Which Activity Stresses The Demand Side Of Water Supplies
Kalali
Mar 26, 2025 · 5 min read
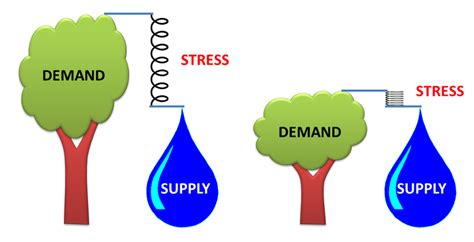
Table of Contents
Which Activities Stress the Demand Side of Water Supplies?
Water scarcity is a growing global concern, impacting billions and threatening ecosystems. While supply-side issues like droughts and pollution are significant, the demand side plays an equally crucial, often overlooked, role. Understanding which activities stress water demand is essential for developing effective water management strategies. This article delves into the key sectors and activities placing immense pressure on our water resources, exploring their impacts and potential solutions.
Agriculture: The Heavyweight Champion of Water Consumption
Agriculture is undeniably the largest consumer of water globally, accounting for over 70% of total withdrawals in many regions. This heavy reliance stems from various factors:
1. Irrigation Practices: A Thirsty Business
Traditional irrigation methods, such as flood irrigation, are incredibly inefficient, losing significant amounts of water through evaporation and runoff. While advancements like drip irrigation and sprinkler irrigation offer improved water use efficiency, their adoption remains uneven, particularly in developing countries where traditional methods persist.
2. Water-Intensive Crops: The Price of Productivity
Certain crops, like rice, cotton, and alfalfa, are notoriously thirsty, requiring vast quantities of water to grow. The cultivation of these crops in water-stressed regions exacerbates existing scarcity issues, forcing difficult choices between food security and water sustainability.
3. Livestock Production: Hidden Water Footprints
The water footprint of livestock production is often underestimated. Raising animals for meat, dairy, and eggs requires substantial water for feed production, animal drinking, and cleaning processes. Intensive livestock farming, in particular, places significant strain on water resources.
Solutions for Agricultural Water Demand:
- Promoting efficient irrigation techniques: Widespread adoption of drip irrigation, sprinkler systems, and other water-saving technologies is paramount.
- Cultivating drought-resistant crops: Investing in research and development of crops that require less water can significantly reduce agricultural water demand.
- Improving water management practices: Implementing water harvesting techniques, soil moisture monitoring, and precision irrigation can optimize water use in agriculture.
- Shifting towards less water-intensive diets: Reducing meat consumption and promoting plant-based diets can significantly lower the overall water footprint of food production.
Industrial Water Use: A Diverse and Growing Demand
Industrial activities represent a significant and diverse source of water demand. The specific needs vary widely depending on the industry:
1. Energy Production: A Power-Hungry Thirst
Power generation, especially thermoelectric power plants, is a major water consumer, utilizing massive amounts of water for cooling purposes. Other energy sectors, such as oil and gas extraction, also require considerable water for various operations.
2. Manufacturing: The Varied Needs of Industry
Manufacturing processes across a wide range of industries, including textiles, food processing, and chemicals, require water for cleaning, cooling, and as a component in production processes. The water intensity varies significantly across different manufacturing sectors.
3. Mining: Extracting Resources, Consuming Water
Mining operations, particularly those involving hydraulic fracturing (fracking), are often extremely water-intensive, demanding large volumes of water for extraction, processing, and waste disposal.
Solutions for Industrial Water Demand:
- Improving industrial water efficiency: Implementing water recycling and reuse systems, adopting water-efficient technologies, and optimizing production processes can significantly reduce industrial water consumption.
- Investing in water-saving technologies: Advanced technologies such as membrane filtration and reverse osmosis can improve water reuse and reduce wastewater discharge.
- Encouraging water-efficient industrial practices: Implementing stricter regulations and incentives for water conservation in industrial settings can promote sustainable water management.
- Promoting closed-loop water systems: Designing industrial processes that minimize water loss and maximize water reuse is crucial for sustainability.
Domestic Water Use: A Growing Population, Growing Demand
Residential water use, encompassing household needs, is a significant contributor to overall water demand. This demand is driven primarily by:
1. Population Growth: More People, More Water
The ever-increasing global population directly translates to higher water demand for drinking, sanitation, and household purposes. Rapid urbanization further intensifies this challenge.
2. Rising Living Standards: Increased Consumption
Improvements in living standards often lead to increased water consumption per capita. Greater access to running water, appliances like washing machines and dishwashers, and larger homes all contribute to higher domestic water usage.
3. Water Leaks and Inefficient Infrastructure: Hidden Losses
Aging and inefficient water infrastructure, including leaky pipes and outdated plumbing, lead to substantial water losses. These hidden losses represent a significant portion of total domestic water consumption.
Solutions for Domestic Water Demand:
- Investing in water infrastructure: Repairing and upgrading aging water infrastructure to minimize leaks and improve efficiency is critical.
- Promoting water conservation practices: Educating the public on water-saving techniques, such as shorter showers, efficient appliances, and water-wise landscaping, can significantly reduce household water consumption.
- Implementing water metering and pricing policies: Accurate water metering and tiered pricing can incentivize water conservation by making consumers more aware of their water usage and its cost.
- Developing water-efficient appliances and fixtures: Promoting the use of low-flow toilets, showerheads, and faucets can significantly reduce household water consumption.
Other Contributing Factors: Beyond the Major Sectors
Beyond the major sectors, several other factors contribute to increased water demand:
- Climate Change: Altered precipitation patterns, increased frequency and intensity of droughts, and rising temperatures all exacerbate water scarcity and increase demand.
- Environmental Degradation: Pollution of water sources reduces the availability of clean water, increasing the demand for treated water.
- Population Displacement: Natural disasters, conflict, and other factors can lead to population displacement, placing additional strain on water resources in receiving areas.
- Tourism: Tourist destinations often experience significant increases in water demand during peak seasons, which can place considerable stress on local water supplies.
Conclusion: A Holistic Approach to Water Management
Addressing the demand-side pressures on water resources requires a multi-faceted approach. It's not enough to simply focus on supply-side solutions like building new dams or desalination plants. A holistic strategy must incorporate a range of measures targeting all major water-consuming sectors, including agriculture, industry, and domestic use. This includes promoting water efficiency, implementing water conservation practices, investing in water-saving technologies, and developing effective water pricing policies. Furthermore, addressing the underlying drivers of water demand, such as population growth and climate change, is crucial for long-term sustainability. By adopting a comprehensive and integrated approach, we can work towards a future where water resources are managed responsibly and sustainably, ensuring their availability for present and future generations. The urgency of this task cannot be overstated, as our collective future depends on it.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 0 Degrees In Fahrenheit To Celsius
Mar 29, 2025
-
The Is The Fundamental Unit Of Life
Mar 29, 2025
-
How Many Cm Is 4 6
Mar 29, 2025
-
100 Of 500 Is What Percent
Mar 29, 2025
-
How Many Grams Is A 8th Of An Ounce
Mar 29, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Activity Stresses The Demand Side Of Water Supplies . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
