Is Barium Hydroxide A Strong Base
Kalali
Mar 13, 2025 · 5 min read
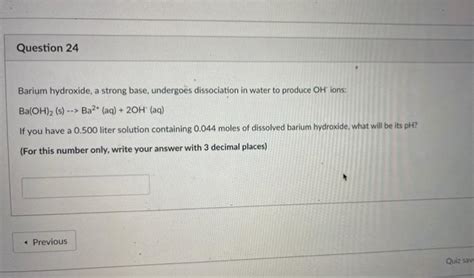
Table of Contents
Is Barium Hydroxide a Strong Base? A Comprehensive Analysis
Barium hydroxide, with its chemical formula Ba(OH)₂, is a well-known inorganic compound. A frequent question among chemistry students and professionals alike revolves around its classification as a strong or weak base. This article delves deep into the properties of barium hydroxide, examining its behavior in aqueous solutions and exploring the factors that determine its strength as a base. We will also cover its applications and safety considerations.
Understanding the Concept of Strong Bases
Before classifying barium hydroxide, it's crucial to understand what defines a strong base. A strong base is a substance that completely dissociates in water, releasing hydroxide ions (OH⁻) into the solution. This complete dissociation leads to a high concentration of OH⁻ ions, resulting in a significantly high pH value (typically above 7). The stronger the base, the more completely it dissociates and the higher the resulting hydroxide ion concentration. Conversely, weak bases only partially dissociate, resulting in a lower concentration of OH⁻ ions and a less alkaline pH.
Barium Hydroxide's Dissociation in Water
Barium hydroxide, when dissolved in water, undergoes complete dissociation, as represented by the following equation:
Ba(OH)₂(s) → Ba²⁺(aq) + 2OH⁻(aq)
This equation clearly shows that one mole of solid barium hydroxide (Ba(OH)₂) dissociates completely into one mole of barium cation (Ba²⁺) and two moles of hydroxide anions (OH⁻). This complete dissociation is the hallmark of a strong base. The high concentration of hydroxide ions generated by this complete ionization is responsible for barium hydroxide's strong alkaline nature. The equilibrium lies heavily to the right, meaning that the concentration of undissociated Ba(OH)₂ is negligible.
Comparing Barium Hydroxide to Other Bases
To further solidify barium hydroxide's classification as a strong base, let's compare it to both strong and weak bases:
Strong Bases:
- Sodium hydroxide (NaOH): Similar to barium hydroxide, sodium hydroxide completely dissociates in water, releasing sodium cations (Na⁺) and hydroxide anions (OH⁻). It is a classic example of a strong base.
- Potassium hydroxide (KOH): Another strong base that completely dissociates in water, releasing potassium cations (K⁺) and hydroxide anions (OH⁻).
- Calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)₂): While also considered a strong base due to its high solubility, its solubility is considerably lower than barium hydroxide. However, the portion that does dissolve dissociates completely.
Weak Bases:
- Ammonia (NH₃): Ammonia only partially dissociates in water, forming ammonium ions (NH₄⁺) and hydroxide ions (OH⁻) in a reversible reaction. This incomplete dissociation makes it a weak base.
- Pyridine (C₅H₅N): Similar to ammonia, pyridine is a weak base due to its incomplete dissociation in water.
The complete dissociation of barium hydroxide, in contrast to the partial dissociation of weak bases, firmly places it within the category of strong bases.
Factors Affecting the Strength of a Base
Several factors influence the strength of a base:
-
Solubility: While complete dissociation is crucial for classifying a base as strong, the solubility of the base plays a significant role. A base might be inherently strong (i.e., it would completely dissociate if it dissolved fully) but if its solubility is low, only a small amount will dissociate, leading to a relatively low concentration of OH⁻ ions. Calcium hydroxide is a good example; while the dissolved portion completely dissociates, its low solubility limits its overall basicity. Barium hydroxide, however, boasts higher solubility, contributing to its strong base classification.
-
Electrostatic Interactions: The strength of the bond between the cation and the hydroxide anion affects the ease of dissociation. Stronger bonds lead to weaker bases as dissociation becomes more difficult.
-
Polarity of the Solvent: The solvent in which the base dissolves also plays a significant role. Water, being a highly polar solvent, facilitates the dissociation of many ionic compounds, including strong bases.
Applications of Barium Hydroxide
Barium hydroxide finds applications in various fields:
- Chemical Synthesis: It's used as a reagent in various chemical synthesis reactions, acting as a strong base.
- Sugar Refining: Barium hydroxide plays a crucial role in the purification of sugarcane juice.
- Wastewater Treatment: Its strong base properties are utilized to neutralize acidic wastewater streams.
- Analytical Chemistry: It is used in titrations to determine the concentration of acids.
Safety Precautions
Barium hydroxide is a corrosive substance and requires careful handling. Direct contact with skin and eyes should be avoided. Appropriate personal protective equipment, including gloves, goggles, and lab coats, must be used when handling this chemical. In case of contact, immediate flushing with water is necessary followed by medical attention.
Conclusion: Barium Hydroxide is a Strong Base
In conclusion, the evidence strongly supports the classification of barium hydroxide as a strong base. Its complete dissociation in water, generating a high concentration of hydroxide ions, is the defining characteristic. While solubility impacts the overall basicity, the dissolved portion of barium hydroxide fully dissociates, further cementing its classification as a strong base. However, it's crucial to remember the safety precautions necessary when handling this corrosive chemical. Its complete dissociation, coupled with its relatively high solubility compared to many other metal hydroxides, makes barium hydroxide a potent and versatile strong base with diverse applications in various industries. Understanding this classification is critical for accurate predictions of its behavior in chemical reactions and proper safety procedures. The high concentration of hydroxide ions, resulting from complete dissociation, makes it an effective reagent in many chemical processes and applications. Always remember to handle this chemical with care due to its corrosive nature.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Does Semi Conservative Replication Help Prevent Mutations
Mar 13, 2025
-
6 5 Feet Is How Many Inches
Mar 13, 2025
-
How Many Inches Are In 27 Feet
Mar 13, 2025
-
What Is 20 25 As A Percent
Mar 13, 2025
-
Which Has More Protons Sulfur Or Iodine
Mar 13, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is Barium Hydroxide A Strong Base . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
