Is Ca Oh 2 A Strong Base
Kalali
Mar 10, 2025 · 5 min read
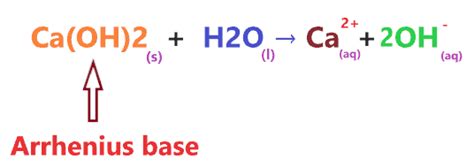
Table of Contents
Is Ca(OH)₂ a Strong Base? A Deep Dive into Calcium Hydroxide's Properties
Calcium hydroxide, Ca(OH)₂, commonly known as slaked lime or hydrated lime, is a widely used chemical compound with numerous industrial and environmental applications. A frequent question arising in chemistry discussions is whether Ca(OH)₂ qualifies as a strong base. The answer, while seemingly straightforward, requires a nuanced understanding of the concepts of strong and weak bases, solubility, and dissociation. This article will delve into the intricacies of Ca(OH)₂'s basicity, exploring its properties, behavior in solution, and practical implications.
Understanding Strong and Weak Bases
Before classifying Ca(OH)₂, it's crucial to define the terms "strong base" and "weak base." A strong base is a base that completely dissociates into its ions in an aqueous solution. This means that when dissolved in water, virtually all of the base molecules break apart into hydroxide ions (OH⁻) and their corresponding cations. This results in a high concentration of OH⁻ ions, leading to a significantly high pH. Examples of strong bases include sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and potassium hydroxide (KOH).
Conversely, a weak base only partially dissociates in water. A significant portion of the weak base molecules remain undissociated, resulting in a lower concentration of OH⁻ ions compared to a strong base at the same concentration. This leads to a lower pH than a strong base of equivalent concentration. Ammonia (NH₃) is a classic example of a weak base.
The Solubility Conundrum of Ca(OH)₂
The classification of Ca(OH)₂ as a strong or weak base is complicated by its low solubility in water. While it does completely dissociate into its ions (Ca²⁺ and 2OH⁻) in the amount that does dissolve, the limited amount that dissolves means the resulting hydroxide ion concentration is relatively low compared to that of truly soluble strong bases like NaOH. This is a key distinction that often leads to confusion.
Solubility vs. Dissociation: A Crucial Difference
It's essential to differentiate between solubility and dissociation. Solubility refers to the maximum amount of a substance that can dissolve in a given amount of solvent at a specific temperature. Dissociation refers to the breaking apart of a compound into its constituent ions. Ca(OH)₂ has high dissociation but low solubility.
Ca(OH)₂ is a strong base because it completely dissociates into ions in the solution it forms. However, its low solubility limits the concentration of OH⁻ ions that can be achieved. This means that while it's strong in terms of dissociation, it doesn't produce the same high concentration of OH⁻ ions as highly soluble strong bases.
Practical Implications of Ca(OH)₂'s Properties
The limited solubility of Ca(OH)₂ significantly impacts its applications. While its strong basicity is exploited in various processes, the low solubility necessitates using higher quantities of the compound to achieve the desired alkalinity.
Industrial Applications:
- Construction: Ca(OH)₂ is a crucial component in cement and mortar, contributing to their setting and hardening. Its basicity helps in neutralizing acidic components and improving durability.
- Water Treatment: It's used to adjust the pH of water, removing impurities and making it suitable for drinking. Its low solubility limits the potential for over-alkalization.
- Agriculture: Ca(OH)₂ helps to neutralize acidic soils, improving their suitability for crop cultivation. Its limited solubility is advantageous here as it prevents over-liming.
- Paper Industry: Ca(OH)₂ plays a role in the pulping process, contributing to the breakdown of lignin and the production of pulp.
Environmental Implications:
- Wastewater Treatment: Ca(OH)₂ helps in removing heavy metal ions from wastewater through precipitation. The precipitate formed is then separated from the water, resulting in cleaner discharge.
- Air Pollution Control: In some applications, Ca(OH)₂ is used to remove acidic gases from industrial emissions, such as SO₂ (sulfur dioxide) and NOx (nitrogen oxides), contributing to cleaner air.
Comparing Ca(OH)₂ to Other Bases
Let's compare Ca(OH)₂ to other bases to solidify its classification:
| Base | Formula | Solubility | Dissociation | Strength Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sodium Hydroxide | NaOH | High | Complete | Strong |
| Potassium Hydroxide | KOH | High | Complete | Strong |
| Calcium Hydroxide | Ca(OH)₂ | Low | Complete | Strong (but low solubility) |
| Ammonia | NH₃ | Moderate | Partial | Weak |
This table highlights that while Ca(OH)₂ completely dissociates (like strong bases), its low solubility distinguishes it from highly soluble strong bases. The "Strong (but low solubility)" classification reflects this unique position.
Measuring the Strength of Ca(OH)₂: pH and pOH
The pH and pOH values provide a quantitative measure of a solution's acidity and basicity. While a highly concentrated solution of NaOH will exhibit a very high pH (close to 14), a saturated solution of Ca(OH)₂ will have a considerably lower pH, closer to 12.5 at room temperature. This lower pH is directly linked to the limited solubility of Ca(OH)₂ rather than a weakness in its ability to dissociate.
The Ksp (solubility product constant) is a relevant parameter in quantifying Ca(OH)₂'s solubility. A lower Ksp indicates lower solubility. The Ksp of Ca(OH)₂ is relatively low, further confirming its low solubility in water. This is the key factor differentiating Ca(OH)₂ from other strong bases like NaOH and KOH.
Conclusion: A Strong Base with Limitations
In summary, Ca(OH)₂ is undoubtedly a strong base because it completely dissociates into its ions in solution. However, its low solubility significantly limits the concentration of hydroxide ions it can produce in an aqueous solution. This distinction is crucial in understanding its properties and applications. While its complete dissociation defines its strength as a base, its low solubility needs to be considered when using it in practical applications. The classification of Ca(OH)₂ as a "strong base with low solubility" accurately reflects its unique chemical behavior. This nuance is essential for those working with this widely used compound in various scientific, industrial, and environmental settings. Therefore, it's essential to consider both the high dissociation capacity and the low solubility when characterizing Ca(OH)₂’s basicity. Failing to account for both aspects can lead to misinterpretations of its behavior and potential applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Long Is 13 Miles In Minutes
Jul 03, 2025
-
What Is Half Of 1 1 2
Jul 03, 2025
-
How Much Do A Sandwich Bag Weigh
Jul 03, 2025
-
Why Did The Obtuse Angle Go To The Beach
Jul 03, 2025
-
How Much Is Three Quarts Of Water
Jul 03, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is Ca Oh 2 A Strong Base . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.