Equation For Decomposition Of Hydrogen Peroxide
Kalali
Mar 18, 2025 · 6 min read
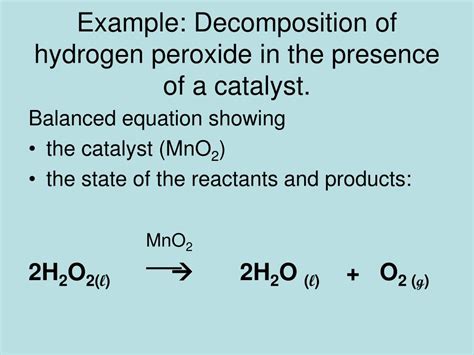
Table of Contents
The Equation for the Decomposition of Hydrogen Peroxide: A Deep Dive
Hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂) is a common chemical compound with a wide range of applications, from antiseptic solutions to industrial bleaching agents. Understanding its decomposition is crucial in various fields, from chemical engineering to biochemistry. This comprehensive article will delve into the equation for the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide, exploring the different factors that influence the reaction rate and the various methods used to catalyze this process.
The Basic Decomposition Equation
The simplest representation of hydrogen peroxide decomposition is a disproportionation reaction, where the same molecule is both oxidized and reduced:
2H₂O₂ → 2H₂O + O₂
This equation shows that two molecules of hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂) decompose into two molecules of water (H₂O) and one molecule of oxygen gas (O₂). This is a redox reaction; hydrogen peroxide is both the oxidizing and reducing agent. In this process, the oxidation state of oxygen changes from -1 in hydrogen peroxide to -2 in water and 0 in oxygen gas.
Understanding the Redox Nature
The decomposition is a redox reaction because oxygen in H₂O₂ undergoes both oxidation and reduction:
- Oxidation: Some oxygen atoms in H₂O₂ lose electrons and are oxidized to O₂ (oxidation state changes from -1 to 0).
- Reduction: Other oxygen atoms gain electrons and are reduced to water (oxidation state changes from -1 to -2).
This self-oxidation-reduction process is characteristic of disproportionation reactions, making the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide a fascinating example in chemistry.
Factors Affecting the Decomposition Rate
The rate at which hydrogen peroxide decomposes is influenced by several factors:
1. Temperature:
Increasing the temperature significantly accelerates the decomposition rate. The reaction is endothermic, meaning it absorbs heat. Higher temperatures provide the necessary activation energy for the reaction to proceed faster. This is explained by the Arrhenius equation, which relates the rate constant of a reaction to temperature and activation energy.
2. pH:
The pH of the solution plays a role in the decomposition rate. Alkaline conditions generally favor faster decomposition compared to acidic conditions. This is because the hydroxide ions (OH⁻) can act as catalysts, facilitating the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide.
3. Concentration:
The rate of decomposition is directly proportional to the concentration of hydrogen peroxide. A higher concentration of H₂O₂ leads to a faster reaction rate due to increased collision frequency between the reactant molecules.
4. Catalysts:
The presence of certain catalysts dramatically increases the rate of decomposition. This is because catalysts provide an alternative reaction pathway with a lower activation energy, making it easier for the reaction to proceed. Several substances act as effective catalysts for hydrogen peroxide decomposition, including:
- Transition metal ions: Ions of transition metals such as manganese (Mn²⁺), iron (Fe²⁺, Fe³⁺), and copper (Cu²⁺) are highly effective catalysts. These ions can participate in redox cycles, facilitating the decomposition process.
- Enzymes: Certain enzymes, like catalase, are biological catalysts that specifically break down hydrogen peroxide. Catalase is found in many living organisms and protects them from the harmful effects of hydrogen peroxide. The activity of catalase is highly dependent on factors such as temperature and pH.
5. Light and Radiation:
Exposure to light, especially ultraviolet (UV) light, can also catalyze the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide. The photons of light provide the necessary energy to initiate the reaction. Similarly, exposure to ionizing radiation can accelerate the decomposition.
