How To Find Diameter Of A Cylinder
Kalali
Mar 19, 2025 · 6 min read
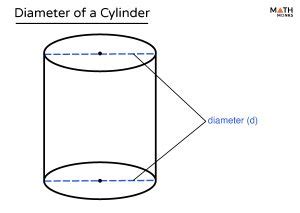
Table of Contents
- How To Find Diameter Of A Cylinder
- Table of Contents
- How to Find the Diameter of a Cylinder: A Comprehensive Guide
- Understanding Cylindrical Geometry: Diameter and Related Concepts
- Methods for Finding the Diameter of a Cylinder
- 1. Direct Measurement using Calipers or Ruler
- 2. Calculating Diameter from Circumference
- 3. Calculating Diameter from Volume and Height
- 4. Calculating Diameter from Cross-Sectional Area
- 5. Using 3D Scanning Technology
- Practical Applications and Examples
- Conclusion: Choosing the Right Method
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
How to Find the Diameter of a Cylinder: A Comprehensive Guide
Determining the diameter of a cylinder is a fundamental task in various fields, from engineering and manufacturing to everyday problem-solving. Whether you're working with a large industrial tank or a small cylindrical container, understanding the methods to accurately measure this crucial dimension is essential. This comprehensive guide explores several techniques, from simple direct measurement to more complex calculations based on other known parameters.
Understanding Cylindrical Geometry: Diameter and Related Concepts
Before diving into the methods, let's clarify some key geometrical concepts related to cylinders. A cylinder is a three-dimensional solid with two parallel circular bases connected by a curved surface. The diameter of a cylinder is the length of a straight line passing through the center of a circular base and connecting two points on the circumference. It's twice the radius, which is the distance from the center of the circle to any point on the circumference. Other important dimensions include the height (or length) of the cylinder, which is the perpendicular distance between the two circular bases, and the circumference, which is the distance around the circle.
Methods for Finding the Diameter of a Cylinder
The most appropriate method for finding the diameter will depend on the circumstances and the tools available. Here's a breakdown of common techniques:
1. Direct Measurement using Calipers or Ruler
This is the simplest and most direct method, suitable for cylinders where direct access to the circular base is available.
-
Using Calipers: Vernier calipers or digital calipers provide the most accurate measurement. Simply position the jaws of the calipers across the diameter of the cylinder's base, ensuring the jaws are perpendicular to the base. The reading on the caliper will give you the diameter directly.
-
Using a Ruler: If calipers aren't available, a ruler can be used, though it will offer less precision. Place the ruler across the diameter, ensuring it's aligned perpendicular to the base. Take the measurement carefully, noting the units (inches, centimeters, etc.). Remember to account for the thickness of the ruler if necessary. This method is particularly useful for larger cylinders where the difference in accuracy between a ruler and calipers is less significant.
Accuracy Considerations: The accuracy of direct measurement depends heavily on the precision of the measuring instrument and the skill of the measurer. Parallax error – the apparent shift in the position of an object when viewed from different angles – can lead to inaccuracies, so ensure your eye is aligned directly above the measurement.
2. Calculating Diameter from Circumference
If direct measurement isn't feasible, you can calculate the diameter if you know the circumference. The relationship between diameter (d) and circumference (C) is given by the formula:
C = πd
Where π (pi) is approximately 3.14159. To find the diameter, rearrange the formula:
d = C/π
This method requires accurate measurement of the circumference, which can be done using a flexible measuring tape. Wrap the tape measure snugly around the cylinder, ensuring it's parallel to the base. The reading on the tape measure represents the circumference. Then, divide the circumference by π to obtain the diameter.
Accuracy Considerations: The accuracy of this method depends on how accurately you can measure the circumference. A flexible measuring tape is essential, and care should be taken to avoid stretching or bending the tape, which can lead to inaccuracies.
