Is The Transfer Of Energy By Electromagnetic Waves
Kalali
Mar 31, 2025 · 6 min read
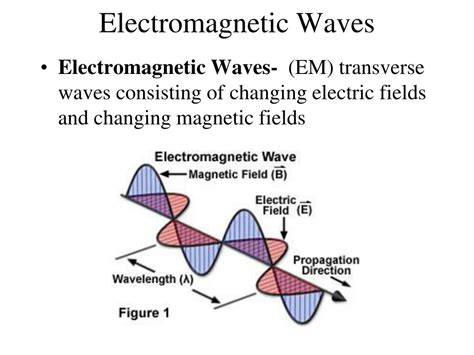
Table of Contents
Is the Transfer of Energy by Electromagnetic Waves?
The transfer of energy by electromagnetic (EM) waves is a fundamental process governing countless phenomena in the universe, from the warmth of sunlight on our skin to the operation of modern communication technologies. Understanding this process requires exploring the nature of EM waves themselves, how they propagate, and the various ways they interact with matter to deposit energy. The short answer is a resounding yes: electromagnetic waves are a highly effective mechanism for transferring energy.
Understanding Electromagnetic Waves
Electromagnetic waves are disturbances that propagate through space by the interplay of oscillating electric and magnetic fields. Unlike mechanical waves, which require a medium to travel (like sound waves needing air or water), EM waves can traverse the vacuum of space. This is because the oscillations are self-sustaining, with the changing electric field generating a changing magnetic field, and vice versa. This continuous cycle allows the wave to propagate at the speed of light (approximately 3 x 10<sup>8</sup> m/s in a vacuum).
The Electromagnetic Spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum encompasses a vast range of frequencies and wavelengths, each with its own unique properties and applications. This spectrum includes:
- Radio waves: The longest wavelengths, used for broadcasting, communication, and radar.
- Microwaves: Used in ovens, radar, and communication systems.
- Infrared (IR) radiation: Experienced as heat, used in thermal imaging and remote controls.
- Visible light: The narrow band of wavelengths detectable by the human eye, responsible for our vision.
- Ultraviolet (UV) radiation: Higher energy than visible light, causing sunburns and used in sterilization.
- X-rays: High-energy radiation used in medical imaging and material analysis.
- Gamma rays: The highest energy EM waves, emitted by radioactive materials and used in cancer treatment.
Mechanisms of Energy Transfer by EM Waves
The transfer of energy by EM waves occurs primarily through two mechanisms: absorption and scattering.
Absorption
When an EM wave interacts with matter, its energy can be absorbed by the atoms or molecules of that matter. This absorption process excites the atoms or molecules, causing them to transition to a higher energy state. The energy of the absorbed wave is then converted into other forms of energy, such as:
- Heat: Infrared radiation is readily absorbed by many materials, causing an increase in their temperature. This is the principle behind solar heating and microwave ovens.
- Chemical energy: Ultraviolet radiation can initiate chemical reactions, such as photosynthesis in plants.
- Kinetic energy: The absorption of EM radiation can cause electrons to be ejected from atoms (photoelectric effect), leading to the generation of electrical current in photovoltaic cells.
The efficiency of absorption depends on the frequency of the EM wave and the properties of the material. Materials that strongly absorb specific frequencies are said to be resonant at those frequencies. For instance, chlorophyll in plants is highly resonant with the frequencies of visible light, leading to its effective absorption for photosynthesis.
Scattering
Scattering is the redirection of EM waves by particles or irregularities in a medium. This redirection can result in a change in the direction of propagation, as well as a change in the wave's intensity. Different scattering mechanisms exist, including:
- Rayleigh scattering: This type of scattering is dominant for particles much smaller than the wavelength of the EM wave. It is responsible for the blue color of the sky, as blue light is scattered more efficiently than red light by air molecules.
- Mie scattering: This occurs when the particles are comparable in size to the wavelength of the EM wave. It is responsible for the white appearance of clouds, as all wavelengths of visible light are scattered equally.
- Non-selective scattering: This occurs when the particles are much larger than the wavelength of the EM wave. All wavelengths are scattered equally, leading to a white or grey appearance.
While scattering doesn't directly convert the energy of the EM wave into other forms, it can redistribute the energy, leading to a reduction in intensity in the original direction of propagation. This redistribution can still have significant implications, such as influencing the visibility of objects or affecting the propagation of signals.
Examples of Energy Transfer by EM Waves
The transfer of energy by EM waves is ubiquitous in our everyday lives and the vastness of the universe. Here are some striking examples:
1. Solar Energy
The sun's energy reaches Earth primarily through EM radiation, predominantly in the visible and infrared regions. This energy drives weather patterns, supports plant life through photosynthesis, and provides a vast source of renewable energy. Solar panels harness this energy by converting the absorbed sunlight into electricity.
2. Microwave Ovens
Microwave ovens utilize microwaves to heat food. The microwaves are absorbed by water molecules in the food, causing them to vibrate rapidly and generate heat. This efficient energy transfer method allows for quick and convenient cooking.
3. Communication Technologies
Radio waves, microwaves, and infrared radiation are essential for various communication technologies. Radio and television broadcasts transmit information through radio waves, while cellular networks and Wi-Fi use microwaves. Remote controls use infrared radiation to transmit signals to electronic devices. In all these cases, the energy carried by the EM waves is used to convey information.
4. Medical Applications
X-rays and gamma rays are used in medical imaging and therapy. X-rays pass through soft tissues but are absorbed by denser materials like bones, allowing for the creation of images of internal structures. Gamma rays, due to their high energy, can be used to destroy cancerous cells in radiation therapy. Here, the energy of the EM waves is used for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes.
5. Remote Sensing
Satellites and aircraft use various forms of EM radiation to observe the Earth's surface and atmosphere. Infrared sensors can detect temperature variations, while visible and near-infrared sensors can monitor vegetation health and land use. Radar uses microwaves to penetrate clouds and detect objects on the ground, even in darkness. This allows scientists and researchers to monitor environmental changes, manage resources, and conduct various scientific studies.
The Inverse Square Law and Energy Density
The intensity of an EM wave decreases with the square of the distance from the source. This is known as the inverse square law. This means that if you double the distance from a source, the intensity of the wave decreases by a factor of four. This is a crucial aspect of energy transfer, as it determines how much energy is available at a given distance from the source. The energy density of an electromagnetic wave, which represents the energy per unit volume, is also directly proportional to the square of the amplitude of the wave.
Conclusion: A Fundamental Process
The transfer of energy by electromagnetic waves is a fundamental process that underpins a vast array of phenomena, shaping our world and the universe at large. From the warmth of sunlight to the operation of our most advanced technologies, EM waves play a crucial role in our lives. Understanding their properties and the mechanisms of energy transfer is essential for harnessing their power and developing new applications in fields ranging from renewable energy to medical technology and space exploration. The ability of these waves to travel through a vacuum and the diverse ways they interact with matter makes them an irreplaceable component of the natural world and human technological advancements. The continued research and development in this field promise even more innovative applications in the years to come.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Do You Copy A Line Segment
Apr 02, 2025
-
Food Chain In The Tropical Rainforest
Apr 02, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is The Transfer Of Energy By Electromagnetic Waves . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