Catalyzed Decomposition: A Deeper Look
The catalyzed decomposition of hydrogen peroxide involves different mechanisms depending on the catalyst used. Let's explore the roles of some common catalysts:
Catalase: The Biological Catalyst
Catalase is an enzyme that efficiently decomposes hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen. The mechanism involves a complex series of steps within the enzyme's active site. The enzyme's heme group, containing iron, plays a crucial role in the catalytic process. The high efficiency of catalase allows living organisms to rapidly neutralize the toxic effects of hydrogen peroxide.
Transition Metal Ions: A Chemical Perspective
Transition metal ions, like Mn²⁺, Fe²⁺, and Cu²⁺, catalyze the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide through redox reactions. These ions can exist in multiple oxidation states, facilitating electron transfer between H₂O₂ molecules. For example, Mn²⁺ can be oxidized to Mn³⁺, then reduced back to Mn²⁺, repeating the cycle and speeding up the overall reaction.
Applications of Hydrogen Peroxide Decomposition
The decomposition of hydrogen peroxide has many practical applications:
- Water purification: The oxygen generated during decomposition can be used to disinfect water, removing harmful bacteria and other microorganisms.
- Rocket propulsion: The rapid decomposition of concentrated hydrogen peroxide, often catalyzed, generates large amounts of hot water vapor and oxygen gas, providing thrust for rockets.
- Bleaching agents: The oxidizing power of hydrogen peroxide, particularly when catalyzed, is used in various bleaching processes for textiles, paper, and hair.
- Wound disinfection: Diluted hydrogen peroxide solutions are commonly used as antiseptics to clean minor wounds, utilizing the oxygen released during decomposition to kill bacteria.
The Importance of Studying Decomposition Kinetics
Studying the kinetics of hydrogen peroxide decomposition is crucial for understanding and optimizing the various applications mentioned above. Factors such as temperature, pH, concentration, and the presence of catalysts significantly affect the reaction rate. By carefully controlling these parameters, it is possible to tailor the decomposition process to specific requirements. Kinetics studies involve determining the rate law, which expresses the relationship between the reaction rate and the concentrations of the reactants.
Advanced Concepts and Further Research
The decomposition of hydrogen peroxide is a complex process, and ongoing research continues to unravel its intricacies. Some advanced concepts include:
- Mechanism studies: Detailed investigations into the reaction mechanisms involving different catalysts are crucial for developing more efficient catalytic systems.
- Computational modeling: Computational methods are increasingly used to simulate and predict the reaction kinetics and mechanisms of hydrogen peroxide decomposition.
- Development of novel catalysts: Research is focused on designing and synthesizing novel catalysts with improved activity and selectivity for specific applications.
Conclusion
The decomposition of hydrogen peroxide, represented by the equation 2H₂O₂ → 2H₂O + O₂, is a fundamental chemical reaction with far-reaching implications. Understanding the factors that influence the decomposition rate, including temperature, pH, concentration, and the presence of catalysts, is essential for controlling and utilizing this reaction in various applications. The study of hydrogen peroxide decomposition continues to be a vibrant area of research, promising further advances in our understanding and utilization of this versatile chemical compound. The interplay of kinetics, redox chemistry, and catalysis makes this a fascinating subject, ripe for continued exploration and discovery. From biological systems utilizing catalase to industrial processes leveraging metal catalysts, the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide remains a vital area of study across numerous disciplines.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 38 Out Of 40 As A Percentage
Mar 19, 2025
-
High Frequency Wave Vs Low Frequency Wave
Mar 19, 2025
-
Temperate Deciduous Forest Oak Tree Adaptations
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Animals Can See Human Bioluminescence
Mar 19, 2025
-
Is Sour Taste A Physical Property
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Equation For Decomposition Of Hydrogen Peroxide . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
