Identifying Intermediates In A Reaction Mechanism
Kalali
Mar 22, 2025 · 5 min read
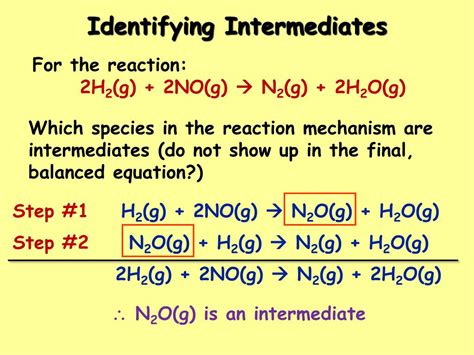
Table of Contents
Identifying Intermediates in a Reaction Mechanism: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding reaction mechanisms is crucial in chemistry. It's not enough to simply know that reactants transform into products; we need to understand the how – the series of elementary steps involved in the transformation. A key element in deciphering these mechanisms is identifying reaction intermediates. This article provides a comprehensive guide on how to identify intermediates, focusing on various techniques and providing practical examples.
What are Reaction Intermediates?
Reaction intermediates are transient species formed during the course of a reaction. Unlike reactants and products, they are highly reactive and exist only for a very short time. They are neither the starting materials nor the final products but are crucial stepping stones in the overall transformation. They are consumed in subsequent steps of the reaction mechanism, preventing their isolation and direct observation in most cases.
A crucial distinction needs to be made between intermediates and transition states. Transition states are high-energy species representing the maximum energy point along the reaction coordinate. They are fleeting and cannot be isolated. Intermediates, on the other hand, represent energy minima along the reaction coordinate, possessing a finite lifetime, albeit short.
Techniques for Identifying Intermediates
Identifying intermediates can be challenging, requiring a combination of experimental and theoretical techniques. Let's explore several commonly employed methods:
1. Kinetic Studies:
Kinetic studies provide valuable insights into the reaction mechanism by examining the rate of reaction as a function of reactant concentrations. The rate law, determined experimentally, reflects the elementary steps involved in the rate-determining step. Deviations from simple rate laws often indicate the presence of intermediates. For example, a rate law that is not simply first-order or second-order in reactants may suggest the formation of an intermediate that participates in subsequent steps. Detailed analysis of the kinetic data can help elucidate the role of intermediates and their involvement in the rate-determining step. Careful consideration of reaction orders and their dependence on reactant concentration is crucial in this approach.
2. Spectroscopic Techniques:
Spectroscopic techniques offer direct or indirect evidence for the presence of intermediates. Various spectroscopic methods, such as UV-Vis, IR, NMR, and ESR spectroscopy, can be used to detect characteristic spectral signatures of intermediates. These techniques can be particularly useful if the intermediate possesses unique absorption bands or chemical shifts that distinguish it from the reactants and products. Time-resolved spectroscopy, where spectra are recorded at very short time intervals, allows for the observation of short-lived intermediates. Matrix isolation is another technique that involves trapping the intermediates in an inert matrix at very low temperatures, allowing for their characterization via spectroscopic methods.
3. Trapping Experiments:
Trapping experiments involve adding a reagent that reacts selectively with the intermediate, converting it into a more stable and isolable derivative. This derivative can then be characterized using various techniques, providing indirect evidence for the existence of the intermediate. The choice of trapping agent is crucial and depends on the nature of the intermediate. The trapping agent should react rapidly and selectively with the intermediate without interfering with other steps in the reaction mechanism.
4. Computational Chemistry:
Computational chemistry has become an indispensable tool in mechanistic studies. Using quantum mechanical methods, it's possible to calculate the energies and structures of reactants, products, intermediates, and transition states. This information can be used to construct potential energy surfaces, providing a detailed picture of the reaction pathway. Computational methods can predict the stability and reactivity of intermediates, offering valuable insights into their involvement in the reaction mechanism. However, it is crucial to carefully validate computational results with experimental data.
5. Isotopic Labeling:
Isotopic labeling involves using isotopes of atoms to trace the movement of atoms during a reaction. By incorporating isotopes into the reactants and analyzing the products, it is possible to determine the fate of specific atoms and deduce the presence of intermediates. For instance, using deuterium (²H) instead of hydrogen (¹H) can reveal the involvement of specific hydrogen atoms in bond breaking and formation, shedding light on the reaction mechanism and the intermediates involved.
Examples of Identifying Intermediates
Let's consider a few examples to illustrate the application of these techniques:
Example 1: SN1 Reaction
In an SN1 (substitution nucleophilic unimolecular) reaction, the rate-determining step involves the formation of a carbocation intermediate. This carbocation can be trapped using a nucleophile, and its presence can be confirmed by kinetic studies exhibiting a first-order dependence on the alkyl halide concentration. Spectroscopic techniques, such as NMR, may also reveal the presence of the carbocation.
Example 2: Free Radical Reactions
Free radical reactions often involve the formation of highly reactive radical intermediates. Electron spin resonance (ESR) spectroscopy is a powerful technique for detecting these intermediates because of their unpaired electrons. Trapping experiments, involving the addition of radical scavengers, can also be employed to convert the radical intermediates into stable products.
Example 3: Enzyme Catalysis
In enzyme catalysis, the enzyme forms a complex with the substrate, which undergoes a series of transformations involving enzyme-bound intermediates. These intermediates are usually short-lived and cannot be isolated. However, their presence can be inferred from kinetic studies, spectroscopic analysis, and the use of site-directed mutagenesis to modify specific amino acid residues in the enzyme’s active site.
Challenges in Identifying Intermediates
Despite the advancements in experimental and computational techniques, identifying intermediates remains a challenge. Some of the difficulties include:
- High reactivity: Intermediates are often highly reactive and exist only for a very short time, making their detection difficult.
- Low concentration: The concentration of intermediates is usually very low, making their detection challenging.
- Complex reaction pathways: Many reactions involve multiple intermediates and competing pathways, making the interpretation of experimental data complex.
- Matrix effects: In spectroscopic studies, matrix effects can complicate the interpretation of the spectra.
Conclusion
Identifying reaction intermediates is crucial for understanding reaction mechanisms. The combination of kinetic studies, spectroscopic techniques, trapping experiments, computational methods, and isotopic labeling provides powerful tools for elucidating the detailed pathways of chemical reactions. Although challenges exist, ongoing advancements in experimental and computational methodologies continue to improve our ability to characterize these elusive species, providing deeper insights into the intricate world of chemical transformations. Further research and development in these areas will undoubtedly lead to even more sophisticated techniques for identifying and characterizing reaction intermediates in the future. The integration of diverse techniques and careful interpretation of data are vital for unraveling the complexities of reaction mechanisms and furthering our understanding of chemical reactivity.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 15 As A Percentage Of 60
Mar 22, 2025
-
Lightning Is An Example Of Static
Mar 22, 2025
-
How Many Valence Electrons In Potassium
Mar 22, 2025
-
One Pint Equals How Many Cups
Mar 22, 2025
-
What Is 39 Degrees C In Fahrenheit
Mar 22, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Identifying Intermediates In A Reaction Mechanism . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
