Why Are Seasons Reversed In The Southern Hemisphere'
Kalali
Mar 31, 2025 · 6 min read
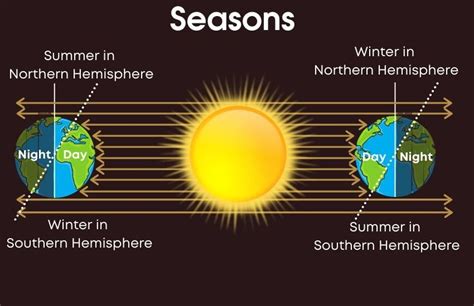
Table of Contents
Why Are the Seasons Reversed in the Southern Hemisphere?
The Earth's tilt, a seemingly simple phenomenon, is the key to understanding why the seasons are reversed in the Southern Hemisphere. While many people grasp the general concept of seasons being linked to the Earth's orbit around the sun, the specifics of how this tilt causes opposite seasons in the two hemispheres often remain a mystery. This article delves deep into the mechanics of Earth's tilt and its profound impact on the distribution of sunlight, explaining why summer in the Northern Hemisphere is winter in the Southern Hemisphere, and vice versa.
Understanding the Earth's Axial Tilt
The Earth isn't perfectly upright as it spins on its axis; instead, it's tilted at an angle of approximately 23.5 degrees. This axial tilt is the fundamental reason for the occurrence of seasons. It's not the Earth's distance from the sun that determines the seasons (although the Earth's elliptical orbit does play a minor role); it's the angle at which sunlight strikes different parts of the planet throughout the year.
The Sun's Path and the Impact of Tilt
Imagine a light shining directly down on a flat surface. The light is concentrated, creating a warm spot. Now, tilt the surface. The same light source now hits the tilted surface at different angles. Some areas receive more direct, concentrated sunlight, while others receive less direct, spread-out sunlight. This is precisely what happens on Earth due to its tilt.
The Mechanics of Seasonal Reversal
As the Earth orbits the sun, different hemispheres are tilted towards or away from the sun. When the Southern Hemisphere is tilted towards the sun, it receives more direct sunlight, leading to longer days and warmer temperatures – summer. Simultaneously, the Northern Hemisphere is tilted away from the sun, resulting in shorter days, less direct sunlight, and cooler temperatures – winter.
Solstices and Equinoxes: Defining Points in the Seasonal Cycle
The solstices and equinoxes mark pivotal points in the seasonal cycle and offer a clear illustration of the seasonal reversal:
-
Summer Solstice (December 21/22 in the Southern Hemisphere): The Southern Hemisphere is maximally tilted towards the sun, experiencing the longest day of the year and the start of summer. The Northern Hemisphere experiences the shortest day and the start of winter.
-
Winter Solstice (June 20/21 in the Southern Hemisphere): The Southern Hemisphere is maximally tilted away from the sun, experiencing the shortest day of the year and the start of winter. The Northern Hemisphere experiences the longest day and the start of summer.
-
Equinoxes (March 20/21 and September 22/23): During the equinoxes, the Earth's axis is neither tilted towards nor away from the sun. Both hemispheres receive roughly equal amounts of sunlight, resulting in nearly equal day and night lengths across the globe. This signifies the transition between seasons.
Beyond Temperature: The Influence on Other Factors
The reversed seasons in the Southern Hemisphere aren't just about temperature differences. The altered angle of sunlight affects various aspects of the environment:
Day Length Variations: More Than Just Temperature
The variation in day length plays a significant role in the seasonal experience. The longer days of summer in the Southern Hemisphere lead to increased sunlight exposure, fueling plant growth and affecting animal behavior. The shorter days of winter reduce sunlight, causing plants to become dormant and impacting animal migration patterns.
Precipitation Patterns: A Complex Interaction
The tilt of the Earth significantly impacts weather patterns and precipitation. The angle of the sun influences air pressure systems, wind currents, and the formation of rain clouds. These factors contribute to distinct rainfall patterns in different seasons across both hemispheres, with a clear reversal between the Northern and Southern Hemisphere experiences. For instance, regions that experience monsoon seasons during the summer in one hemisphere will experience dry seasons during the same period in the other.
Ocean Currents and Their Impact: Global Influence
Ocean currents play a crucial role in distributing heat around the globe. The tilt of the Earth influences the direction and strength of these currents, impacting the climate of coastal regions. The temperature of ocean currents varies seasonally, contributing to the overall seasonal differences experienced in coastal areas of both hemispheres.
The Southern Hemisphere's Unique Characteristics
The Southern Hemisphere's geography plays a significant role in its unique climate patterns. The dominance of oceans in the Southern Hemisphere means that temperature fluctuations are generally less extreme compared to the Northern Hemisphere, which has a larger landmass. The prevailing westerly winds, which circle Antarctica, significantly impact weather patterns across the Southern Hemisphere, creating distinct climates in different regions.
The Role of the Antarctic Circumpolar Current
The Antarctic Circumpolar Current, the strongest ocean current in the world, is a major factor in regulating the Southern Hemisphere's climate. This current transports vast amounts of heat and water, influencing the temperatures and precipitation patterns of surrounding regions. The current's seasonal variations add another layer of complexity to the already intricate interplay of factors influencing the Southern Hemisphere's seasons.
Human Impact and Climate Change
Human activities, primarily through the emission of greenhouse gases, are altering the Earth's climate. While the fundamental mechanics of seasonal reversal remain unchanged, climate change is intensifying existing patterns and leading to more unpredictable weather events. The impact of climate change is particularly visible in the Southern Hemisphere, especially in the Antarctic region, where melting ice sheets and rising sea levels are significant concerns.
The Antarctic Ice Sheet and Global Sea Levels
The Antarctic ice sheet, the largest body of ice on Earth, is highly susceptible to climate change. Melting of this ice sheet contributes significantly to rising global sea levels, impacting coastal communities worldwide. The implications for the Southern Hemisphere, particularly the coastal regions, are substantial, with the potential for increased coastal erosion, flooding, and displacement of populations.
Understanding the Reversal: A Crucial Perspective
Understanding the reversal of seasons in the Southern Hemisphere is not merely an academic exercise. It provides a crucial perspective on the interconnectedness of global climate systems. Knowing the underlying mechanisms of seasonal changes helps us to better comprehend the impacts of climate change and to develop strategies for mitigation and adaptation.
The Need for Global Collaboration
Addressing the challenges posed by climate change requires international collaboration. Understanding the subtle nuances of climate dynamics in different regions of the globe, such as the seasonal reversal in the Southern Hemisphere, is paramount to developing effective strategies for environmental protection and sustainable development.
Conclusion: A Balanced Perspective
The reversed seasons in the Southern Hemisphere are a direct consequence of the Earth's axial tilt. This tilt creates a beautifully complex interplay of sunlight, temperature, precipitation, and ocean currents, resulting in distinct seasonal experiences across different regions of the globe. By understanding these intricate mechanisms, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the dynamics of our planet and the urgency of addressing the challenges of climate change. The information in this article serves as a foundation for broader understanding of global climate and the importance of considering the impact of this phenomenon on a global scale. Continued research and collaboration will be crucial in ensuring the well-being of our planet and its inhabitants.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
8 6 As A Mixed Number
Apr 02, 2025
-
Cuanto Es 71 Grados Fahrenheit En Centigrados
Apr 02, 2025
-
How Many Grams Is 4 Kilograms
Apr 02, 2025
-
12 Is What Percent Of 30
Apr 02, 2025
-
10 Is 30 Percent Of What Number
Apr 02, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Why Are Seasons Reversed In The Southern Hemisphere' . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
