A Quadrilateral With 4 Congruent Sides
Kalali
Mar 26, 2025 · 6 min read
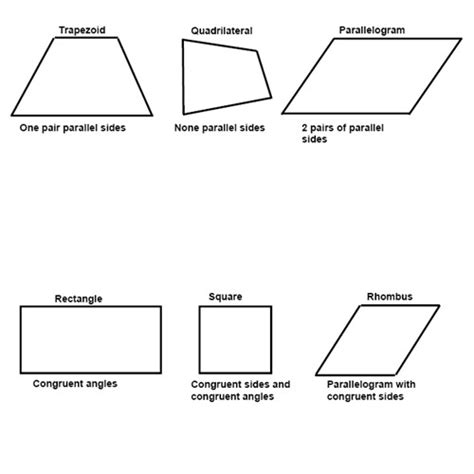
Table of Contents
A Quadrilateral with 4 Congruent Sides: Exploring the Rhombus
A quadrilateral, by definition, is a polygon with four sides. Within this broad category lies a fascinating subset of shapes where all four sides are of equal length – these are known as equilateral quadrilaterals. While this simple definition might seem restrictive, it actually encompasses a surprisingly rich family of shapes, the most prominent member of which is the rhombus. This article delves deep into the properties, characteristics, and applications of this intriguing geometric figure.
Understanding the Rhombus: More Than Just Equal Sides
A rhombus, also known as a diamond (especially in informal contexts), is a quadrilateral characterized by its four congruent sides. This defining feature, however, is not its only remarkable property. Its unique geometry gives rise to a variety of other fascinating characteristics, making it a cornerstone of geometry and a frequent subject in mathematical explorations.
Key Properties of a Rhombus:
-
Four Congruent Sides: This is the fundamental defining property. All four sides possess equal length. This property is what immediately distinguishes a rhombus from other quadrilaterals.
-
Opposite Sides are Parallel: This property stems directly from the equal side lengths. The parallelism of opposite sides elevates the rhombus to the status of a parallelogram. This means it shares many characteristics with parallelograms, which we will explore further.
-
Opposite Angles are Congruent: Just like in parallelograms, the opposite angles of a rhombus are equal in measure. This property contributes to the overall symmetry of the shape.
-
Consecutive Angles are Supplementary: Any two angles that share a common side add up to 180 degrees. This property is a direct consequence of the opposite sides being parallel.
-
Diagonals Bisect Each Other: The diagonals of a rhombus intersect at a point that divides each diagonal into two equal segments. This intersection point is also the center of symmetry for the rhombus.
-
Diagonals are Perpendicular Bisectors: Not only do the diagonals bisect each other, but they also intersect at a right angle (90 degrees). This property is crucial in many applications and calculations involving rhombuses.
-
Diagonals Bisect the Angles: Each diagonal bisects (divides into two equal angles) a pair of opposite angles. This property further underscores the symmetrical nature of the rhombus.
The Rhombus in Relation to Other Quadrilaterals
The rhombus holds a unique position within the broader family of quadrilaterals. Understanding its relationships to other shapes helps to clarify its distinctive features and properties.
Rhombus as a Special Case of a Parallelogram:
All rhombuses are parallelograms, but not all parallelograms are rhombuses. A parallelogram is a quadrilateral with opposite sides parallel. The rhombus adds the constraint of all sides being equal in length. Therefore, a rhombus inherits all the properties of a parallelogram, plus the additional properties stemming from its congruent sides.
Rhombus as a Special Case of a Kite:
A kite is a quadrilateral with two pairs of adjacent sides that are congruent. A rhombus can be considered a special case of a kite where both pairs of adjacent sides are congruent. However, unlike a general kite, a rhombus has opposite sides parallel and opposite angles equal.
Rhombus Compared to a Square:
A square is a special type of rhombus (and also a special type of rectangle). A square satisfies all the conditions of a rhombus but adds the further constraint that all angles are right angles (90 degrees). Thus, every square is a rhombus, but not every rhombus is a square.
