of the two numbers. This means:
LCM(a, b) x GCD(a, b) = a x b
To use this method, we first need to find the GCD of 18 and 24. We can use the Euclidean algorithm for this:
- Divide 24 by 18: 24 = 18 x 1 + 6
- Divide 18 by the remainder 6: 18 = 6 x 3 + 0
The last non-zero remainder is the GCD, which is 6.
Now, we can use the formula:
LCM(18, 24) = (18 x 24) / GCD(18, 24) = (18 x 24) / 6 = 72
This method is efficient for larger numbers and elegantly connects LCM and GCD.
The Answer: LCM(18, 24) = 72
Using any of the three methods described above, we arrive at the same conclusion: the least common multiple of 18 and 24 is 72. This means 72 is the smallest positive integer divisible by both 18 and 24.
Real-World Applications of LCM
Beyond the theoretical realm, LCM finds numerous practical applications:
-
Calendars: Determining when specific events will coincide, such as the alignment of planetary cycles or the simultaneous occurrence of two recurring events.
-
Construction: Coordinating tasks in construction projects requiring materials delivered at different intervals.
-
Music: Understanding rhythmic patterns and harmonic intervals.
-
Manufacturing: Synchronizing machinery operating at different speeds.
-
Cooking: Measuring ingredients in recipes that require fractional amounts.
Beyond the Basics: Extending LCM Concepts
The concept of LCM extends beyond just two numbers. You can calculate the LCM for three or more numbers by using the prime factorization method, extending the process to include all prime factors present in each number's factorization. For example, to find the LCM of 12, 18, and 24:
-
Prime Factorization:
- 12 = 2² x 3
- 18 = 2 x 3²
- 24 = 2³ x 3
-
Highest Powers:
- Highest power of 2: 2³ = 8
- Highest power of 3: 3² = 9
-
LCM: LCM(12, 18, 24) = 2³ x 3² = 8 x 9 = 72
Therefore, the LCM of 12, 18, and 24 is 72.
Conclusion: Mastering LCM for Mathematical Proficiency
Understanding and calculating the least common multiple is a vital skill in mathematics. This guide has provided a comprehensive overview of the concept, explored various calculation methods, and highlighted its numerous practical applications. By mastering LCM, you'll enhance your problem-solving abilities across various mathematical domains and real-world scenarios. Remember, whether you use the listing multiples, prime factorization, or GCD method, the key is to find the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the given numbers. The understanding gained here will empower you to tackle more complex mathematical challenges with confidence and efficiency. Further exploration of related concepts like GCD and prime factorization will further strengthen your mathematical foundation.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Do You Pass Level 12 On Bloxorz
Jul 12, 2025
-
How Far Is 0 4 Miles To Walk
Jul 12, 2025
-
What Is 20 Percent Of 800 000
Jul 12, 2025
-
Words That Start With Y In Science
Jul 12, 2025
-
Prevent An Expressway Emergency By Merging Without
Jul 12, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Lcm For 18 And 24 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.