What's The Inverse Operation Of Division
Kalali
Mar 19, 2025 · 6 min read
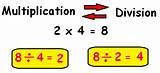
Table of Contents
What's the Inverse Operation of Division? A Comprehensive Guide
Division, a fundamental arithmetic operation, plays a crucial role in various mathematical and real-world applications. Understanding its inverse operation is equally important for mastering mathematical concepts and solving diverse problems efficiently. This comprehensive guide delves deep into the inverse operation of division, exploring its definition, practical applications, and significance in different mathematical contexts.
Understanding Division
Before diving into the inverse operation, let's solidify our understanding of division itself. Division is essentially the process of splitting a quantity into equal parts or determining how many times one quantity is contained within another. We represent division using various symbols, including the division sign (÷), the slash (/), and the fraction bar (—).
For example, 12 ÷ 3 = 4 signifies that when we divide 12 into 3 equal parts, each part contains 4 units. Similarly, 20/5 = 4 indicates that 5 goes into 20 four times. The fraction 12/3 also represents the same division operation, resulting in 4. In each case, 12 is the dividend, 3 is the divisor, and 4 is the quotient.
Identifying the Inverse Operation: Multiplication
The inverse operation of division is multiplication. This is because multiplication and division are fundamentally related; they are inverse operations that "undo" each other. If you divide a number by another and then multiply the result by the original divisor, you'll retrieve the original number. Conversely, if you multiply a number by another and then divide the result by the original multiplier, you'll obtain the original number.
This reciprocal relationship is the core principle of inverse operations. This principle is crucial in solving equations and performing calculations in various mathematical fields like algebra, calculus, and even more advanced areas.
Let's illustrate this with a few examples:
-
Example 1: 15 ÷ 3 = 5. The inverse operation is 5 × 3 = 15, bringing us back to the original dividend.
-
Example 2: 28 / 7 = 4. The inverse operation is 4 × 7 = 28, again returning the original dividend.
-
Example 3: A fraction like 24/6 can be understood as a division problem (24 ÷ 6 = 4). The inverse operation would be 4 × 6 = 24.
This relationship between division and multiplication holds true for all real numbers (except division by zero, which is undefined). The ability to seamlessly transition between division and multiplication is fundamental to simplifying expressions and solving equations.
Practical Applications of the Inverse Relationship
The inverse relationship between division and multiplication isn't just a theoretical concept; it has numerous practical applications in various fields:
1. Solving Equations:
Many algebraic equations involve division. To isolate a variable and solve for its value, we often utilize the inverse operation of multiplication.
Example: Solve for 'x' in the equation x / 5 = 10.
To isolate 'x', we multiply both sides of the equation by 5:
x / 5 * 5 = 10 * 5
x = 50
2. Unit Conversions:
Converting units frequently involves division and its inverse, multiplication. For example, converting kilometers to meters involves multiplying by 1000 (since there are 1000 meters in a kilometer), while the inverse conversion from meters to kilometers involves division by 1000.
3. Ratio and Proportion:
Ratios and proportions extensively use division and multiplication. Finding equivalent ratios often involves multiplying or dividing both terms of a ratio by the same number. Solving proportion problems often requires employing the inverse operation to find an unknown quantity.
4. Financial Calculations:
Division and multiplication are pivotal in financial calculations, such as calculating interest, determining profit margins, or splitting costs among multiple parties. The inverse relationship allows for easy conversion between different financial metrics.
5. Geometry and Measurement:
Calculating areas, volumes, and other geometric properties frequently utilizes division and multiplication. Finding the average of a set of numbers also involves division, and its inverse is helpful in various geometric computations.
6. Data Analysis and Statistics:
Division plays a vital role in data analysis, particularly in calculating averages, percentages, and other statistical measures. Its inverse operation, multiplication, is essential for scaling data or adjusting for different factors.
Understanding the Concept of Reciprocal
The concept of a reciprocal is closely tied to the inverse operation of division. The reciprocal of a number is simply 1 divided by that number. For example:
- The reciprocal of 5 is 1/5 or 0.2.
- The reciprocal of 2/3 is 3/2 or 1.5.
- The reciprocal of 0.75 is 1/0.75 or 4/3.
Multiplying a number by its reciprocal always results in 1. This property is crucial in simplifying algebraic expressions and solving equations.
When we divide by a number, it’s equivalent to multiplying by its reciprocal. This equivalence is fundamental to understanding the interconnectedness of division and multiplication as inverse operations. For instance, 12 ÷ 3 is the same as 12 x (1/3), both equaling 4.
Dealing with Zero
One crucial exception to the inverse relationship between division and multiplication involves the number zero. Division by zero is undefined in mathematics. This means you cannot have an inverse operation for a division problem where the divisor is zero. Attempting such an operation leads to undefined results and errors in calculations.
Advanced Applications and Concepts
The inverse relationship between division and multiplication extends beyond basic arithmetic. It forms the foundation for more complex mathematical concepts:
- Algebraic manipulations: Solving complex algebraic equations often requires utilizing the inverse operation to isolate variables and determine their values. This involves skillful manipulation of equations using multiplication and division to achieve the desired solution.
- Calculus: Differentiation and integration, core concepts in calculus, inherently involve operations that are intimately related to division and multiplication, reflecting the inverse relationship in a more advanced mathematical framework.
- Linear Algebra: Matrix operations, a fundamental aspect of linear algebra, frequently employ multiplication and its inverse, highlighting the inverse relationship in a different mathematical context.
- Computer Science: Many computer algorithms rely on division and multiplication for various operations, including data processing, image manipulation, and numerical analysis. The inverse nature of these operations is often exploited for efficiency and optimization in algorithms.
Conclusion
The inverse operation of division is multiplication. Their reciprocal relationship is a cornerstone of mathematics, enabling efficient problem-solving in diverse applications, from basic arithmetic to advanced mathematical fields. Understanding this inverse relationship is crucial for mastering mathematical concepts, solving equations, performing unit conversions, and tackling various real-world problems across multiple disciplines. The principle of reciprocal values further reinforces the close ties between division and multiplication, providing powerful tools for simplifying expressions and achieving elegant mathematical solutions. Remember, however, the important exception of division by zero, which remains undefined. This exception underscores the importance of careful consideration when dealing with these fundamental arithmetic operations.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Grams Is 2 5 Pounds
Mar 19, 2025
-
How To Turn On Mic On Chromebook
Mar 19, 2025
-
26 Out Of 32 As A Percentage
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Is 17 25 As A Percent
Mar 19, 2025
-
How Many Ml In 0 5 Oz
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What's The Inverse Operation Of Division . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
