Is The Inverse Of A Function Always A Function
Kalali
Mar 21, 2025 · 5 min read
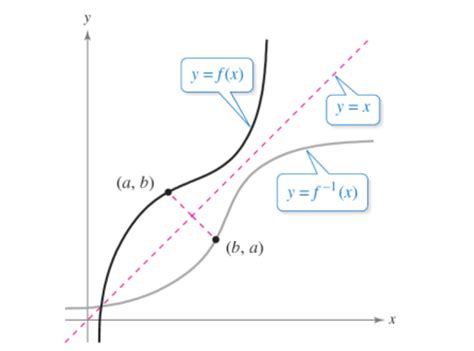
Table of Contents
Is the Inverse of a Function Always a Function?
The question of whether the inverse of a function is always a function is a crucial concept in mathematics, particularly in algebra and calculus. The short answer is: no, the inverse of a function is not always a function. Understanding why this is the case requires a deeper dive into the definitions of functions and their inverses, and exploring the concept of one-to-one (injective) functions.
Understanding Functions and Their Inverses
Let's begin with the fundamental definitions:
Function: A function is a relation between a set of inputs (domain) and a set of possible outputs (codomain) with the property that each input is related to exactly one output. We can represent this using function notation: f: A → B, where 'f' is the function, 'A' is the domain, and 'B' is the codomain. For every element 'a' in A, there is exactly one element 'b' in B such that f(a) = b.
Inverse Function: The inverse of a function, denoted as f⁻¹(x), "undoes" the operation of the original function. If f(a) = b, then f⁻¹(b) = a. In simpler terms, if you apply a function and then its inverse, you should get back your original input.
The Crucial Condition: One-to-One (Injective) Functions
The key to whether a function's inverse is also a function lies in the concept of a one-to-one or injective function. A function is one-to-one if each element in the codomain is mapped to by at most one element in the domain. In other words, no two different inputs produce the same output. Visually, this means the horizontal line test holds true: no horizontal line intersects the graph of the function more than once.
Why the Inverse Might Not Be a Function
If a function is not one-to-one, its inverse will fail the definition of a function. This is because a single input to the inverse function could map to multiple outputs, violating the fundamental rule of a function—one input, one output.
Let's illustrate this with an example:
Consider the function f(x) = x². This function maps both x = 2 and x = -2 to the output y = 4. Graphically, you can see this clearly; a horizontal line at y = 4 intersects the parabola at two points.
Now, let's attempt to find the inverse: To find the inverse, we swap x and y and solve for y:
x = y²
Taking the square root of both sides, we get:
y = ±√x
Notice that for any positive value of x, we get two possible values of y: the positive and negative square roots. This means the inverse relation is not a function because a single input (e.g., x = 4) maps to two outputs (y = 2 and y = -2).
Making the Inverse a Function: Restriction of the Domain
The problem arises when the original function is not one-to-one. To ensure the inverse is a function, we need to restrict the domain of the original function to make it one-to-one. This means we limit the inputs to a subset where each output has only one corresponding input.
Returning to our example, f(x) = x², we can restrict the domain to x ≥ 0. This creates a new function, let's call it g(x), defined as g(x) = x² for x ≥ 0. The graph of g(x) is only the right half of the parabola. Now, the horizontal line test is satisfied.
The inverse of g(x), which we can now denote as g⁻¹(x), is simply:
g⁻¹(x) = √x (for x ≥ 0)
In this case, the inverse is a function because each input has exactly one output. We've successfully created a function whose inverse is also a function by carefully restricting the domain.
Examples and Further Exploration
Let's examine additional examples to solidify our understanding:
1. f(x) = sin(x): The sine function is periodic, meaning it repeats its values infinitely many times. It's clearly not one-to-one. To find an inverse (arcsin or sin⁻¹), we restrict the domain to [-π/2, π/2]. Within this restricted domain, the sine function is one-to-one, and its inverse is a function.
2. f(x) = x³: This function is one-to-one, as each input maps to a unique output (it passes the horizontal line test). Therefore, its inverse, f⁻¹(x) = ³√x, is also a function.
3. f(x) = |x|: The absolute value function is not one-to-one (|2| = |-2| = 2). To obtain an inverse, we would need to restrict the domain (e.g., to x ≥ 0 or x ≤ 0) to create a one-to-one function. If we restrict it to x ≥ 0, the inverse would simply be f⁻¹(x) = x (for x ≥ 0).
Applications and Significance
The concept of inverse functions and the necessity of one-to-one functions is critical in various mathematical fields:
- Calculus: Finding derivatives and integrals often involves working with inverse functions. Ensuring the inverse is a function is essential for the validity of these operations.
- Differential Equations: Solving differential equations often requires finding inverses of functions.
- Cryptography: Many encryption algorithms rely on functions and their inverses. The security of the system depends on the properties of these functions, including whether their inverses are well-defined and easily computable.
- Linear Algebra: Invertible matrices represent linear transformations. A matrix is invertible if and only if the corresponding linear transformation is one-to-one and onto.
Conclusion
In summary, while not every function has an inverse that is also a function, understanding one-to-one functions provides the key to determining when this is the case. By carefully restricting the domain of a function to make it one-to-one, we can ensure that its inverse is also a well-defined and mathematically useful function. This concept is fundamental to numerous areas within mathematics and its applications in various scientific and technological fields. The ability to determine whether a function's inverse is a function is a crucial skill for any student or professional working with mathematical functions. Remember to always consider the domain and the horizontal line test when dealing with functions and their inverses. Mastering these concepts opens doors to a deeper understanding of advanced mathematical principles.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Percentage Is 4 Of 6
Mar 28, 2025
-
How Many Grams Is 1 5 Oz
Mar 28, 2025
-
27 Degrees C Is What In Fahrenheit
Mar 28, 2025
-
How Many Cups Are In 60 Oz
Mar 28, 2025
-
Cuanto Es 160 Grados Celsius En Fahrenheit
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is The Inverse Of A Function Always A Function . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