Calculating Area and Perimeter of a Rhombus
Knowing how to calculate the area and perimeter of a rhombus is crucial for various applications. The formulas are relatively straightforward but require understanding the rhombus's properties.
Calculating the Perimeter:
The perimeter of a rhombus is simply the sum of the lengths of its four sides. Since all four sides are congruent, the formula simplifies to:
Perimeter = 4 * side length
Where 'side length' refers to the length of any one side of the rhombus.
Calculating the Area:
The area calculation is slightly more complex and offers several approaches:
- Using the diagonals: The area of a rhombus can be calculated using the lengths of its diagonals. The formula is:
Area = (1/2) * d1 * d2
Where 'd1' and 'd2' represent the lengths of the two diagonals. This formula leverages the fact that the diagonals are perpendicular bisectors.
- Using trigonometry: If you know the length of one side and the measure of one angle, trigonometry can be used to calculate the area. The formula is:
Area = side² * sin(θ)
Where 'side' is the length of any side and 'θ' is the measure of any angle of the rhombus.
- Using the base and height: Like any other parallelogram, the area of a rhombus can also be calculated using the base and height:
Area = base * height
Where 'base' is the length of any side and 'height' is the perpendicular distance between that side and the opposite side.
Real-World Applications of Rhombuses
The rhombus's geometric properties make it relevant in a surprising number of real-world applications:
-
Engineering and Architecture: The strength and stability of the rhombus shape are utilized in structural designs, such as bridges and roofs. Its rigid structure makes it efficient for load distribution.
-
Art and Design: The visual appeal of rhombuses has made them a popular element in art, design, and architecture throughout history. They appear in various forms of art, including paintings, mosaics, and sculptures. Tessellations, repeating patterns formed by geometric shapes, often feature rhombuses.
-
Crystallography: The rhombus shape appears in the crystalline structures of many minerals. Understanding the geometry of these structures is vital in material science.
-
Kites: Traditional kites often utilize rhombus-like shapes for their aerodynamics and stability in flight.
-
Games and Puzzles: Rhombuses appear in various games and puzzles, often playing a crucial role in their mechanisms or visual design.
Advanced Concepts and Theorems Related to Rhombuses
Beyond the basic properties, several advanced concepts and theorems relate to rhombuses, enhancing our understanding of their geometric richness:
-
Brahmagupta's Formula: This formula allows for the calculation of the area of a cyclic quadrilateral (a quadrilateral that can be inscribed in a circle). Although a rhombus is not always cyclic, the formula can still be applied under specific conditions.
-
Vectors and Rhombuses: Vector geometry provides another powerful tool for analyzing rhombuses. Vector operations can be used to prove properties and solve problems related to rhombuses in a concise and elegant manner.
-
Rhombuses in Higher Dimensions: The concept of a rhombus can be extended to higher dimensions. In three dimensions, the analogue of a rhombus is a rhombohedron, a three-dimensional shape with six rhombus faces.
Conclusion: The Enduring Significance of the Rhombus
The rhombus, despite its seemingly simple definition, is a geometric shape brimming with rich properties and applications. From its basic geometric characteristics to its advanced mathematical connections and real-world uses, the rhombus remains a fascinating subject of study. Its symmetrical structure and inherent stability make it a valuable component in various fields, highlighting the enduring significance of this fundamental geometric form. Understanding the rhombus is not just an exercise in geometry; it's a gateway to appreciating the intricate beauty and practical applications of mathematical concepts. Further exploration of its properties and relationships with other geometric shapes will undoubtedly reveal even more of its compelling mathematical richness.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Sides Does Rhombus Have
Mar 29, 2025
-
Number Of Valence Electrons For Potassium
Mar 29, 2025
-
How Much Is 7 8 In Inches
Mar 29, 2025
-
4 Is What Percent Of 14
Mar 29, 2025
-
How Many Seconds Is 15 Minutes
Mar 29, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about A Quadrilateral With 4 Congruent Sides . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
