How Does A Doorbell Utilize An Electromagnet
Kalali
Apr 03, 2025 · 6 min read
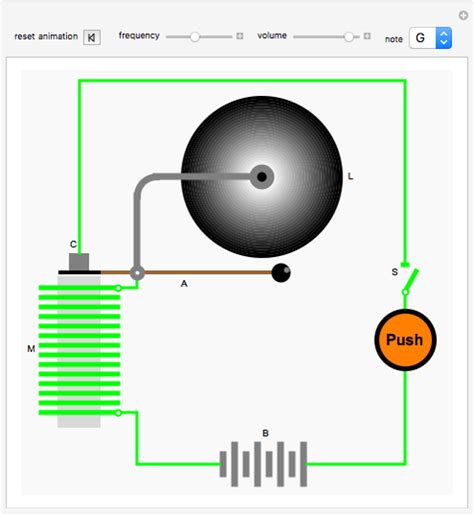
Table of Contents
How Does a Doorbell Utilize an Electromagnet? A Deep Dive into the Physics of a Familiar Sound
The humble doorbell. A seemingly simple device that announces the arrival of guests, yet it encapsulates a fascinating interplay of physics and engineering. At the heart of its operation lies the electromagnet, a component that transforms electrical energy into mechanical motion, producing the characteristic ding-dong we all recognize. This article will delve deep into the mechanics of a doorbell, exploring the crucial role of the electromagnet, its underlying principles, and the broader context of its application in various technologies.
Understanding the Electromagnet: The Heart of the Doorbell
An electromagnet is a temporary magnet created by passing an electric current through a coil of wire wrapped around a ferromagnetic core, typically made of iron. The current generates a magnetic field, which magnetizes the core. The strength of the magnetic field, and thus the strength of the electromagnet, is directly proportional to the amount of current flowing through the coil. This is the fundamental principle that governs the functionality of a doorbell.
The Role of the Ferromagnetic Core
The ferromagnetic core is crucial because it significantly enhances the magnetic field produced by the coil. Ferromagnetic materials, such as iron, nickel, and cobalt, possess domains – regions where the magnetic moments of atoms are aligned. When an external magnetic field (in this case, from the current-carrying coil) is applied, these domains align themselves with the field, dramatically increasing the overall magnetic field strength. Without this core, the magnetic field generated by the coil alone would be far too weak to operate the doorbell's mechanism.
The Current Flow: The On/Off Switch
The doorbell's operation hinges on the intermittent flow of electricity through the electromagnet. When the button is pressed, a circuit is completed, allowing current to flow through the coil. This energizes the electromagnet, generating a magnetic field. Releasing the button breaks the circuit, stopping the current flow and de-energizing the electromagnet, causing its magnetic field to collapse. This on/off cycle is what creates the oscillatory motion required to ring the bell.
The Doorbell Mechanism: From Electricity to Sound
The electromagnet in a doorbell doesn't directly strike the bell itself. Instead, it interacts with a metal armature, a small piece of ferromagnetic material attached to a spring and the striking mechanism.
The Armature's Dance: Attraction and Repulsion
When the electromagnet is energized, it attracts the armature towards it. This movement causes the striker (a small hammer) attached to the armature to hit the bell, producing the sound. As the electromagnet is de-energized, the spring pulls the armature back to its original position, preparing it for the next cycle. This continuous cycle of attraction and recoil creates the ringing sound.
The Spring: The Restoring Force
The spring plays a critical role in the doorbell's operation. It provides the restoring force that returns the armature to its initial position after being attracted by the electromagnet. Without the spring, the armature would remain stuck to the electromagnet, and the bell would not ring. The stiffness of the spring determines the speed and intensity of the armature's movement, influencing the sound produced by the bell.
The Bell: Amplifying the Sound
The bell itself acts as a resonator, amplifying the sound produced by the impact of the striker. The shape and material of the bell are carefully designed to enhance the resonance frequency, creating a clear and audible sound. Different designs can result in variations in the tone and pitch of the doorbell's sound.
Variations in Doorbell Design and Technology
While the basic principle remains the same, there are variations in doorbell designs and technologies.
AC vs. DC Doorbells: A Subtle Difference
Traditional doorbells often use alternating current (AC) electricity from the household power supply. The continuous changing direction of the AC current ensures that the electromagnet continuously attracts and releases the armature, producing a continuous ringing sound as long as the button is pressed. However, some doorbells use direct current (DC), often powered by batteries or low-voltage transformers. In DC doorbells, the ringing might require a slightly different mechanical design to achieve the continuous ringing effect.
Wireless Doorbells: The Rise of Modern Technology
Wireless doorbells utilize radio frequency (RF) technology to transmit a signal from the button to the chime unit. While they also employ electromagnets in the chime unit to create the sound, the triggering mechanism is entirely different, relying on electronic circuits and RF signals rather than a direct electrical connection. However, the fundamental principle of using an electromagnet to create the sound remains.
The Evolution of Sounds and Aesthetics: Beyond the Traditional Ding-Dong
Modern doorbells offer a wider range of sounds and aesthetics. From simple chimes to complex melodies, the sound is controlled by more sophisticated electronic circuitry. The doorbell's physical design has also diversified greatly, ranging from sleek minimalist designs to antique-inspired models. Yet, the underlying principle – the use of an electromagnet to produce the mechanical movement that creates the sound – remains a cornerstone of their technology.
The Broader Application of Electromagnets: Beyond the Doorbell
The principle behind the doorbell's electromagnet is a foundation for numerous other applications in various fields.
Relays: Switching Larger Currents
Electromagnets are crucial components in relays, electrical switches that use a small current to control a larger current. This is particularly useful in high-power circuits, where it's impractical or dangerous to switch high currents directly. The electromagnet acts as the actuator, closing or opening the larger current circuit.
Solenoids: Linear Motion Control
Solenoids, a type of electromagnet with a movable core, are widely used for linear motion control. In various applications, from car locks to industrial automation, solenoids provide precise and controlled linear movement based on electrical input. The principle of attracting a ferromagnetic core is fundamental to their operation.
Motors: Rotary Motion Generation
Electric motors, in many ways, are sophisticated forms of electromagnets. These devices use the interaction between multiple electromagnets (or coils) and a rotor to generate rotary motion, which is the basis for countless applications, from powering household appliances to running industrial machinery. The principles of electromagnetism are fundamental to how these powerful machines work.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Medical Applications
Perhaps one of the most impressive uses of electromagnets is in Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) machines. These sophisticated medical devices use powerful superconducting electromagnets to generate incredibly strong magnetic fields, allowing doctors to visualize internal organs and tissues with unparalleled detail.
Conclusion: A Tiny Magnet, a Big Impact
The seemingly simple doorbell contains a sophisticated piece of technology based on electromagnetism. Understanding its operation gives us a glimpse into the broader world of electromagnetism and its applications across many technologies. From the humble "ding-dong" to the advanced imaging of an MRI machine, the electromagnet's ability to transform electrical energy into mechanical motion has revolutionized our world. The next time you hear a doorbell ring, take a moment to appreciate the intricate physics and engineering that makes that familiar sound possible. The technology, though seemingly simple, is a testament to the power and versatility of electromagnetism.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Oz In A Cup Of Butter
Apr 04, 2025
-
8 3 As A Mixed Number
Apr 04, 2025
-
What Type Of Symmetry Do Sponges Have
Apr 04, 2025
-
Oz In A Liter Of Water
Apr 04, 2025
-
How Far Is Venus From Sun
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Does A Doorbell Utilize An Electromagnet . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
