How Did The Internet Transform Scientific Research
Kalali
Mar 19, 2025 · 7 min read
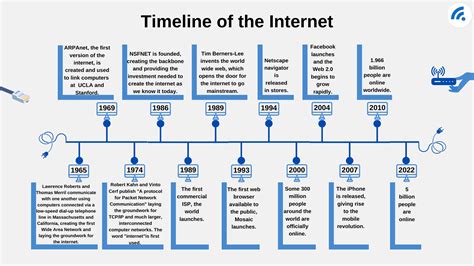
Table of Contents
How the Internet Transformed Scientific Research
The internet's impact on scientific research is nothing short of revolutionary. From fundamentally altering how scientists communicate and collaborate to democratizing access to information and accelerating the pace of discovery, its influence is woven into the very fabric of modern science. This article explores the profound ways the internet has reshaped scientific research, examining both its benefits and its challenges.
The Rise of Digital Communication and Collaboration
Before the widespread adoption of the internet, scientific communication relied heavily on snail mail, fax machines, and infrequent conferences. The dissemination of research findings was slow, often delayed by months or even years. Collaboration, too, was geographically restricted, limiting the potential for diverse perspectives and expertise to converge on a single project.
Email and Instant Messaging: The Dawn of Real-time Communication
The advent of email and instant messaging revolutionized scientific communication. Scientists could now exchange ideas, data, and drafts of papers instantaneously, irrespective of geographical location. This fostered a more dynamic and responsive research environment, enabling rapid feedback and iterative improvements. The ability to quickly clarify doubts and seek immediate assistance from collaborators significantly accelerated the research process.
Online Forums and Discussion Groups: Fostering Community and Knowledge Sharing
Online forums and discussion groups dedicated to specific scientific disciplines emerged as vibrant hubs for knowledge sharing and collaboration. These platforms allowed researchers to engage in discussions, pose questions, and seek expert opinions from a global community of peers. This facilitated the rapid dissemination of new findings and best practices, fostering a sense of shared purpose and accelerating the overall advancement of scientific knowledge. The speed at which information could be disseminated and debated vastly surpassed traditional methods.
Video Conferencing and Webinars: Bridging Geographical Barriers
Video conferencing tools transformed the way scientists interact. The ability to conduct virtual meetings, attend conferences remotely, and deliver presentations to a global audience broke down geographical barriers. This significantly reduced travel costs and time, increasing accessibility for researchers in remote locations or with limited funding. Moreover, it allowed scientists to participate in multiple events concurrently, maximizing their engagement with the broader research community.
The Democratization of Scientific Information
The internet dramatically increased access to scientific information. The rise of digital libraries, online databases, and open-access journals democratized access to research papers, datasets, and other resources that were previously confined to the walls of university libraries or behind expensive paywalls.
Digital Libraries and Online Databases: Expanding Access to Knowledge
Digital libraries like JSTOR and PubMed offer comprehensive archives of scholarly literature, accessible to anyone with an internet connection. Online databases like Web of Science and Scopus provide tools for searching and analyzing scientific publications, enabling researchers to easily identify relevant literature and track research trends. This readily available information has significantly expanded the scope of research possibilities for scientists worldwide.
Open Access Publishing: Breaking Down Paywalls and Promoting Transparency
The open-access movement has significantly changed the landscape of scientific publishing. By making research papers freely available online, open-access journals remove financial barriers to accessing scientific knowledge, facilitating broader dissemination and impact. This fosters transparency and accountability, encouraging greater scrutiny and collaboration within the research community. The increased visibility has also accelerated the pace of discovery by allowing researchers to build upon the work of others more rapidly.
Data Sharing Platforms and Repositories: Facilitating Collaboration and Reproducibility
The internet also facilitated the development of data sharing platforms and repositories. These platforms allow researchers to share their datasets, code, and other research materials with the wider community, promoting collaboration, reproducibility, and transparency. This combats the reproducibility crisis in scientific research by enabling independent verification of results and fostering a more robust and reliable scientific record. Sharing methodologies and data also allows other researchers to build upon existing work, potentially leading to unexpected breakthroughs.
The Acceleration of Scientific Discovery
The internet has fundamentally accelerated the pace of scientific discovery. The rapid dissemination of information, enhanced collaboration, and improved access to resources have shortened the time between research breakthroughs and their widespread application.
