Distance Between Earth And Sun In Light Years
Kalali
Mar 28, 2025 · 4 min read
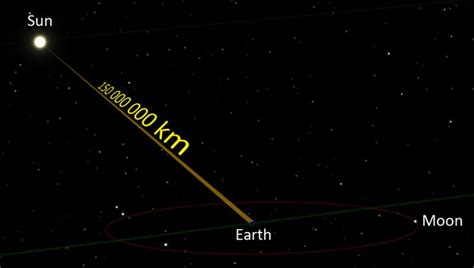
Table of Contents
The Distance Between the Earth and the Sun: Not Quite Light-Years, But a Vital Astronomical Unit
The question, "What's the distance between the Earth and the Sun in light-years?" often arises in discussions about space and astronomy. While the answer isn't a whole number of light-years, understanding the actual distance and the concept of light-years is crucial for grasping the vastness of our solar system and the universe beyond. This article delves deep into the subject, explaining the true distance, the concept of light-years, and why this unit of measurement isn't commonly used for Earth-Sun distance.
Understanding Astronomical Units (AU)
Before we even touch upon light-years, it's essential to understand the standard unit used to measure distances within our solar system: the Astronomical Unit (AU). One AU is defined as the average distance between the Earth and the Sun. This isn't a constant number because the Earth's orbit is slightly elliptical, meaning the distance varies throughout the year. However, the average distance is approximately 149.6 million kilometers (93 million miles).
This is a far more practical unit for measuring distances within our solar system than light-years. Light-years are designed for measuring interstellar and intergalactic distances – incredibly vast spans far exceeding the scale of our own solar system. Using light-years to describe the Earth-Sun distance would be akin to measuring the length of a pencil with a yardstick designed to measure the distance between continents.
Why Light-Years Aren't Used for Earth-Sun Distance
A light-year is the distance light travels in one year. Light travels at an astonishing speed of approximately 299,792 kilometers per second (186,282 miles per second). Therefore, a light-year is a colossal distance, roughly equivalent to 9.461 × 10<sup>12</sup> kilometers (5.878 × 10<sup>12</sup> miles).
The distance between the Earth and the Sun, approximately 149.6 million kilometers, is incredibly small compared to a light-year. Converting this distance to light-years yields a minuscule fraction – approximately 0.0000158 light-years. Using such a small, fractional value would be cumbersome and impractical for everyday astronomical calculations within our solar system.
Calculating the Earth-Sun Distance in Light-Years (for demonstration purposes)
While impractical, let's perform the calculation to illustrate the concept:
- Earth-Sun distance in kilometers: 149,600,000 km
- Speed of light in kilometers per second: 299,792 km/s
- Seconds in a year: 31,536,000 seconds (approximately)
To find the distance in light-years, we would need to perform the following calculation:
(149,600,000 km) / (299,792 km/s * 31,536,000 s/year) ≈ 0.0000158 light-years
As you can see, the result is a very small decimal fraction, highlighting the inappropriateness of using light-years for this specific measurement.
The Importance of Understanding Scale in Astronomy
The difference in scale between the Earth-Sun distance and interstellar distances underscores the vastness of the universe. While the Earth orbits the Sun at a relatively short distance in astronomical terms, other stars are light-years, and even parsecs (another unit of astronomical distance), away from us. Understanding the appropriate units of measurement is key to grasping the scale of these astronomical distances.
Beyond the Earth-Sun Distance: Exploring the Vastness of Space
Moving beyond our immediate solar neighborhood, we encounter distances that truly necessitate the use of light-years. For instance:
- Proxima Centauri, the nearest star: Approximately 4.24 light-years away.
- The center of the Milky Way Galaxy: Approximately 26,000 light-years away.
- The Andromeda Galaxy: Approximately 2.537 million light-years away.
These distances highlight the sheer immensity of space and the incredible distances light must travel to reach us from these celestial objects. The vastness emphasizes the importance of using units like light-years to convey these distances effectively.
Different Units for Different Distances
Astronomers utilize various units of measurement depending on the distance they are trying to represent. This is crucial for clarity and accuracy. The choice of units reflects the scale of the distances involved.
- Kilometers and Miles: Suitable for relatively short distances, such as those within our solar system (though AU is preferred for solar system distances).
- Astronomical Units (AU): The standard unit for distances within our solar system.
- Light-Years: For distances between stars and galaxies.
- Parsecs: Another unit used for interstellar and intergalactic distances, often preferred by professional astronomers due to its relationship to parallax measurements.
Conclusion: Context is Key in Astronomical Measurements
In conclusion, the distance between the Earth and the Sun is not typically measured in light-years. While it can be converted, the resulting minuscule fraction makes it impractical. The Astronomical Unit (AU) is the preferred and far more practical unit for this specific distance. Understanding the scale of astronomical distances and selecting the appropriate unit of measurement – whether it's AU, light-years, or parsecs – is crucial for accurate and meaningful communication about the vastness and wonders of the cosmos. The choice of units reflects the scale of the distances involved, demonstrating the importance of contextual understanding in astronomy. Remember, the vastness of space demands a diverse toolkit of units to effectively communicate its grand scale.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Cuantos Grados Son 49 Fahrenheit En Centigrados
Mar 31, 2025
-
Why Are Seasons Reversed In The Southern Hemisphere
Mar 31, 2025
-
What Types Of Intermolecular Forces Are Found In Ch2cl2
Mar 31, 2025
-
Cuanto Es 8 Onzas En Litros
Mar 31, 2025
-
What Is 160 Degrees Fahrenheit In Celsius
Mar 31, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Distance Between Earth And Sun In Light Years . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
