Which Taxon Includes The Broadest Characteristics
Kalali
Mar 18, 2025 · 5 min read
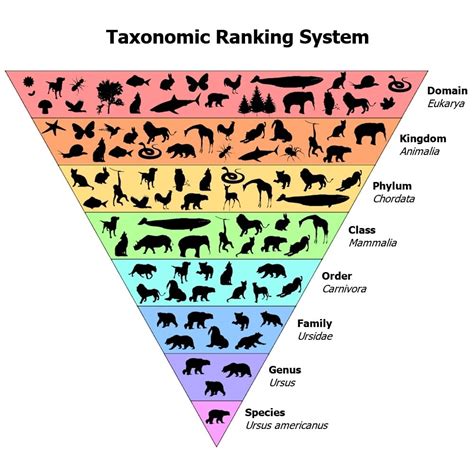
Table of Contents
Which Taxon Includes the Broadest Characteristics? Exploring the Hierarchy of Life
The question of which taxon encompasses the broadest characteristics is fundamentally a question about the organization of life itself. Taxonomy, the science of classifying organisms, utilizes a hierarchical system to categorize biodiversity, reflecting evolutionary relationships and shared traits. From the most specific to the most inclusive, this system traditionally proceeds: species, genus, family, order, class, phylum (or division in plants), kingdom, and domain. But which of these ranks truly represents the broadest characteristics? The answer, surprisingly, isn't straightforward and depends on how we define "broadest."
Understanding Taxonomic Ranks and Their Characteristics
Before diving into the central question, let's briefly review each taxonomic rank and the characteristics they typically encompass:
-
Species: This is the most specific rank, representing a group of organisms capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring. Characteristics are highly specific, often including morphological, physiological, behavioral, and genetic similarities.
-
Genus: A genus groups together closely related species sharing a common ancestor and significant similarities. Characteristics at this level are still relatively specific but represent broader patterns than those observed within a single species.
-
Family: Families group genera based on shared evolutionary history and characteristics. Similarities become more generalized, with fewer detailed shared features than those found within a genus.
-
Order: Orders encompass related families, exhibiting broader evolutionary relationships and increasingly generalized shared characteristics.
-
Class: Classes group orders that share significant characteristics, highlighting key evolutionary divergences. The characteristics at this level are quite broad, reflecting major adaptations and body plans.
-
Phylum (or Division): Phyla (or divisions in plants) represent major evolutionary lineages, grouping together classes with fundamental similarities in body plan and developmental patterns. Characteristics become extremely broad, often reflecting fundamental differences in body organization.
-
Kingdom: Kingdoms group together phyla based on broad similarities in cell structure, mode of nutrition, and other fundamental features. This rank represents a substantial leap in inclusivity, grouping together organisms with widely varying characteristics, yet sharing some core features of life.
-
Domain: This is the most inclusive taxonomic rank, currently recognizing three domains: Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya. Domains represent the fundamental divisions of life based on cellular organization and genetic makeup. Characteristics at this level are incredibly broad, encompassing the most fundamental differences in cellular structure and evolutionary history.
The Case for Domains as the Broadest Taxon
At first glance, the domain seems the most obvious answer. Domains represent the three fundamental lineages of life—Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya—differing profoundly in their cellular structures, genetic makeup, and evolutionary history. Bacteria and Archaea are both prokaryotes (lacking a nucleus), while Eukarya are eukaryotes (possessing a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles). This single characteristic alone underscores the vast differences encompassed within the domains.
The characteristics included within a domain are incredibly diverse. Consider the vast array of organisms within the Eukarya domain: plants, animals, fungi, and protists. These groups exhibit an immense range of morphologies, physiologies, and ecological roles. The same holds true for the prokaryotic domains, encompassing diverse metabolic strategies, habitats, and evolutionary adaptations.
The Nuances of "Broadest Characteristics"
However, declaring domains as definitively possessing the "broadest" characteristics requires careful consideration. The term "broadest" can be interpreted in several ways:
-
Phylogenetic breadth: Domains undeniably possess the greatest phylogenetic breadth, representing the deepest branches of the tree of life.
-
Morphological breadth: While domains encompass a wide range of morphologies, the morphological diversity within a single kingdom (like Animalia) might seem equally, if not more, striking to the casual observer.
-
Functional breadth: The metabolic and ecological diversity within domains is enormous, but specific kingdoms or phyla might display equally impressive functional diversity.
-
Genetic breadth: Domains represent the most fundamental genetic differences, but the genetic variation within domains is also vast.
Challenges in Defining "Broadest"
The difficulty in definitively answering the question arises from the inherently hierarchical nature of taxonomy. Each rank builds upon the previous one, with each successive level encompassing a broader range of characteristics. There's no single, universally agreed-upon definition of what constitutes "broadest" in this context. It depends heavily on the criteria used for comparison.
Exploring Alternative Perspectives
The choice of "broadest" can depend on the lens through which we view life's diversity. For example:
-
Ecological perspective: An ecological approach might emphasize the incredible diversity of ecosystems and ecological roles encompassed within the domains, highlighting the breadth of adaptation and functionality.
-
Metabolic perspective: A focus on metabolism could emphasize the diverse metabolic strategies found across all domains, from photosynthesis to chemosynthesis to aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
-
Genomic perspective: A genomic perspective would emphasize the fundamental genetic differences between domains, particularly in the structure and function of ribosomes, cell walls, and other cellular components.
Conclusion: A Multifaceted Answer
Ultimately, there's no single "correct" answer to the question of which taxon includes the broadest characteristics. The domains represent the deepest branches of the tree of life and encompass the most fundamental differences in cellular organization and evolutionary history. However, other taxonomic ranks, like kingdoms and phyla, exhibit remarkable diversity in morphology, function, and ecology. The "broadest" taxon depends on the specific criteria used for comparison and the perspective adopted. The true beauty of the taxonomic system lies in its ability to organize and understand the staggering biodiversity of life on Earth, highlighting the interconnectedness and vastness of all living things, regardless of the taxonomic level at which we choose to categorize them. The continuous refinement of our understanding of evolutionary relationships through genomics and other advanced techniques continues to shape and reshape our understanding of the tree of life, and consequently, our understanding of which taxon might truly claim the title of "broadest." Further research and new discoveries in various fields of biology will continue to inform our understanding and refine these classifications, potentially leading to a re-evaluation of the existing taxonomic hierarchy and our understanding of which taxon includes the broadest characteristics.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Kilos Are 20 Pounds
Mar 19, 2025
-
11 Out Of 30 As A Percentage
Mar 19, 2025
-
Cuanto Es 92 Grados Fahrenheit En Centigrados
Mar 19, 2025
-
How To Get Magnitude Of Force
Mar 19, 2025
-
How Can You Separate Sugar From Water
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Taxon Includes The Broadest Characteristics . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
