How Many Neutrons Does Boron Have
Kalali
Mar 10, 2025 · 5 min read
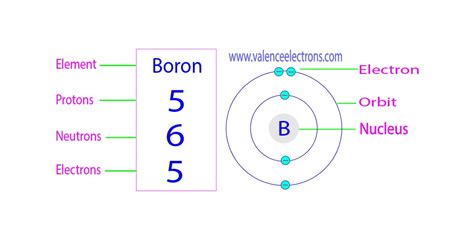
Table of Contents
How Many Neutrons Does Boron Have? A Deep Dive into Isotopes and Nuclear Physics
Boron, a metalloid element crucial in various applications, presents a fascinating study in nuclear physics due to its isotopic variability. Understanding the number of neutrons in boron requires exploring its isotopes and the concept of atomic structure. This article will delve into the details, clarifying the question, "How many neutrons does boron have?", and expanding upon related concepts.
Understanding Atomic Structure: Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons
Before we pinpoint the neutron count in boron, let's refresh our understanding of atomic structure. Every atom consists of three fundamental subatomic particles:
-
Protons: Positively charged particles residing in the atom's nucleus. The number of protons defines the element's atomic number and determines its identity. Boron's atomic number is 5, meaning every boron atom contains 5 protons.
-
Neutrons: Neutral particles (no charge) also found in the atom's nucleus. Neutrons contribute to the atom's mass but not its charge. The number of neutrons can vary within the same element, leading to isotopes.
-
Electrons: Negatively charged particles orbiting the nucleus in electron shells. The number of electrons usually equals the number of protons in a neutral atom.
Isotopes: The Key to Understanding Boron's Neutron Count
The crucial point to understanding boron's neutron number is the concept of isotopes. Isotopes are atoms of the same element (same number of protons) but with differing numbers of neutrons. This means isotopes have the same atomic number but different mass numbers (the sum of protons and neutrons).
Boron has two naturally occurring stable isotopes:
-
Boron-10 (¹⁰B): This isotope has 5 protons (as all boron isotopes do) and 5 neutrons (10 – 5 = 5). It constitutes approximately 19.9% of naturally occurring boron.
-
Boron-11 (¹¹B): This isotope possesses 5 protons and 6 neutrons (11 – 5 = 6). It makes up about 80.1% of naturally occurring boron.
Therefore, there isn't a single answer to "How many neutrons does boron have?". The answer depends on which boron isotope you're considering.
Calculating Neutron Number: A Simple Formula
The number of neutrons in any isotope can be easily calculated using the following formula:
Number of neutrons = Mass number - Atomic number
Where:
- Mass number: The total number of protons and neutrons in the atom's nucleus (represented as a superscript before the element's symbol, e.g., ¹⁰B).
- Atomic number: The number of protons in the atom's nucleus (the element's position on the periodic table).
Boron's Isotopic Abundance and its Impact
The relative abundance of Boron-10 and Boron-11 significantly influences the properties and applications of boron. The weighted average of the neutron count, considering the isotopic abundance, provides an average neutron number for naturally occurring boron. However, it's essential to remember that individual boron atoms will have either 5 or 6 neutrons.
Applications of Boron Isotopes
The different properties of Boron-10 and Boron-11 lead to their diverse applications:
Boron-10:
-
Neutron capture therapy (BNCT): Boron-10's high neutron capture cross-section makes it useful in cancer treatment. When bombarded with neutrons, Boron-10 undergoes nuclear fission, releasing alpha particles that destroy nearby cancer cells.
-
Nuclear reactors: Boron-10 is used as a neutron absorber in nuclear reactors to control the chain reaction.
-
Neutron detectors: Its high neutron capture cross-section makes it suitable for use in neutron detectors.
Boron-11:
-
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy: Boron-11 NMR is used in chemical analysis to study the structure and bonding of boron-containing compounds.
-
Material science: Boron-11 is incorporated into various materials to improve their properties, such as hardness and strength.
Beyond the Stable Isotopes: Radioactive Boron Isotopes
While Boron-10 and Boron-11 are stable, several radioactive isotopes of boron exist, albeit with short half-lives. These isotopes are created artificially through nuclear reactions and have various applications in research and specific technological processes. These radioactive isotopes also have different neutron counts, further demonstrating the variability in neutron numbers within boron.
Understanding Nuclear Stability: The Role of Neutrons
The stability of an atomic nucleus depends on the balance between the strong nuclear force (holding protons and neutrons together) and the electromagnetic repulsion between protons. For lighter elements like boron, a roughly equal number of protons and neutrons generally leads to stability. However, as the atomic number increases, the number of neutrons required for stability exceeds the number of protons. This is why Boron-11, with its slightly higher neutron count, is more abundant than Boron-10.
The Importance of Isotopic Analysis
Accurate determination of the isotopic composition of boron is crucial in various fields:
-
Geochemistry: Isotopic analysis helps understand geological processes and the origins of materials.
-
Environmental science: Boron isotope ratios can be used as tracers in environmental studies.
-
Forensic science: Isotopic analysis can provide valuable information in forensic investigations.
Conclusion: A Variable Neutron Count Defines Boron
The question, "How many neutrons does boron have?" doesn't have a single definitive answer. Boron exists as two naturally occurring stable isotopes, Boron-10 with 5 neutrons and Boron-11 with 6 neutrons. The prevalence of Boron-11 contributes significantly to the overall properties observed in naturally occurring boron. Understanding boron's isotopic composition is vital in diverse fields, highlighting the importance of considering isotopic variations when studying elemental properties and applications. Further exploration into radioactive boron isotopes expands the range of neutron counts even further. The variations in neutron numbers within boron atoms showcase the rich complexity of nuclear physics and the element's significance across numerous scientific disciplines.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Does Slope Of Vt Graph Represent
Mar 10, 2025
-
1 To The Power Of 4
Mar 10, 2025
-
250 Cm In Inches And Feet
Mar 10, 2025
-
How Much Is 6 Feet In Inches
Mar 10, 2025
-
How Many Degrees Fahrenheit Is 180 Celsius
Mar 10, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Neutrons Does Boron Have . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