3. Calculating Diameter from Volume and Height
If you know the volume (V) and height (h) of the cylinder, you can calculate its diameter. The volume of a cylinder is given by the formula:
V = πr²h
Where 'r' is the radius. To find the diameter:
- Solve for the radius: Rearrange the volume formula to solve for the radius: r = √(V/(πh))
- Calculate the diameter: Since the diameter is twice the radius, d = 2r = 2√(V/(πh))
This method is useful when direct measurement is impossible, but requires accurate measurements of both volume and height. Volume can be determined by various methods, including water displacement (for solid cylinders) or known fill capacity (for hollow cylinders). Height can be measured using a ruler or other suitable measuring device.
Accuracy Considerations: The accuracy of this method relies heavily on the precision of the volume and height measurements. Inaccurate measurements of either will significantly impact the calculated diameter. Consider the potential errors associated with measuring volume and height when evaluating the final result.
4. Calculating Diameter from Cross-Sectional Area
If you know the cross-sectional area (A) of the cylinder, you can determine its diameter. The cross-sectional area of a cylinder is the area of its circular base, given by:
A = πr²
To find the diameter:
- Solve for the radius: Rearrange the area formula to solve for the radius: r = √(A/π)
- Calculate the diameter: d = 2r = 2√(A/π)
This method is particularly useful if you have information about the cross-sectional area from engineering drawings or other sources. Accurate determination of the cross-sectional area is vital for obtaining an accurate diameter. Inaccuracies in area measurement directly translate into inaccuracies in the calculated diameter.
5. Using 3D Scanning Technology
For complex or irregularly shaped cylinders, or situations requiring extremely high accuracy, 3D scanning technology offers a powerful solution. A 3D scanner captures a point cloud representing the cylinder's surface. Specialized software then processes this data to create a 3D model, from which various dimensions, including the diameter, can be accurately measured. This technique eliminates the limitations and potential for error associated with manual measurement.
Accuracy Considerations: 3D scanning technology can provide highly accurate measurements, but the accuracy depends on factors such as the scanner's resolution, the surface characteristics of the cylinder (e.g., reflectivity, texture), and the expertise of the user in preparing the object and processing the scan data.
Practical Applications and Examples
The ability to find the diameter of a cylinder is crucial in many real-world situations:
-
Engineering and Manufacturing: Determining the diameter is essential for designing and manufacturing parts, ensuring proper fit and functionality. Inaccurate diameter measurements can lead to manufacturing defects or failures.
-
Construction and Civil Engineering: Calculating diameters is critical for designing and constructing cylindrical structures, such as pipes, tanks, and pillars. Accurate measurements ensure structural integrity and stability.
-
Packaging and Logistics: Knowing the diameter helps in designing packaging and optimizing storage and transportation of cylindrical goods.
-
Scientific Research: Measuring the diameter is essential in various scientific experiments and measurements, particularly in fields like physics and chemistry, where precise dimensions are crucial.
Example 1: A cylindrical pipe has a circumference of 31.4 cm. What is its diameter?
Using the formula d = C/π, we get: d = 31.4 cm / 3.14159 ≈ 10 cm
Example 2: A cylindrical tank has a volume of 1570 cubic centimeters and a height of 10 centimeters. What is its diameter?
Using the formula d = 2√(V/(πh)), we get: d = 2√(1570 cm³ / (3.14159 * 10 cm)) ≈ 20 cm
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Method
Choosing the appropriate method for determining the diameter of a cylinder depends on the available tools, the desired level of accuracy, and the context of the measurement. Direct measurement using calipers is generally the simplest and most accurate method for readily accessible cylinders. However, when direct measurement isn't feasible, calculations based on circumference, volume, cross-sectional area, or advanced techniques like 3D scanning provide viable alternatives. Always consider the potential sources of error and select the method that best balances accuracy and practicality for your specific needs. Remember to always double-check your measurements and calculations to ensure accuracy and reliability. By mastering these techniques, you'll be well-equipped to tackle a wide range of cylindrical measurement challenges.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Inches Is 6 5 Cm
Mar 20, 2025
-
What Is 16 Celsius In Fahrenheit
Mar 20, 2025
-
Reactions Which Do Not Continue To Completion Are Called Reactions
Mar 20, 2025
-
18 To The Power Of 2
Mar 20, 2025
-
How Many Grams In Quarter Ounce
Mar 20, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How To Find Diameter Of A Cylinder . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