Faster Communication and Feedback Loops: Streamlining the Research Process
Instantaneous communication enables researchers to swiftly disseminate new findings, receive feedback, and adjust their research accordingly. This dramatically reduces the time required to complete a research project, allowing for a more agile and efficient research process. The rapid exchange of ideas also allows for more rapid course correction, minimizing wasted resources and effort on unproductive avenues of research.
Enhanced Collaboration and Interdisciplinarity: Fostering Innovation
The internet has enabled scientists from diverse disciplines to collaborate on complex research problems. This interdisciplinary approach fosters innovation by bringing together diverse perspectives and expertise, leading to novel solutions and breakthroughs that might not have been possible otherwise. Breaking down the traditional silos between scientific disciplines has led to significant advancements in fields like bioinformatics, nanotechnology, and climate science.
Crowdsourcing and Citizen Science: Engaging a Broader Community
The internet has also enabled the participation of a wider community in scientific research through crowdsourcing and citizen science initiatives. These projects leverage the collective intelligence and contributions of a large number of volunteers to address complex scientific challenges. This democratizes scientific research, allowing for a wider range of perspectives and potentially accelerating the pace of discovery.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
While the internet has profoundly benefited scientific research, it also presents challenges and ethical considerations.
Information Overload and Misinformation: Navigating the Digital Landscape
The sheer volume of information available online can be overwhelming. Researchers must carefully evaluate the credibility and reliability of sources to avoid misinformation and biases. This necessitates enhanced critical thinking skills and the ability to discern trustworthy information from unreliable sources. The rise of "fake news" and pseudoscience further complicates this challenge.
Data Security and Privacy: Protecting Sensitive Information
The increasing reliance on digital data raises concerns about data security and privacy. Researchers must ensure that sensitive data is appropriately protected from unauthorized access and misuse. This requires implementing robust data security protocols and adhering to ethical guidelines for data handling and management. The potential for data breaches and misuse is a serious concern that needs constant attention and updated safeguards.
Digital Divide and Equity: Ensuring Inclusive Access
Unequal access to technology and internet connectivity creates a digital divide, potentially exacerbating existing inequalities in scientific research. Efforts must be made to ensure that all researchers, regardless of their geographical location or socioeconomic status, have equal access to the resources and opportunities afforded by the internet. This requires proactive initiatives to improve internet access and digital literacy in underserved communities.
The Future of Internet-Driven Scientific Research
The internet's influence on scientific research will only continue to grow. Emerging technologies like artificial intelligence, big data analytics, and virtual and augmented reality are poised to further transform how science is conducted, communicated, and disseminated.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: Automating and Accelerating Research
AI and machine learning are already being used to automate various aspects of scientific research, including data analysis, literature review, and hypothesis generation. These technologies have the potential to significantly accelerate the pace of discovery and enable scientists to tackle more complex research problems.
Big Data Analytics: Uncovering Hidden Patterns and Insights
The ability to collect, store, and analyze vast amounts of data is revolutionizing many scientific fields. Big data analytics allows researchers to identify hidden patterns and insights that would be impossible to uncover using traditional methods. This is particularly impactful in fields like genomics, climate science, and astronomy.
Virtual and Augmented Reality: Enhancing Collaboration and Visualization
Virtual and augmented reality technologies are creating immersive and interactive research environments. These technologies can enhance collaboration by enabling scientists to work together remotely as if they were in the same physical space. They can also improve visualization and understanding of complex scientific concepts.
In conclusion, the internet has fundamentally reshaped scientific research, accelerating the pace of discovery, democratizing access to information, and fostering unprecedented levels of collaboration. While challenges and ethical considerations remain, the continued integration of innovative technologies promises to further revolutionize how science is conducted, leading to even greater advancements in our understanding of the world around us. The internet has not only changed how science is done, but also who can participate, leading to a more inclusive and globally connected scientific community.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
In Fully Contracted Muscles The Actin Filaments Lie Side By Side
Mar 19, 2025
-
How Many Calories Are In 1g Of Uranium
Mar 19, 2025
-
10 Of 100 Is How Much
Mar 19, 2025
-
How Many Meters Is 150 Ft
Mar 19, 2025
-
105 Out Of 150 As A Percentage
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Did The Internet Transform Scientific Research . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
