High Frequency Wave Vs Low Frequency Wave
Kalali
Mar 19, 2025 · 6 min read
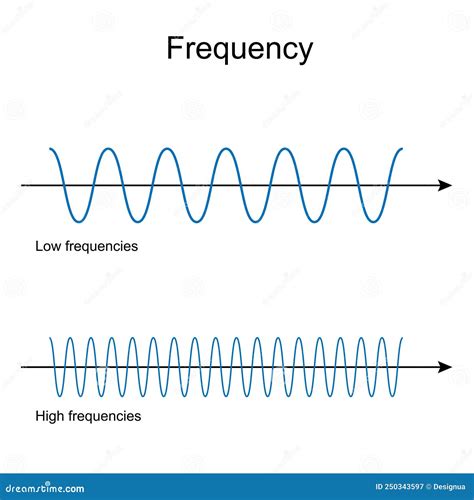
Table of Contents
High Frequency Waves vs. Low Frequency Waves: A Deep Dive into the Electromagnetic Spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum is a vast and fascinating landscape, encompassing a wide range of waves with varying frequencies and wavelengths. Understanding the differences between high-frequency and low-frequency waves is crucial in appreciating their diverse applications and impacts on our world. From the radio waves that power our communication systems to the gamma rays used in medical treatments, the spectrum's versatility stems directly from the fundamental properties of these waves. This comprehensive guide delves into the key distinctions between high and low-frequency waves, exploring their characteristics, applications, and potential effects.
Defining Frequency and Wavelength
Before we delve into the specifics of high and low-frequency waves, let's establish a clear understanding of the core concepts: frequency and wavelength. These two properties are inversely proportional; as one increases, the other decreases.
-
Frequency: This refers to the number of wave cycles that pass a fixed point in one second. It's measured in Hertz (Hz), where 1 Hz equals one cycle per second. A higher frequency means more cycles per second, signifying a faster oscillation.
-
Wavelength: This is the distance between two consecutive crests (or troughs) of a wave. It's measured in meters (m) or other units of length. A shorter wavelength means the wave is more compact, while a longer wavelength indicates a more stretched-out wave.
The relationship between frequency (f), wavelength (λ), and the speed of light (c) is given by the equation: c = fλ. Since the speed of light in a vacuum is constant, a higher frequency implies a shorter wavelength, and vice-versa.
High-Frequency Waves: Characteristics and Applications
High-frequency waves occupy the higher end of the electromagnetic spectrum, characterized by their short wavelengths and high frequencies. This category includes ultraviolet (UV) radiation, X-rays, and gamma rays.
Ultraviolet (UV) Radiation:
UV radiation possesses frequencies higher than visible light. It's further categorized into UVA, UVB, and UVC, with UVA having the lowest frequency and UVC the highest.
-
Characteristics: UV radiation is invisible to the human eye and carries more energy than visible light.
-
Applications: UVA is used in tanning beds (although the health risks are significant), while UVB plays a crucial role in vitamin D synthesis in our skin. UVC, due to its high energy, is used for sterilization and disinfection, killing bacteria and viruses.
-
Effects: While essential in moderation, excessive exposure to UV radiation can lead to sunburn, premature aging, and an increased risk of skin cancer. It can also damage the eyes.
X-rays:
X-rays have even higher frequencies and shorter wavelengths than UV radiation. Their penetrating power allows them to pass through soft tissues but are absorbed by denser materials like bones.
-
Characteristics: Highly energetic and penetrating.
-
Applications: Medical imaging (radiography), airport security scanners, and industrial non-destructive testing.
-
Effects: Overexposure to X-rays can cause damage to cells and DNA, increasing the risk of cancer. Therefore, appropriate safety measures are essential during X-ray procedures.
Gamma Rays:
Gamma rays represent the highest-frequency and shortest-wavelength portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. They possess immense energy and penetrating power.
-
Characteristics: Extremely high energy and penetrating.
-
Applications: Cancer radiotherapy, sterilization of medical equipment, and industrial gauging.
