Which Shape Has 8 Angles And 8 Vertices
Kalali
Mar 18, 2025 · 5 min read
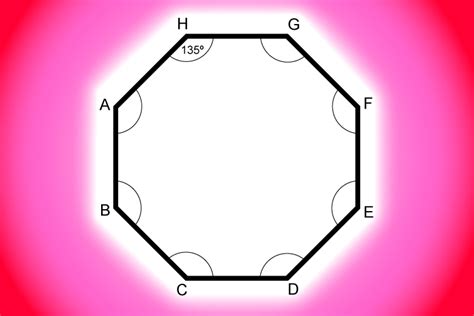
Table of Contents
Which Shape Has 8 Angles and 8 Vertices? Unraveling the Octagon
The question, "Which shape has 8 angles and 8 vertices?" points directly to a specific polygon: the octagon. While seemingly simple, understanding the octagon's properties, its diverse applications, and its place within the broader world of geometry offers a fascinating exploration. This article will delve deep into the octagon, covering its definition, types, properties, real-world applications, and even some intriguing mathematical explorations related to its angles and vertices.
Defining the Octagon: Angles, Vertices, and Sides
An octagon is a two-dimensional geometric shape characterized by eight sides, eight angles, and eight vertices. Each of these features plays a crucial role in defining the octagon and differentiating it from other polygons. The vertices are the points where two sides meet, forming the angles. The angles are the measurements of the space between two adjacent sides at a vertex. And finally, the sides are the line segments that connect the vertices.
Understanding Polygons: A Broader Perspective
Before focusing solely on the octagon, let's briefly establish its place within the larger family of polygons. Polygons are closed, two-dimensional shapes composed of straight line segments. They are categorized by the number of sides and angles they possess. For example:
- Triangle: 3 sides and 3 angles
- Quadrilateral: 4 sides and 4 angles
- Pentagon: 5 sides and 5 angles
- Hexagon: 6 sides and 6 angles
- Heptagon (or Septagon): 7 sides and 7 angles
- Octagon: 8 sides and 8 angles
- Nonagon: 9 sides and 9 angles
- Decagon: 10 sides and 10 angles
And so on, with the number of sides and angles increasing infinitely. The octagon, with its eight sides, sits firmly in the middle of this sequence, exhibiting properties shared with other polygons but also possessing unique characteristics.
Types of Octagons: Regular vs. Irregular
Octagons are not all created equal. They can be classified into two main categories: regular and irregular. This classification is based on the length of their sides and the measure of their angles.
Regular Octagon: Symmetry and Precision
A regular octagon is characterized by its perfect symmetry. All eight sides are of equal length, and all eight angles are equal in measure. This symmetry creates a visually appealing and mathematically consistent shape. The measure of each interior angle in a regular octagon is 135 degrees. This is calculated using the formula for the sum of interior angles of a polygon: (n-2) * 180 degrees, where 'n' is the number of sides. For an octagon (n=8), the sum is (8-2) * 180 = 1080 degrees. Dividing this by 8 (the number of angles) gives us 135 degrees per angle.
Irregular Octagon: A World of Variations
An irregular octagon, on the other hand, lacks the perfect symmetry of its regular counterpart. Its sides can have varying lengths, and its angles can have different measures. This results in a wide range of possible shapes, each with its own unique characteristics. The only defining feature of an irregular octagon is that it has eight sides and eight angles. The sum of interior angles remains 1080 degrees, but the individual angle measures vary.
Real-World Applications of Octagons
The octagon's unique properties make it a versatile shape with numerous applications in various fields:
Architecture and Design
Octagonal structures have been used throughout history and across different cultures. From ancient temples to modern buildings, the octagon's symmetrical nature lends itself to aesthetically pleasing and structurally sound designs. The stop sign, a ubiquitous symbol of traffic control, is a classic example of an octagon's practical application. Its shape is easily recognizable and its eight sides provide a balanced and visually distinct form.
Engineering and Construction
Octagons find use in various engineering projects. Certain types of nuts and bolts use octagonal shapes for improved grip. Some structural designs leverage octagonal components for strength and stability.
Nature's Octagons
While not perfectly regular, octagonal patterns can be observed in nature. Certain crystals and some biological structures exhibit approximate octagonal symmetry.
Exploring the Mathematics of Octagons: Angles and Beyond
The mathematical properties of octagons, particularly its angles and vertices, provide opportunities for further exploration.
Calculating Interior Angles: A Step-by-Step Guide
As previously mentioned, the sum of interior angles of an octagon is 1080 degrees. In a regular octagon, each angle measures 135 degrees. For irregular octagons, the individual angle measures will vary, but their sum will always be 1080 degrees.
Exterior Angles: A Complementary Perspective
The exterior angles of a polygon are the angles formed by extending one side of the polygon. In any polygon, the sum of its exterior angles always equals 360 degrees. This is true for octagons as well, regardless of whether they are regular or irregular.
Area Calculation: Different Approaches
Calculating the area of an octagon depends on whether it is regular or irregular. For a regular octagon, a formula involving the side length can be used. For irregular octagons, more complex methods might be necessary, potentially involving dividing the octagon into smaller, simpler shapes.
Tessellations: Octagons and Their Neighbors
Octagons can be used to create tessellations, which are patterns formed by repeating shapes to cover a plane without gaps or overlaps. However, regular octagons alone cannot tessellate; they require the incorporation of other shapes, like squares.
Conclusion: The Enduring Significance of the Octagon
The seemingly simple question of which shape has 8 angles and 8 vertices opens the door to a rich exploration of geometry, symmetry, and the fascinating applications of mathematical shapes in the real world. From its precise definition to its varied applications in architecture, engineering, and even nature, the octagon reveals a depth and complexity that extends beyond its eight sides and angles. Understanding its properties, appreciating its diversity, and exploring its mathematical intricacies highlight the enduring significance of this remarkable polygon. The next time you encounter an octagon, remember the multifaceted story it holds within its eight sides and eight vertices.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Is Sour Taste A Physical Property
Mar 19, 2025
-
How Many Kilos Are 20 Pounds
Mar 19, 2025
-
11 Out Of 30 As A Percentage
Mar 19, 2025
-
Cuanto Es 92 Grados Fahrenheit En Centigrados
Mar 19, 2025
-
How To Get Magnitude Of Force
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Shape Has 8 Angles And 8 Vertices . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
