How Will Grazing Animals Help Plants To Become Established
Kalali
Mar 21, 2025 · 6 min read
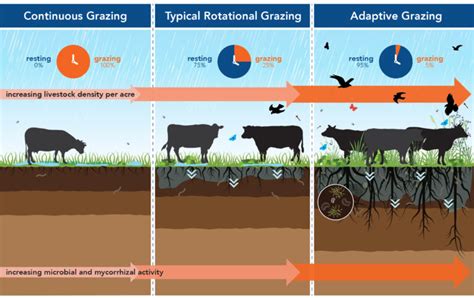
Table of Contents
How Grazing Animals Help Plants Become Established: A Surprisingly Symbiotic Relationship
The image of grazing animals and thriving plant life might seem contradictory. After all, herbivores consume plants; how can their presence contribute to plant establishment and growth? The reality is far more nuanced and complex, revealing a surprisingly symbiotic relationship where controlled grazing can significantly benefit plant communities. This article delves into the multifaceted ways grazing animals act as crucial players in plant establishment, exploring the mechanisms behind this often-overlooked ecological synergy.
Understanding the Role of Grazing in Plant Communities
Traditionally, grazing has been viewed primarily as a destructive force, leading to overgrazing and land degradation. While uncontrolled grazing can certainly have detrimental effects, moderate and managed grazing can play a vital role in shaping plant communities and fostering the establishment of new plant species. This is achieved through a complex interplay of several factors:
1. Seed Dispersal and Soil Disturbance
Grazing animals contribute significantly to seed dispersal. Seeds can adhere to their fur or hooves and be transported considerable distances, effectively broadening the range of plant species. The act of grazing itself creates soil disturbance through trampling and the removal of vegetation cover. This disturbance can:
- Create bare patches: These patches offer ideal germination sites for seeds that require direct sunlight and minimal competition. Many plant species are specifically adapted to colonize disturbed areas.
- Improve soil aeration: The trampling action can improve soil aeration, allowing for better root penetration and water infiltration. This is crucial for seedling establishment and growth.
- Increase nutrient availability: Grazing animals deposit manure, which acts as a natural fertilizer, enriching the soil with essential nutrients and enhancing the growth of established plants and seedlings.
2. Selective Grazing and Competitive Release
Grazing animals are often selective in their feeding habits. They tend to prefer certain plant species over others, leading to a process called selective grazing. This selectivity can have profound effects on plant community composition:
- Competitive release: By preferentially consuming dominant or aggressive plant species, grazing animals can reduce competition for resources (light, water, and nutrients) for less competitive species. This allows less dominant species to establish and thrive, leading to increased plant diversity.
- Shifting community dynamics: Over time, the selective grazing pressure can lead to shifts in the dominant plant species present in the grazing area. This prevents the development of monocultures, which are often less resilient to environmental changes and more susceptible to pests and diseases.
3. Enhanced Nutrient Cycling
Grazing animals significantly influence nutrient cycling in ecosystems. Their grazing activity, coupled with their waste products, creates a dynamic system that enhances nutrient availability for plant growth:
- Nutrient redistribution: Grazing animals move nutrients from areas of high plant biomass to areas where they defecate, effectively redistributing nutrients throughout the ecosystem. This ensures more even nutrient distribution and promotes more widespread plant growth.
- Increased decomposition rates: Grazing animals' dung enhances decomposition rates, releasing nutrients back into the soil more rapidly. This accelerated nutrient cycling provides a readily available nutrient source for plant growth.
- Improved soil structure: The organic matter contained within dung improves soil structure, enhancing water retention and overall soil health. This better soil quality directly benefits plant establishment and growth.
The Importance of Managed Grazing
The benefits of grazing animals for plant establishment are not automatic. Uncontrolled grazing can lead to overgrazing, a situation where the grazing intensity exceeds the regenerative capacity of the vegetation. Overgrazing results in:
- Soil erosion: The loss of vegetation cover exposes the soil to the elements, leading to increased erosion and loss of topsoil.
- Desertification: Severe and prolonged overgrazing can lead to desertification, transforming productive land into barren, unproductive areas.
- Reduced biodiversity: Overgrazing eliminates less competitive species, leading to a decrease in plant diversity.
Therefore, managed grazing is crucial to maximize the benefits while minimizing the risks. Managed grazing strategies include:
- Rotational grazing: Moving grazing animals regularly between different paddocks allows vegetation to recover fully before grazing resumes.
- Rest-rotation grazing: Similar to rotational grazing, but includes periods of complete rest for vegetation recovery.
- Adaptive management: Adjusting grazing intensity and frequency based on the condition of the vegetation and environmental factors.
These managed grazing strategies help prevent overgrazing and ensure the long-term health of the ecosystem, maximizing the positive effects of grazing animals on plant establishment.
Specific Examples of Grazing's Impact on Plant Establishment
Several studies illustrate the positive impact of grazing on plant establishment in various ecosystems. For example, research on savannas has shown that controlled grazing promotes the coexistence of grasses and trees, preventing the dominance of one type of vegetation. The selective grazing of grasses by herbivores creates space for tree seedlings to establish themselves, contributing to the characteristic savanna mosaic landscape.
In grasslands, moderate grazing can prevent the dominance of aggressive grasses and encourage the establishment of forbs (flowering herbaceous plants). This increased diversity in plant species leads to a healthier and more resilient grassland ecosystem. Similarly, in some alpine ecosystems, grazing can stimulate the growth of certain plant species by removing competing vegetation.
The Role of Different Grazing Animals
Different grazing animals have different feeding habits and impacts on plant communities. For instance, some animals are grazers, consuming primarily grasses, while others are browsers, feeding on leaves, twigs, and other woody vegetation. The type of grazing animal present will influence the plant species that thrive and the overall structure of the plant community.
Larger animals, due to their greater impact on soil disturbance and seed dispersal, might have a more profound effect than smaller animals. The introduction of specific grazing animal species can be a strategic tool in ecological restoration projects, aimed at promoting the establishment of particular plant species or restoring degraded land.
Conclusion: A Dynamic and Beneficial Interaction
The interaction between grazing animals and plant communities is far from simple. While uncontrolled grazing can lead to devastating consequences, managed grazing can be a powerful tool for enhancing plant establishment and fostering biodiversity. Through a complex interplay of seed dispersal, selective grazing, nutrient cycling, and soil disturbance, grazing animals can play a vital role in shaping plant communities and maintaining healthy ecosystems. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for developing sustainable land management practices that balance the needs of livestock with the preservation of biodiversity and ecosystem health. By embracing a holistic understanding of this symbiotic relationship, we can unlock the significant potential of grazing animals in promoting thriving plant communities and resilient landscapes. This knowledge is particularly critical in the face of climate change and increasing threats to biodiversity, highlighting the need for innovative and sustainable approaches to land management. Further research and a deeper understanding of these interactions will be crucial for ensuring the future health and productivity of our ecosystems.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
9 Inch Cube Has A Volume Of
Mar 28, 2025
-
6 Is What Percent Of 10
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Is The Mean Of Sample Means
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Is 32 Mm In Inches
Mar 28, 2025
-
How Many Cups Is 125 Ml
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Will Grazing Animals Help Plants To Become Established . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