-
Effects: Gamma rays are highly ionizing and can cause significant damage to living tissues. Exposure should be strictly controlled and minimized.
Low-Frequency Waves: Characteristics and Applications
Low-frequency waves occupy the lower end of the electromagnetic spectrum, characterized by their long wavelengths and low frequencies. This category includes radio waves, microwaves, and infrared (IR) radiation.
Radio Waves:
Radio waves have the longest wavelengths and lowest frequencies within the electromagnetic spectrum. They are widely used for communication purposes.
-
Characteristics: Low energy and easily transmitted over long distances.
-
Applications: Radio broadcasting, television broadcasting, cellular communication, Wi-Fi, and satellite communication.
-
Effects: Exposure to radio waves at typical levels poses minimal health risks. However, extremely high levels can potentially cause heating effects.
Microwaves:
Microwaves have shorter wavelengths and higher frequencies than radio waves. Their ability to excite water molecules makes them ideal for heating food.
-
Characteristics: Higher energy than radio waves, capable of heating materials containing water.
-
Applications: Microwave ovens, radar systems, satellite communication, and medical treatments.
-
Effects: Excessive exposure to microwaves can cause heating of body tissues, leading to burns. Proper shielding is crucial in microwave-based applications.
Infrared (IR) Radiation:
Infrared radiation falls between microwaves and visible light in the electromagnetic spectrum. It's often associated with heat.
-
Characteristics: Emits heat; invisible to the human eye.
-
Applications: Thermal imaging, remote controls, infrared heaters, and optical fiber communication.
-
Effects: While generally safe, high levels of IR radiation can cause burns to the skin and eyes.
Comparing High and Low Frequency Waves: A Summary Table
| Feature | High-Frequency Waves (UV, X-rays, Gamma Rays) | Low-Frequency Waves (Radio, Microwaves, IR) |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency | High | Low |
| Wavelength | Short | Long |
| Energy | High | Low |
| Penetration | High (especially X-rays and Gamma rays) | Low (except for some applications of microwaves) |
| Ionizing Power | High (UV, X-rays, and Gamma rays are ionizing) | Low (non-ionizing) |
| Biological Effects | Can cause significant damage to living tissues | Generally less harmful, but high levels can cause heating effects |
| Applications | Medical imaging, radiotherapy, sterilization | Communication, heating, thermal imaging |
The Importance of Understanding the Electromagnetic Spectrum
Understanding the distinctions between high and low-frequency waves is vital for numerous reasons. It allows us to:
-
Develop safe and effective technologies: Knowing the potential hazards of high-frequency waves enables us to develop safety protocols for their use in medical and industrial applications.
-
Advance communication technologies: Harnessing the properties of radio waves and microwaves has revolutionized communication, enabling global connectivity.
-
Improve medical treatments: High-frequency waves are crucial in medical imaging and cancer therapy, improving diagnostic and treatment capabilities.
-
Protect our environment: Understanding the impact of electromagnetic radiation on the environment is crucial for developing sustainable technologies and minimizing potential harm.
-
Enhance our understanding of the universe: Astronomers rely on observing different wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation to study celestial objects and understand the universe's vastness.
The electromagnetic spectrum is a powerful tool that has transformed our world. By understanding the nuances of high-frequency and low-frequency waves, we can better appreciate their impact and harness their potential responsibly and effectively. Continuous research and innovation in this field continue to expand our capabilities and understanding, paving the way for future technological advancements. The exploration of the electromagnetic spectrum remains a dynamic and ever-evolving field of study, promising groundbreaking discoveries and applications in years to come.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How To Calculate The Ph At The Equivalence Point
Mar 19, 2025
-
Why Cant Freshwater Fish Survive In Saltwater
Mar 19, 2025
-
29 Inches Is How Many Centimeters
Mar 19, 2025
-
126 Inches Is How Many Feet
Mar 19, 2025
-
Cuanto Es El 3 Porciento De 1000
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about High Frequency Wave Vs Low Frequency Wave . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
