How Many Sides Does A Polygon Have
Kalali
Mar 07, 2025 · 5 min read
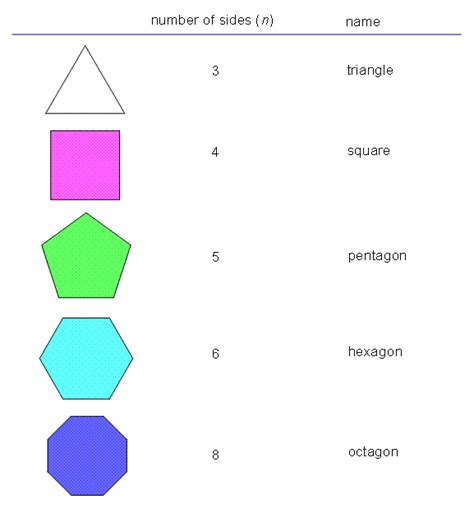
Table of Contents
How Many Sides Does a Polygon Have? A Deep Dive into Polygons
The seemingly simple question, "How many sides does a polygon have?" opens a fascinating door into the world of geometry. While the immediate answer might seem straightforward, the reality is far richer and more nuanced. This comprehensive guide will explore polygons, their properties, classifications, and the intriguing relationship between their sides and angles. We'll delve into the diverse world of polygons, from the simplest to the most complex, equipping you with a thorough understanding of this fundamental geometric concept.
Understanding Polygons: The Basics
A polygon is a closed two-dimensional figure formed by connecting a finite number of straight line segments. These segments are called the sides of the polygon, and the points where the sides meet are called the vertices or angles. Crucially, a polygon must be closed; it cannot have any open ends. The number of sides directly dictates the polygon's classification and many of its properties.
Key Characteristics of Polygons:
- Sides: The straight line segments forming the polygon.
- Vertices: The points where two sides intersect. The number of vertices always equals the number of sides.
- Angles: The interior angles formed at each vertex. The sum of the interior angles of a polygon is a function of its number of sides.
- Interior Angles: Angles formed inside the polygon.
- Exterior Angles: Angles formed by extending one side of the polygon. The sum of exterior angles always equals 360 degrees.
Classifying Polygons Based on the Number of Sides
Polygons are classified primarily by their number of sides. Here's a breakdown of some common polygons:
- 3 Sides: Triangle - The simplest polygon, possessing three sides and three angles. Triangles can be further classified as equilateral (all sides equal), isosceles (two sides equal), or scalene (all sides unequal).
- 4 Sides: Quadrilateral - A polygon with four sides. This category encompasses various shapes like squares, rectangles, rhombuses, parallelograms, trapezoids, and kites, each with its own unique properties.
- 5 Sides: Pentagon - A polygon with five sides. Regular pentagons, with all sides and angles equal, are particularly interesting due to their unique geometric properties.
- 6 Sides: Hexagon - A polygon with six sides. Hexagons are common in nature, such as honeycombs.
- 7 Sides: Heptagon (or Septagon)
- 8 Sides: Octagon
- 9 Sides: Nonagon
- 10 Sides: Decagon
- 11 Sides: Hendecagon (or Undecagon)
- 12 Sides: Dodecagon
- 15 Sides: Pentadecagon
- 20 Sides: Icosagon
- n Sides: n-gon - This is a general term used to represent a polygon with 'n' sides.
The Relationship Between Sides and Angles
A fundamental relationship exists between the number of sides of a polygon and the sum of its interior angles. This relationship is expressed by the formula:
(n - 2) * 180°
Where 'n' is the number of sides.
For example:
- Triangle (n=3): (3 - 2) * 180° = 180° (The sum of interior angles in a triangle is always 180°)
- Quadrilateral (n=4): (4 - 2) * 180° = 360°
- Pentagon (n=5): (5 - 2) * 180° = 540°
- Hexagon (n=6): (6 - 2) * 180° = 720°
This formula allows us to calculate the sum of interior angles for any polygon, regardless of its shape or regularity.
Regular vs. Irregular Polygons
Polygons can be further categorized as regular or irregular:
-
Regular Polygons: All sides are equal in length, and all angles are equal in measure. Examples include a square, an equilateral triangle, and a regular hexagon. Regular polygons exhibit a high degree of symmetry.
-
Irregular Polygons: The sides and angles are not all equal. Most quadrilaterals, apart from squares and rhombuses, are irregular polygons.
Concave and Convex Polygons
Another crucial distinction is between concave and convex polygons:
-
Convex Polygons: A polygon is convex if all its interior angles are less than 180°. In simpler terms, a line segment connecting any two points within the polygon will always lie entirely within the polygon.
-
Concave Polygons: A polygon is concave if at least one of its interior angles is greater than 180°. This creates an inward-pointing section of the polygon.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Polygon Concepts
The world of polygons extends far beyond these fundamental concepts. More advanced topics include:
-
Tessellations: The arrangement of polygons to completely cover a surface without overlaps or gaps. Certain polygons, such as triangles and squares, tessellate easily.
-
Star Polygons: Formed by extending the sides of a polygon to create intersecting lines and a star-like shape.
-
Complex Polygons: Polygons with intersecting sides or intricate shapes.
Applications of Polygons
Polygons are not just abstract geometric shapes; they have numerous practical applications in various fields:
-
Architecture and Engineering: Polygons form the basis of building designs, structural frameworks, and many engineered objects.
-
Computer Graphics and Design: Polygons are the building blocks of digital images and 3D models.
-
Cartography: Polygons are used to represent geographical areas on maps.
-
Art and Design: Polygons appear in various forms of art and design, from paintings to mosaics.
-
Nature: Many natural structures, like honeycombs and crystals, exhibit polygonal patterns.
Solving Problems Involving Polygons
Numerous problems involve determining the number of sides of a polygon based on given information. Here are some examples:
Problem 1: The sum of the interior angles of a polygon is 1260°. How many sides does it have?
Solution: Using the formula (n - 2) * 180° = 1260°, we can solve for 'n':
(n - 2) * 180 = 1260 n - 2 = 1260 / 180 n - 2 = 7 n = 9
Therefore, the polygon has 9 sides (a nonagon).
Problem 2: A regular polygon has an interior angle of 144°. How many sides does it have?
Solution: First, find the exterior angle: 180° - 144° = 36°. Since the sum of exterior angles in any polygon is 360°, the number of sides is 360° / 36° = 10. The polygon has 10 sides (a decagon).
Conclusion
The question of how many sides a polygon has leads to a rich exploration of geometric concepts, classifications, and applications. Understanding the relationship between the number of sides, interior angles, and various polygon types is crucial in various fields. From the simple triangle to the complex n-gon, the study of polygons provides a solid foundation in geometry and its practical applications in the world around us. This comprehensive guide has equipped you with the knowledge to confidently approach and solve problems involving polygons, regardless of their complexity. Remember to always consider the specific properties of the polygon in question – whether it’s regular or irregular, convex or concave – to accurately determine its characteristics and solve related geometric problems.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Equation Relating Electric Field And Voltage
Mar 14, 2025
-
What Is The Percentage Of 9 12
Mar 14, 2025
-
Force Acting Over A Distance Is The Definition Of
Mar 14, 2025
-
How Many Meters Is 5 Km
Mar 14, 2025
-
Which Characteristic Is Given By The Angular Momentum Quantum Number
Mar 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Sides Does A Polygon Have . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
